1.Go-copy函式、sort排序、雙向連結串列、list操作和雙向迴圈連結串列
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-08-04
1.1.copy函式
通過copy函式可以把一個切片內容複製到另一個切片中
(1)把長切片拷貝到短切片中
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s1 := []int {1,2}
s2 := []int{3,4,5,6}
//copy的是角標,不會增加元切片的長度
copy(s1,s2)
fmt.Println(s1) //[3 4]
fmt.Println(s2) //[3 4 5 6]
}
(2)把短切片拷貝到長切片中
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s1 := []int {1,2}
s2 := []int{3,4,5,6}
//copy的是角標,不會增加元切片的長度
copy(s2,s1)
fmt.Println(s1) //[1 2]
fmt.Println(s2) //[1 2 5 6]
}
(3)把切片片段拷貝到切片中
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s1 := []int {1,2}
s2 := []int{3,4,5,6}
//copy的是角標,不會增加元切片的長度
copy(s1,s2[1:3])
fmt.Println(s1) //[[4 5]
fmt.Println(s2) //[3 4 5 6]
}
1.2.sort排序
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
)
func main() {
num := []int{1,7,3,5,2}
//升序排序
sort.Ints(num)
fmt.Println(num) //[1 2 3 5 7]
//降序排序
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(sort.IntSlice(num)))
fmt.Println(num) //[7 5 3 2 1]
}1.3.雙向連結串列
(1)雙向連結串列的結構
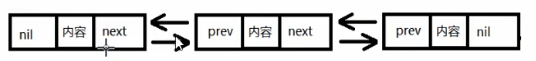
雙向連結串列結構中元素在記憶體中不是緊鄰空間,而是每個元素中存放上一個元素和後一個元素的地址
- 第一個元素稱為(頭)元素,前連線(前置指標域)為nil
- 最後一個元素稱為 尾(foot)元素,後連線(後置指標域)尾nil
雙向連結串列的優點
- 在執行新增元素或刪除元素時效率高,獲取任意一個元素,可以方便的在這個元素前後插入元素
- 充分利用記憶體空間,實現記憶體靈活管理
- 可實現正序和逆序遍歷
- 頭元素和尾元素新增或刪除時效率較高
雙向連結串列的缺點
- 連結串列增加了元素的指標域,空間開銷比較大
- 遍歷時跳躍性查詢內容,大量資料遍歷效能低
(2)雙向連結串列容器List
在Go語言標準庫的container/list包提供了雙向連結串列List
List結構體定義如下
- root表示根元素
- len表示連結串列中有多少元素
// List represents a doubly linked list.
// The zero value for List is an empty list ready to use.
type List struct {
root Element // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
}
其中Element結構體定義如下
- next表示下一個元素,使用Next()可以獲取到
- prev表示上一個元素,使用Prev()可以獲取到
- list表示元素屬於哪個連結串列
- Value表示元素的值,interface()在Go語言中表示任意型別
// Element is an element of a linked list.
type Element struct {
// Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
// To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
// as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
// list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
// element (l.Front()).
next, prev *Element
// The list to which this element belongs.
list *List
// The value stored with this element.
Value interface{}
}
1.4.操作List
(1)直接使用container/list包下的New()新建一個空的List
新增,遍歷,取首尾,取中間元素
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//例項化
mylist := list.New()
fmt.Println(mylist)
//新增
mylist.PushFront("a") //["a"]
mylist.PushBack("b") //["a","b"]
mylist.PushBack("c") //["a","b","c"]
//在最後一個元素的前面新增
mylist.InsertBefore("d",mylist.Back()) //["a","b","d","c"]
mylist.InsertAfter("e",mylist.Front()) //["a","e","b","d","c"]
//遍歷
for e := mylist.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next(){
fmt.Print(e.Value, " ") //a e b d c
}
fmt.Println("")
//取首尾
fmt.Println(mylist.Front().Value) //a
fmt.Println(mylist.Back().Value) //c
//取中間的元素,通過不斷的Next()
n := 3
var curr *list.Element
if n > 0 && n <= mylist.Len(){
if n == 1 {
curr = mylist.Front()
}else if n == mylist.Len(){
curr = mylist.Back()
}else {
curr = mylist.Front()
for i := 1; i < n; i++{
curr = curr.Next()
}
}
}else {
fmt.Println("n的數值不對")
}
fmt.Println(curr.Value) //b
}
(2)移動元素
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//例項化
mylist := list.New()
fmt.Println(mylist)
//新增
mylist.PushFront("a") //["a"]
mylist.PushBack("b") //["a","b"]
mylist.PushBack("c") //["a","b","c"]
//在最後一個元素的前面新增
mylist.InsertBefore("d",mylist.Back()) //["a","b","d","c"]
mylist.InsertAfter("e",mylist.Front()) //["a","e","b","d","c"]
//移動,把第一個元素一道最後一個元素的前面
mylist.MoveBefore(mylist.Front(),mylist.Back())
//mylist.MoveAfter(mylist.Back(),mylist.Front())
//把最後一個元素移動到最前面
//mylist.MoveToFront(mylist.Back())
//把第一個元素移動到最後面
//mylist.MoveToBack(mylist.Front())
for e := mylist.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next(){
fmt.Print(e.Value, " ") //e b d a c
}
}
(3)刪除
mylist.Remove(mylist.Front())
1.5.雙向迴圈列表
(1)迴圈連結串列特點是沒有節點的指標域為nil,通過任何一個元素都可以找到其它元素
環形連結串列結構如下
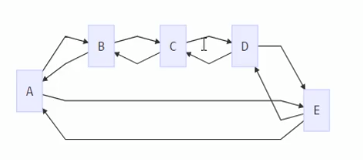
雙向迴圈連結串列和雙向連結串列區別
- 雙向迴圈連結串列沒有嚴格意義上的頭元素和尾元素
- 沒有元素的前連線和後連線為nil
- 一個長度為n的雙向迴圈連結串列,通過某個元素向某個方向移動,在查詢最多n-1次,一定會找到另一個元素
(2)在container/ring包下結構體Ring原始碼如下
- 官方明確說明了Ring是迴圈連結串列的元素,又是環形連結串列
- 實際使用時Ring遍歷就是環形連結串列第一個元素
// A Ring is an element of a circular list, or ring.
// Rings do not have a beginning or end; a pointer to any ring element
// serves as reference to the entire ring. Empty rings are represented
// as nil Ring pointers. The zero value for a Ring is a one-element
// ring with a nil Value.
//
type Ring struct {
next, prev *Ring
Value interface{} // for use by client; untouched by this library
}
(3)建立和檢視
package main
import (
"container/ring"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//r代表整個迴圈連結串列,又代表第一個元素
r := ring.New(5)
r.Value = 0
r.Next().Value = 1
r.Next().Next().Value = 2
//r.Next().Next().Next().Value = 3
//r.Next().Next().Next().Next().Value = 4
r.Prev().Value = 4
r.Prev().Prev().Value = 3
//檢視元素內容
//迴圈連結串列有幾個元素,func就執行幾次,i當前執行元素的內容
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 1 2 3 4
})
fmt.Println("")
//取中間元素,用移動
fmt.Println(r.Move(3).Value) //3
}
(4)增加
package main
import (
"container/ring"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//r代表整個迴圈連結串列,又代表第一個元素
r := ring.New(5)
r.Value = 0
r.Next().Value = 1
r.Next().Next().Value = 2
//r.Next().Next().Next().Value = 3
//r.Next().Next().Next().Next().Value = 4
r.Prev().Value = 4
r.Prev().Prev().Value = 3
//增加
r1 := ring.New(2)
r1.Value = 5
r1.Next().Value = 6
r.Link(r1)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 5 6 1 2 3 4
})
}
(5)刪除
package main
import (
"container/ring"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//r代表整個迴圈連結串列,又代表第一個元素
r := ring.New(5)
r.Value = 0
r.Next().Value = 1
r.Next().Next().Value = 2
//r.Next().Next().Next().Value = 3
//r.Next().Next().Next().Next().Value = 4
r.Prev().Value = 4
r.Prev().Prev().Value = 3
//刪除
r.Unlink(1)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 2 3 4
})
}
刪除後面兩個
//刪除
r.Unlink(2)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 3 4
})
r.Next()刪除
//刪除
r.Next().Unlink(2)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 1 4
})qu
超出範圍,取5的餘數
//刪除
r.Unlink(6)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 2 3 4
})
