從 axios 原始碼中瞭解到的 Promise 鏈與請求的取消
|
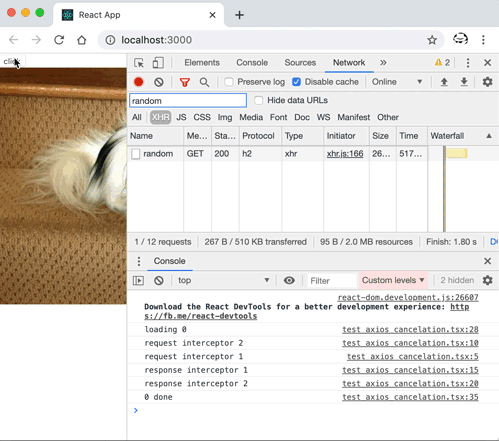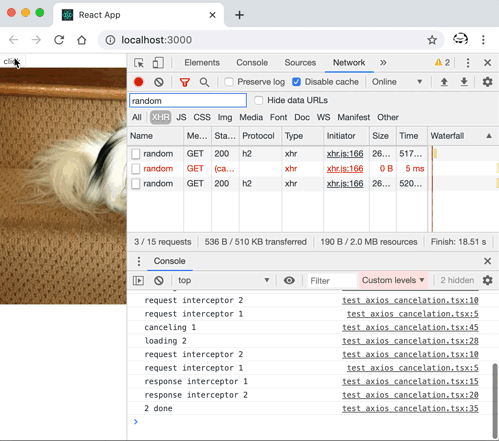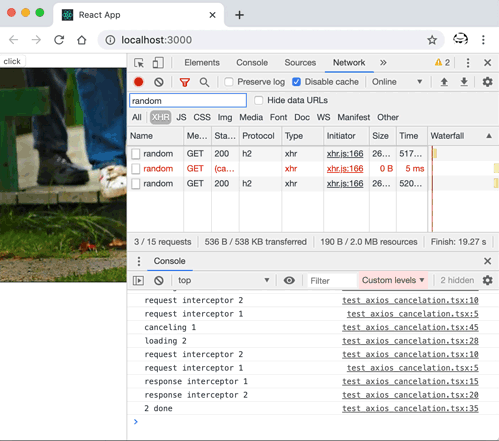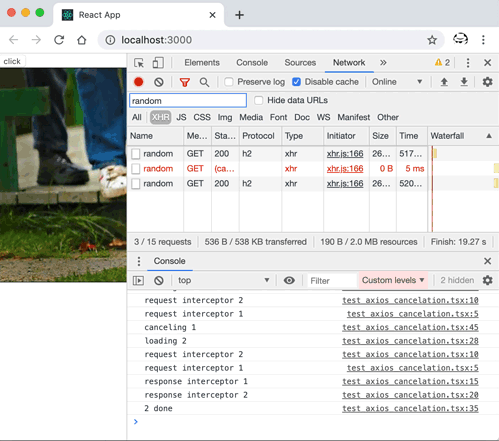
axios 中一個請求取消的示例: axios 取消請求的示例程式碼import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import axios, { AxiosResponse } from "axios";
export default function App() {
const [index, setIndex] = useState(0);
const [imgUrl, setImgUrl] = useState("");
useEffect(() => {
console.log(`loading ${index}`);
const source = axios.CancelToken.source();
axios
.get("https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/image/random", {
cancelToken: source.token
})
.then((res: AxiosResponse<{ message: string; status: string }>) => {
console.log(`${index} done`);
setImgUrl(res.data.message);
})
.catch(err => {
if (axios.isCancel(source)) {
console.log(err.message);
}
});
return () => {
console.log(`canceling ${index}`);
source.cancel(`canceling ${index}`);
};
}, [index]);
return (
<div>
<button
onClick={() => {
setIndex(index + 1);
}}
>
click
</button>
<div>
<img src={imgUrl} alt="" />
</div>
</div>
);
}
axios 中一個請求取消的示例 通過解讀其原始碼不難實現出一個自己的版本。Here we go... Promise 鏈與攔截器這個和請求的取消其實關係不大,但不妨先來了解一下,axios 中如何組織起來一個 Promise 鏈(Promise chain),從而實現在請求前後可執行一個攔截器(Interceptor)的。 簡單來說,通過 axios 發起的請求,可在請求前後執行一些函式,來實現特定功能,比如請求前新增一些自定義的 header,請求後進行一些資料上的統一轉換等。 用法首先,通過 axios 例項配置需要執行的攔截器: axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
console.log('before request')
return config;
}, function (error) {
return Promise.reject(error);
});
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
console.log('after response');
return response;
}, function (error) {
return Promise.reject(error);
});然後每次請求前後都會打印出相應資訊,攔截器生效了。 axios({
url: "https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/image/random",
method: "GET"
}).then(res => {
console.log("load success");
});
下面編寫一個頁面,放置一個按鈕,點選後發起請求,後續示例中將一直使用該頁面來測試。 import React from "react";
import axios from "axios";
export default function App() {
const sendRequest = () => {
axios.interceptors.request.use(
config => {
console.log("before request");
return config;
},
function(error) {
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
axios.interceptors.response.use(
response => {
console.log("after response");
return response;
},
function(error) {
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
axios({
url: "https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/image/random",
method: "GET"
}).then(res => {
console.log("load success");
});
};
return (
<div>
<button onClick={sendRequest}>click me</button>
</div>
);
}
點選按鈕後執行結果: 攔截器機制的實現實現分兩步走,先看請求前的攔截器。 請求前攔截器的實現Promise 的常規用法如下: new Promise(resolve,reject); 假如我們封裝一個類似 axios 的請求庫,可以這麼寫: interface Config {
url: string;
method: "GET" | "POST";
}
function request(config: Config) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open(config.method, config.url);
xhr.onload = () => {
resolve(xhr.responseText);
};
xhr.onerror = err => {
reject(err);
};
xhr.send();
});
}
除了像上面那個直接 Promise.resolve(value).then(()=>{ /**... */ });
這種方式建立 Promise 的好處是,我們可以從 function request(config: Config) {
return Promise.resolve(config)
.then(config => {
console.log("interceptor 1");
return config;
})
.then(config => {
console.log("interceptor 2");
return config;
})
.then(config => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open(config.method, config.url);
xhr.onload = () => {
resolve(xhr.responseText);
};
xhr.onerror = err => {
reject(err);
};
xhr.send();
});
});
}
將前面示例中 axios 替換為我們自己寫的 這裡,已經實現了 axios 中請求前攔截器的功能。仔細觀察,上面三個 於是我們可以將他們抽取成三個函式,每個函式就是一個攔截器。 function interceptor1(config: Config) {
console.log("interceptor 1");
return config;
}
function interceptor2(config: Config) {
console.log("interceptor 2");
return config;
}
function xmlHttpRequest<T>(config: Config) {
return new Promise<T>((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open(config.method, config.url);
xhr.onload = () => {
resolve(xhr.responseText as any);
};
xhr.onerror = err => {
reject(err);
};
xhr.send();
});
}
接下來要做的,就是從 Promise 鏈的頭部 function request<T = any>(config: Config) {
let chain: Promise<any> = Promise.resolve(config);
chain = chain.then(interceptor1);
chain = chain.then(interceptor2);
chain = chain.then(xmlHttpRequest);
return chain as Promise<T>;
}
然後,將上面硬編碼的寫法程式化一下,就實現了任意個請求前攔截器的功能。 擴充套件配置,以接收攔截器: interface Config {
url: string;
method: "GET" | "POST";
interceptors?: Interceptor<Config>[];
}
建立一個數組,將執行請求的函式做為預設的元素放進去,然後將使用者配置的攔截器壓入陣列前面,這樣形成了一個攔截器的陣列。最後再遍歷這個陣列形成 Promise 鏈。 function request<T = any>({ interceptors = [], ...config }: Config) {
// 傳送請求的攔截器為預設,使用者配置的攔截器壓入陣列前面
const tmpInterceptors: Interceptor<any>[] = [xmlHttpRequest];
interceptors.forEach(interceptor => {
tmpInterceptors.unshift(interceptor);
});
let chain: Promise<any> = Promise.resolve(config);
tmpInterceptors.forEach(interceptor => (chain = chain.then(interceptor)));
return chain as Promise<T>;
}
使用: request({
url: "https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/image/random",
method: "GET",
interceptors: [interceptor1, interceptor2]
}).then(res => {
console.log("load success");
});
執行結果: 注意這裡順序為傳入的攔截器的反序,不過這不重要,可通過傳遞的順序來控制。 響應後攔截器上面實現了在請求前執行一序列攔截函式,同理,如果將攔截器壓入到陣列後面,即執行請求那個函式的後面,便實現了響應後的攔截器。 繼續擴充套件配置,將請求與響應的攔截器分開: interface Config {
url: string;
method: "GET" | "POST";
interceptors?: {
request: Interceptor<Config>[];
response: Interceptor<any>[];
};
}
更新 function request<T = any>({
interceptors = { request: [], response: [] },
...config
}: Config) {
const tmpInterceptors: Interceptor<any>[] = [xmlHttpRequest];
interceptors.request.forEach(interceptor => {
tmpInterceptors.unshift(interceptor);
});
interceptors.response.forEach(interceptor => {
tmpInterceptors.push(interceptor);
});
let chain: Promise<any> = Promise.resolve(config);
tmpInterceptors.forEach(interceptor => (chain = chain.then(interceptor)));
return chain as Promise<T>;
}
類似 function interceptor3<T>(res: T) {
console.log("interceptor 3");
return res;
}
function interceptor4<T>(res: T) {
console.log("interceptor 4");
return res;
}
測試程式碼: request({
url: "https://dog.ceo/api/breeds/image/random",
method: "GET",
interceptors: {
request: [interceptor1, interceptor2],
response: [interceptor3, interceptor4]
}
}).then(res => {
console.log("load success");
});
執行結果: 不難看出,當我們發起一次 axios 請求時,其實是發起了一次 Promise 鏈,鏈上的函式順次執行。 因為拉弓沒有回頭箭,請求發出後,能夠取消的是後續操作,而不是請求本身,所以上面的 Promise 鏈中,需要實現 |