Angular 從入坑到挖坑 - 元件食用指南
一、Overview
angular 入坑記錄的筆記第二篇,介紹元件中的相關概念,以及如何在 angular 中通過使用元件來完成系統功能的實現
對應官方文件地址:
- 顯示資料
- 模板語法
- 使用者輸入
- 元件之間的互動
- 管道
- 生命週期鉤子
配套程式碼地址:angular-practice/src/components-guide
二、Contents
- Angular 從入坑到棄坑 - Angular 使用入門
- Angular 從入坑到挖坑 - 元件食用指南
三、Knowledge Graph
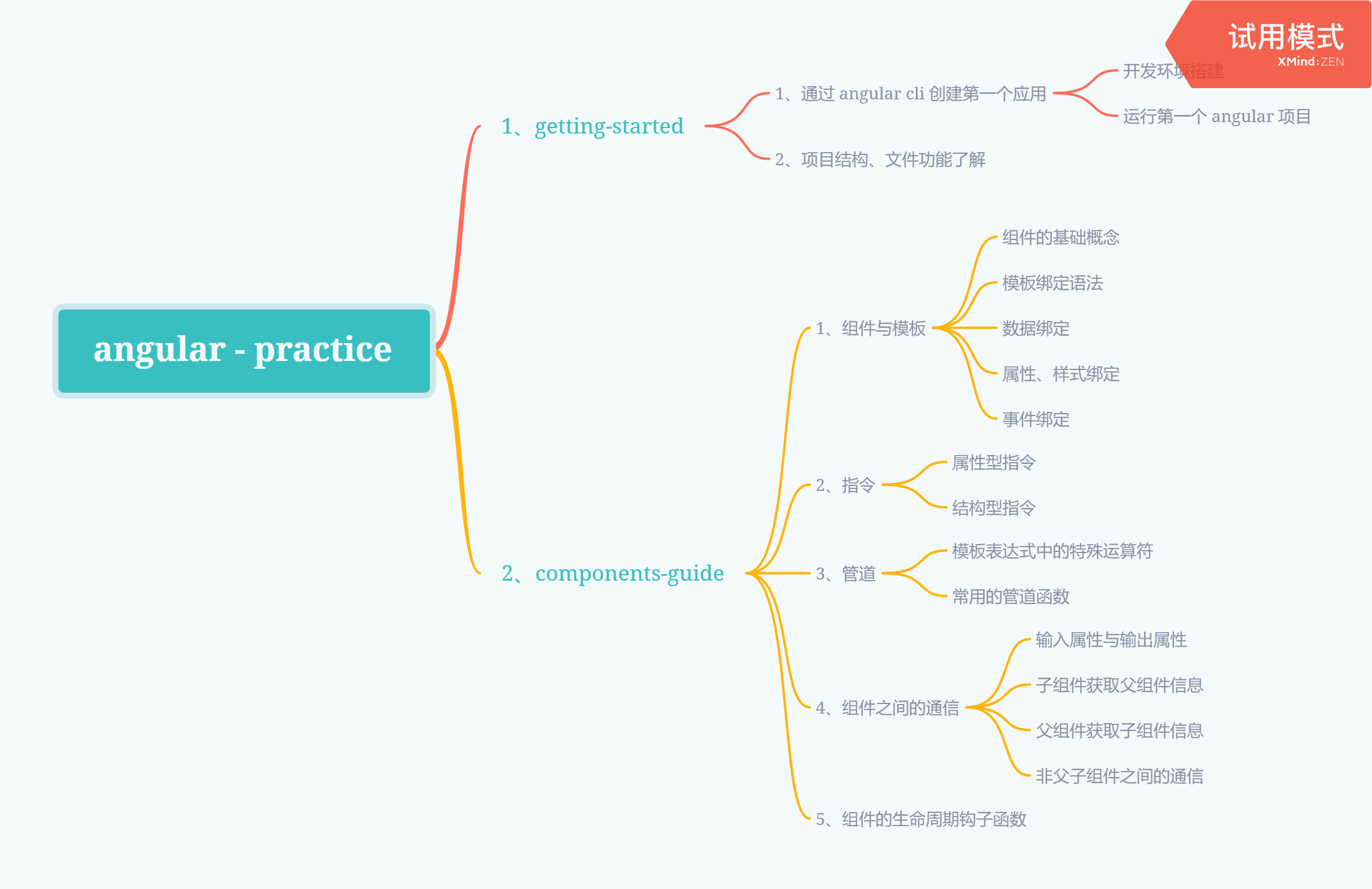
四、Step by Step
4.1、元件與模板
4.1.1、元件的基礎概念
元件包含了一組特定的功能,每個元件的功能都單一且獨立,可以進行重複使用;元件可以通過 angular cli 進行建立,生成的元件位於工作空間的 src/app/ 路徑下面
## 建立一個 product-list 元件
ng g component product-list當需要將元件放置在某個指定的目錄下時,可以直接在 ng g 命令中新增路徑
## 將 hero 元件生成到 components 路徑下
ng g component components/hero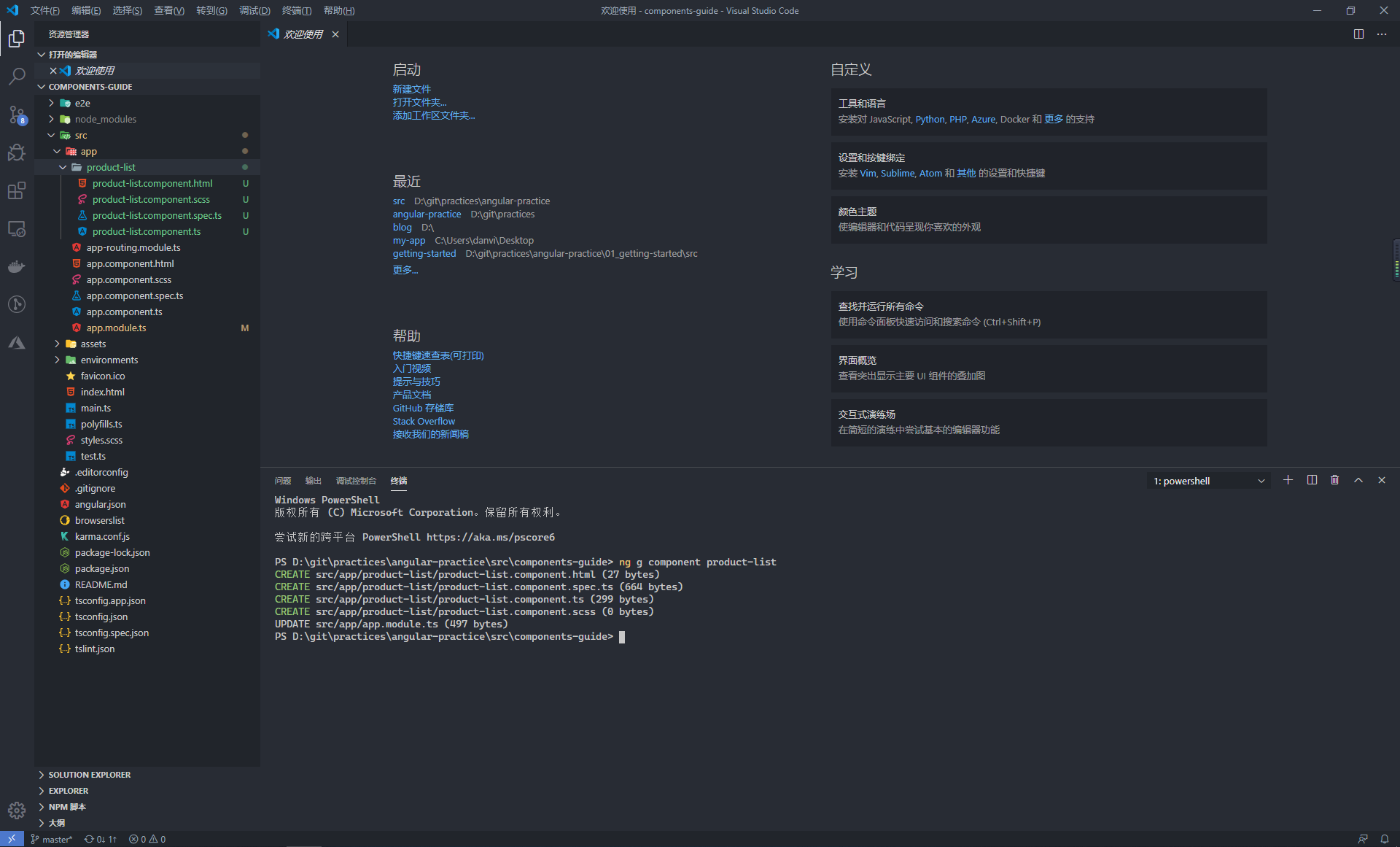
angular 應用就是通過一個個的元件所構成的元件樹,一個元件包含了如下的四個部分
- product-list.component.ts:元件類,用來處理資料和功能,為檢視呈現提供支援
- product-list.component.html:元件對應的頁面 HTML 模板,用來呈現元件的功能
- product-list.component.scss:只針對當前元件的樣式
- product-list.component.spec.ts:當前元件的單元測試檔案(非必須)
當通過命令列建立一個新的元件之後,會自動將新建立的元件註冊到應用的根模組(app.module.ts)中
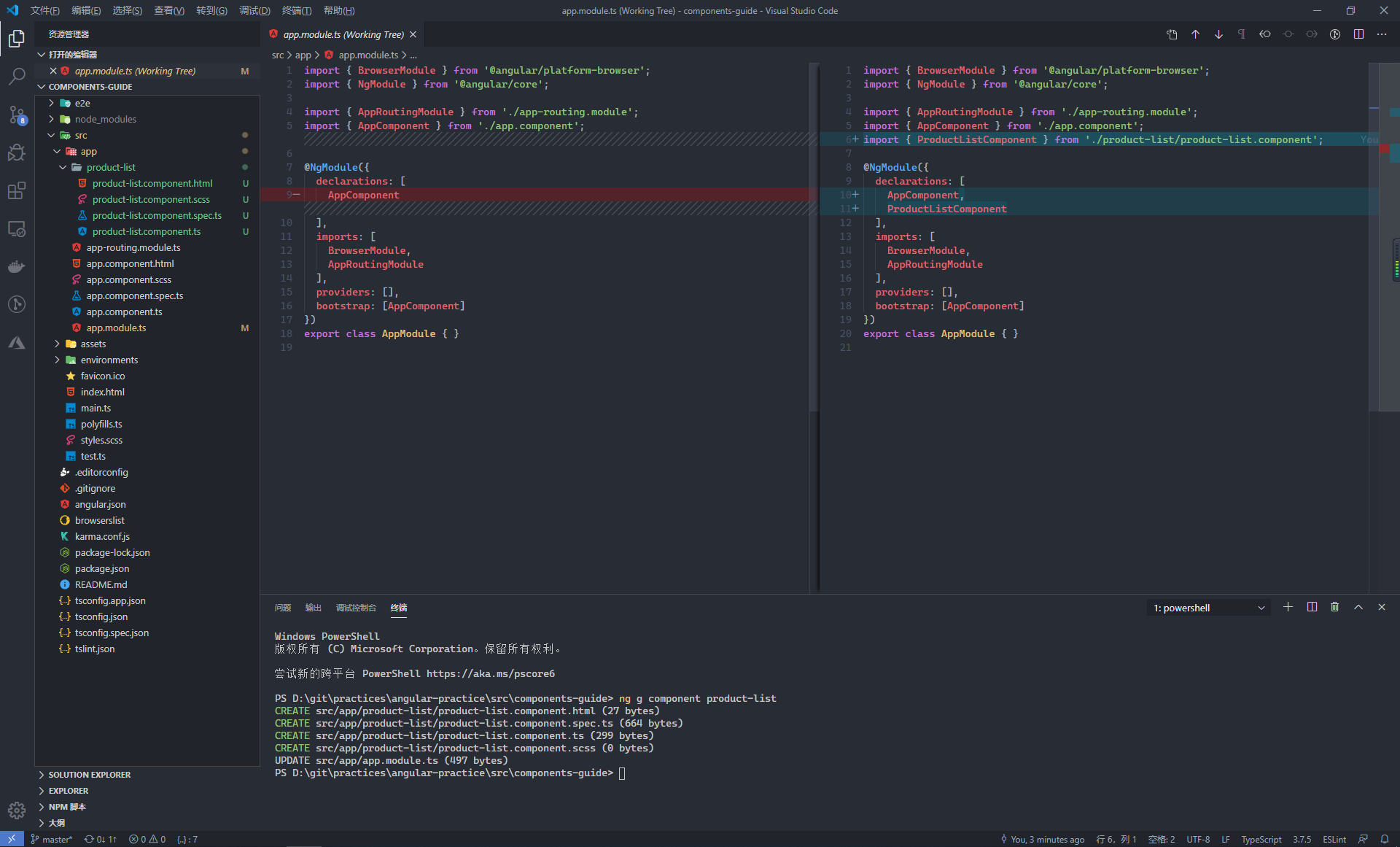
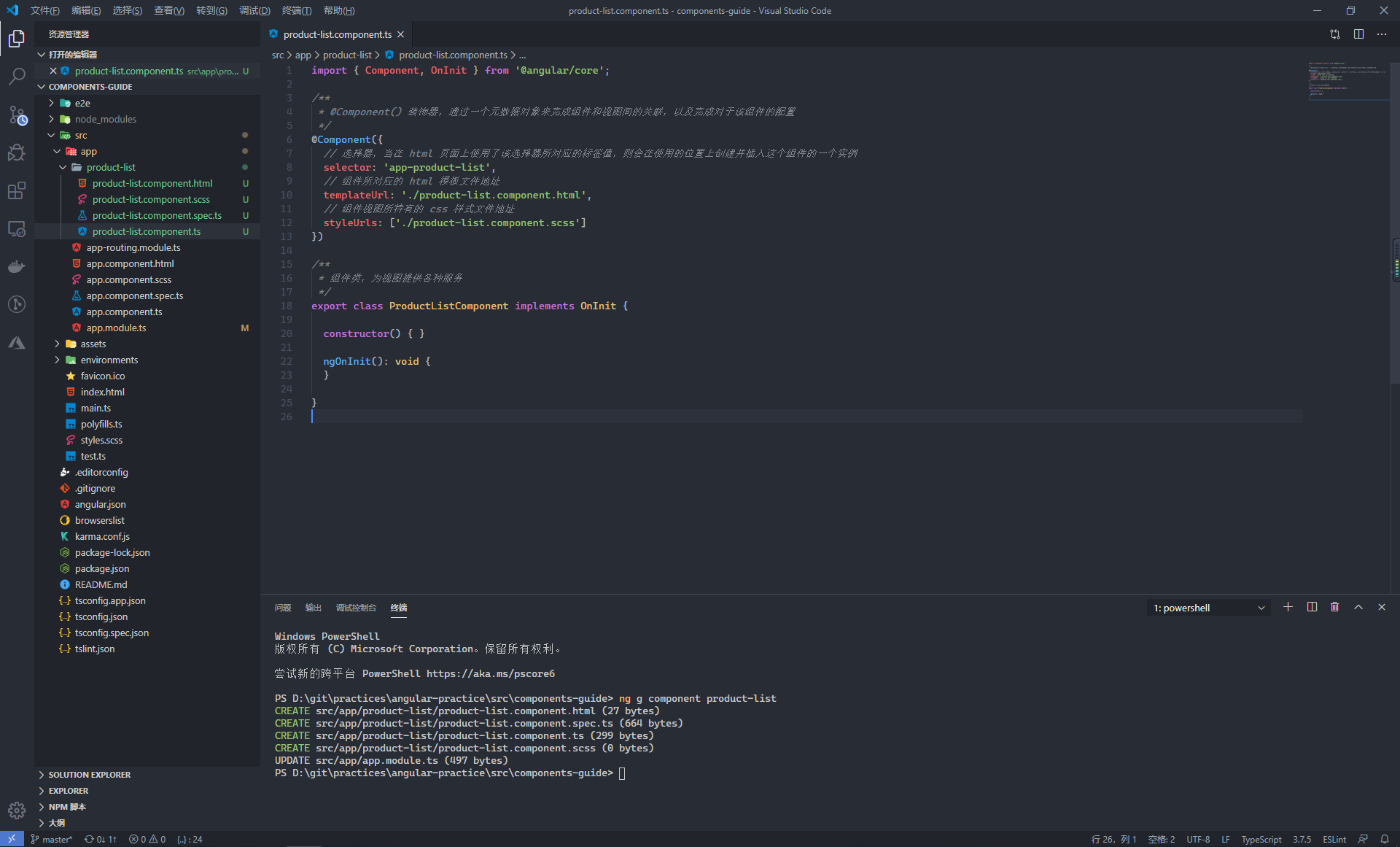
在元件類中,通過使用 @Component 裝飾器 1 用來將類宣告為元件類,併為這個元件類配置一些元資料 2,以決定該元件在執行期間該如何處理、例項化和使用
裝飾器中存在三個基礎的配置引數,用來完成元件與檢視之間的關聯
- selector:選擇器,當我們在頁面上添加了這個選擇器指定的標籤(
<app-product-list></app-product-list>)後,就會在當前使用位置上建立並插入這個元件的一個例項 - templateUrl:該元件所對應的 HTML 模板檔案地址
- styleUrls:該元件檢視所特有的 css 樣式檔案地址
當需要使用這個元件時,直接在頁面上新增選擇器對應的標籤就可以了
4.1.2、模板繫結語法
在 angular 應用中,元件扮演著控制器或是檢視模型的作用,在建立元件時會關聯一個 html 檔案,這個 html 檔案則是一個基礎的 angular 模板檔案
在這個模板檔案中,可以通過 angular 內建的模板語法與 html 元素進行結合,從而告訴 angular 如何根據我們的應用邏輯和資料來渲染頁面
4.1.2.1、插值表示式
插值表示式可以將元件中的屬性值或者是模板上的資料通過模板表示式運算子進行計算,最終將值渲染到檢視頁面上
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-product-list',
templateUrl: './product-list.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss']
})
export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit {
public title = '我是 title 屬性值';
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
}<p>title:{{title}}</p>
<p>1+2+3+4+5={{1+2+3+4+5}}</p>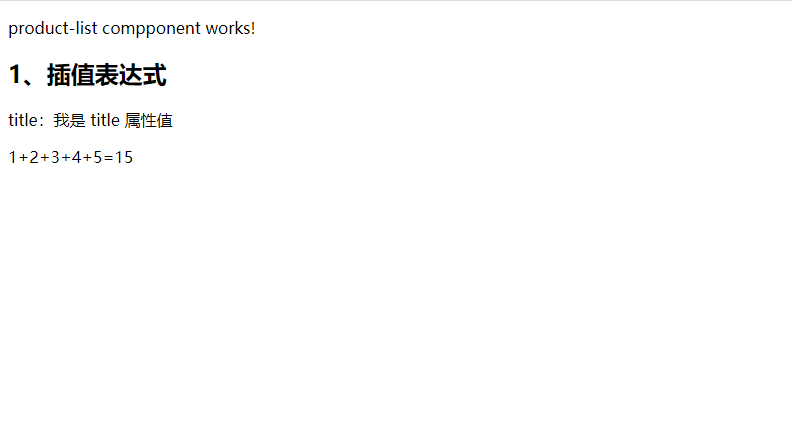
模板表示式的變數來源
- 模板本身的變數
- 指令的上下文變數
- 元件的成員資訊(屬性 or 方法)
在使用模板表示式時,如果變數名在多個來源中都存在的話,則模板變數是最優先的,其次是指令的上下文變數,最後是元件的成員
在使用模板表示式時應該遵循如下的原則
- 簡單:正常情況下,應該將業務邏輯或是資料運算放到元件中,模板表示式只作為屬性或方法的呼叫
- 快速執行:模板表示式得出的資料應該快速結束,否則就會對於使用者體驗造成影響
- 沒有可見的副作用:模板表示式只作為資料的展示,不應該改變任何的資料;應該構建出冪等的表示式,除非依賴的值發生變化,否則多次呼叫時,應該返回相同的資料資訊
4.1.2.2、模板繫結語法
通過資料繫結機制,將資料來源與檢視進行繫結,從而實現源資料與使用者呈現的一致性
- 從資料來源到檢視:插值、元件中的屬性、dom 元素的 property 3、css 樣式、css 類
- 從檢視到資料來源:事件
- 檢視與資料來源之間的雙向繫結:資料物件
| 分類 | 語法 |
|---|---|
| 單向 從資料來源到檢視 |
1、插值表示式:{{expression}} 2、使用 [] 進行繫結: <a [href]='expression'></a>3、使用 bind 進行繫結: <a bind-href='expression'></a> |
| 單向 從檢視到資料來源 |
1、使用 () 進行繫結:<a (click)='statement'></a>2、使用 on 進行繫結: <a on-click='statement'></a> |
| 雙向 檢視到資料來源;資料來源到檢視 |
1、使用 [()] 進行繫結:<input type="text" [(ngModel)]="product.Name">2、使用 bindon 進行繫結: <input type="text" bindon-ngModel="product.Name"> |
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-product-list',
templateUrl: './product-list.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss']
})
export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit {
public title = '我是 title 屬性值';
public styleProperty = '<b>我是包含 html 標籤的屬性</b>';
public fontColor = 'red';
public url = 'https://yuiter.com';
public name: string;
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
getUser() {
alert('111111111');
}
}<h3>2.1、從資料來源到檢視</h3>
<p>
<a href='{{url}}'>使用插值表示式進行繫結</a>
</p>
<p>
<a [href]='url' [style.color]='fontColor'>使用 [] 進行繫結</a>
</p>
<p>
<a bind-href='url'>使用 bind 進行繫結</a>
</p>
<p>
<span [innerHtml]="styleProperty"></span>
</p>
<h3>2.2、從檢視到資料來源</h3>
<p>
<button (click)="getUser()">使用 () 進行繫結</button>
</p>
<p>
<button on-click="getUser()">使用 on 進行繫結</button>
</p>
<h3>2.3、資料雙向繫結 --- 需要在 AppModule 中新增對於 FormsModule 的引用</h3>
<p>
<input type="text" id="userName" [(ngModel)]="name">
</p>
<p>
<input type="text" bindon-ngModel="name">
</p>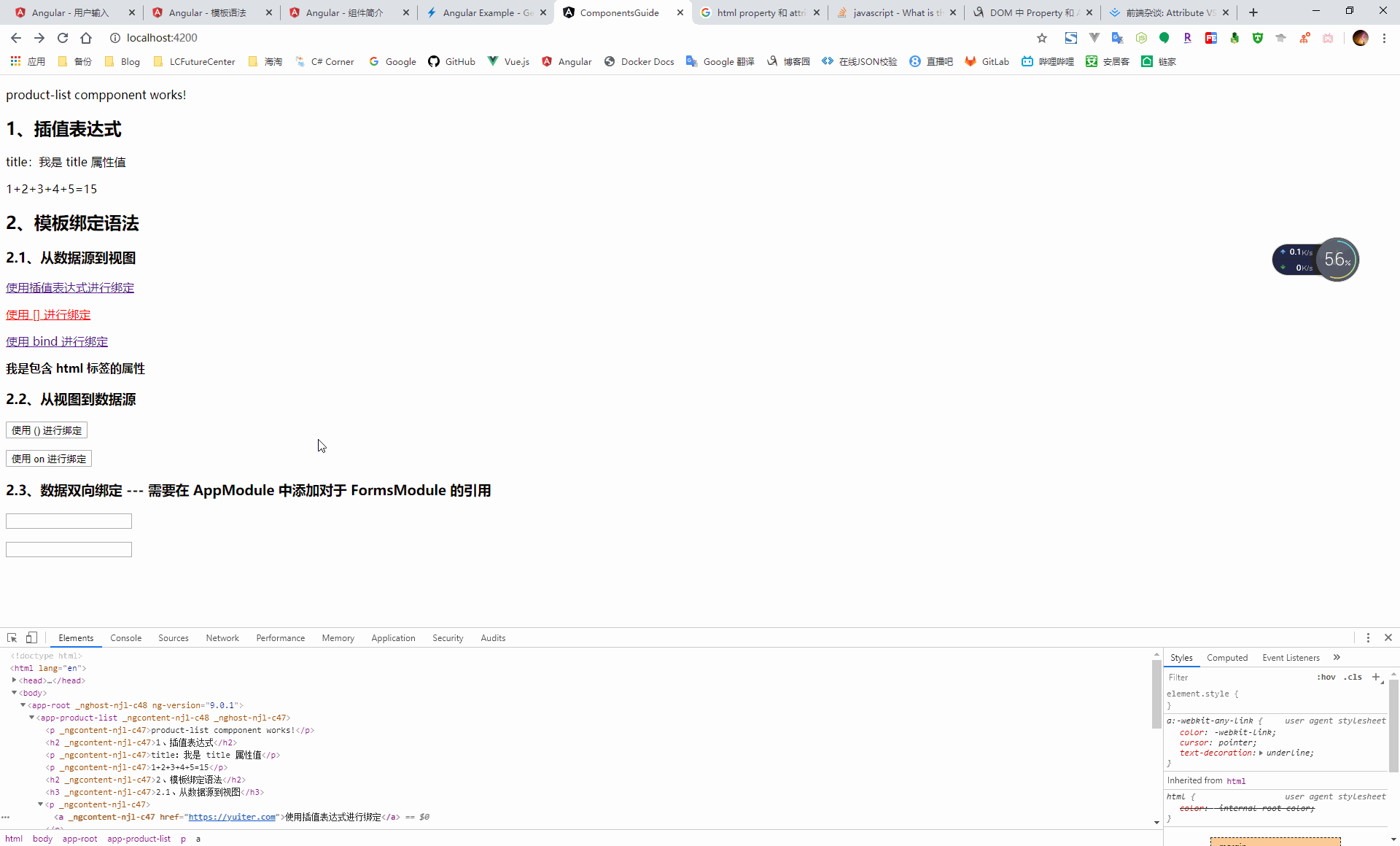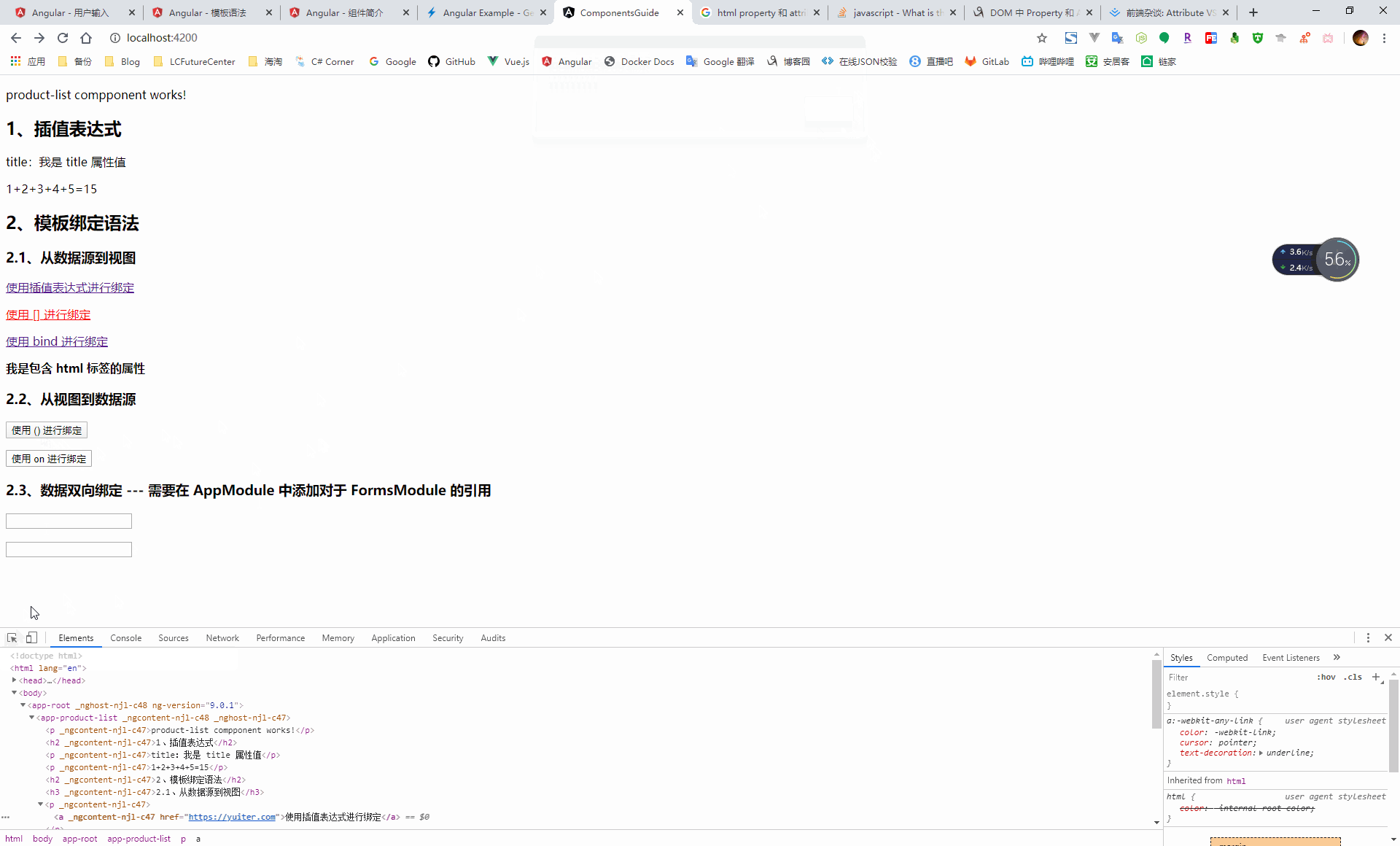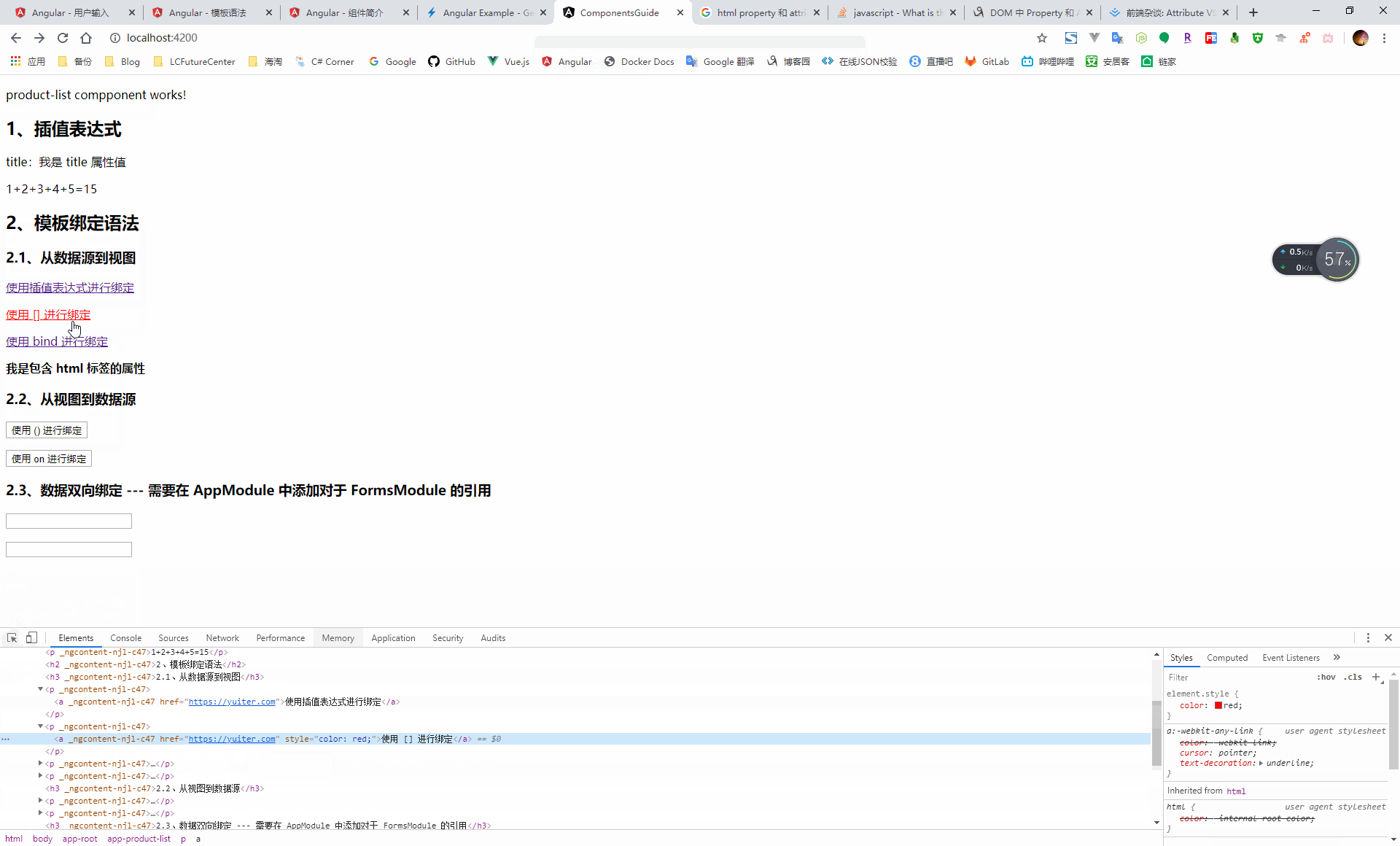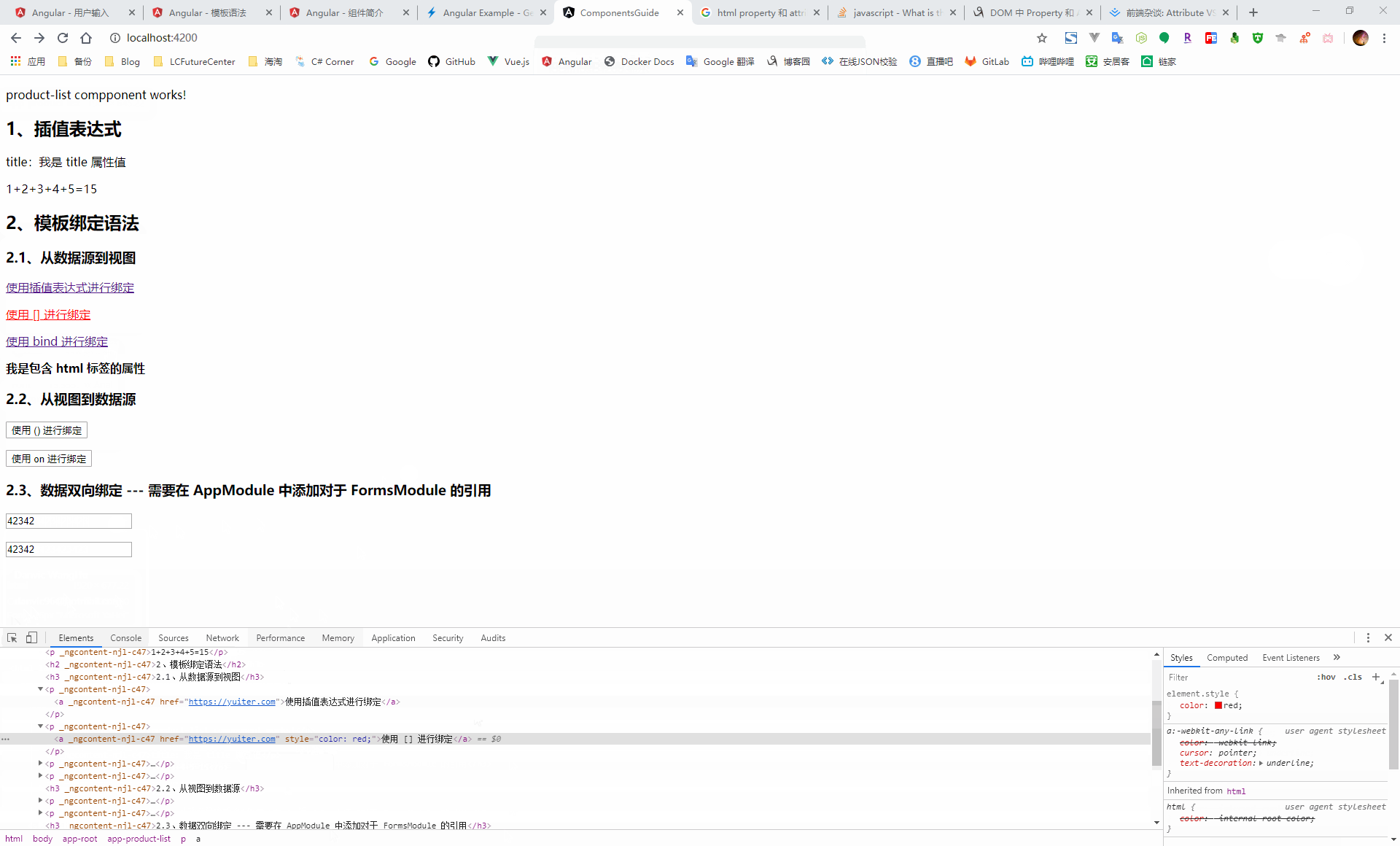
4.1.3、資料繫結
單向資料繫結
<p>{{title}}</p>雙向資料繫結
<input type="text" id="userName" [(ngModel)]="name"> <!-- 當沒有 NgModel 時,雙向資料繫結等同於下面的寫法 --> <input type="text" id="userName" [value]="name" (input)="name=$event.target.value">
4.1.4、屬性、樣式繫結
dom 元素的 property 繫結
<img [src]="productImageUrl"> <img bind-src="productImageUrl">html 標籤的 attribute 繫結
attribute 繫結的語法類似於 property 繫結,由字首
attr、點(.)和 attribute 名稱組成attribute 繫結的主要用例之一是設定 ARIA attribute(給殘障人士提供便利)
<button [attr.aria-label]="actionName">{{actionName}} with Aria</button>style 內聯樣式繫結
// 1、[style.width]="width" :string | undefined | null public width = "100px"; //2、[style.width.px]="width":number | undefined | null public width = "20"; // 3、[style]="styleExpr":string public styleExpr = "width: 100px; color:red"; // 4、[style]="styleExpr":{key:value} public styleExpr = {width: '100px', height: '100px'}; // 5、[style]="styleExpr":array public styleExpr = ["width", "100px"];class 屬性繫結
// 1、[class.foo]="hasFoo":bool | undefined | null public hasFoo = true; // 2、[class]="classExpr":string public classExpr = "my-class1 my-class2"; // 3、[class]="classExpr":{key:value} public classExpr= {my-class1: true, my-class2: true}; // 4、[class]="classExpr":array public classExpr= ["my-class1", "my-class2"];
4.1.5、事件繫結
在事件繫結中,可以通過 $event 引數獲取到 dom 事件物件的屬性從而獲取到模板資訊
<input type="text" (keyup)="getMsg($event)">
<p>輸入的值:{{msg}}</p>import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-product-list',
templateUrl: './product-list.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss']
})
export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit {
public msg: string;
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
getMsg(event: KeyboardEvent) {
console.log(event);
this.msg = (event.target as HTMLInputElement).value;
}
}
通過使用 $event 作為方法的引數會將許多用不到的模板資訊傳遞到元件中,導致我們在僅僅是為了獲取資料的前提下,卻需要對於頁面元素十分了解,違背了模板(使用者所能看到的)與元件(應用如何去處理使用者資料)之間的關注點分類的原則。因此,這裡應該使用模板引用變數的方式獲取資料資訊。
模板引用變數是對模板中 DOM 元素的引用,提供了從模組中直接訪問元素的能力。
<input type="text" #refMsgInput (keyup)="getRefMsg(refMsgInput.value)">
<p>通過模板引入變數的方式獲取到輸入的值:{{refMsg}}</p>import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-product-list',
templateUrl: './product-list.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss']
})
export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit {
public refMsg: string;
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
getRefMes(msg: string) {
this.refMsg = msg;
}
}模板引用變數的作用域是整個模板,因此要確保一個模板中的引用變數名稱是唯一的,同時,在宣告引用變數時,也可以使用 ref- 代替 #
<input type="text" ref-refMsgInput (keyup)="getRefMsg(refMsgInput.value)">
<p>通過模板引入變數的方式獲取到輸入的值:{{refMsg}}</p>4.2、指令
4.2.1、屬性型指令
屬性型指令被應用在檢視 dom 元素上,用來改變 dom 元素的外觀或行為
NgClass:用來設定元素的多個 css 類屬性,如果只設置一個 css 類,應該使用模板繫結語法中 class 類繫結
<p [ngClass]="inlineStyle">NgClass 屬性指令</p>import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-product-list', templateUrl: './product-list.component.html', styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss'] }) export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit { public inlineStyle: {}; constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { this.setInlineStyle(); } setInlineStyle() { this.inlineStyle = { 'text-red': true, 'bg-blue': false, }; } }這裡的 text-red、bg-blue 都是 css 類名,如果想要在指定的元素上新增該類,則 css 類名對應的值為 true,反之則為 false
NgStyle:用來設定元素的多個內聯樣式,如果只設置一個內聯樣式,應該使用模板繫結語法中的樣式繫結
<p [ngStyle]="currentStyles">NgStyle 屬性指令</p>import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-product-list', templateUrl: './product-list.component.html', styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss'] }) export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit { public currentStyles: {}; constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { this.setCurrentStyles(); } setCurrentStyles() { this.currentStyles = { 'font-style': 'italic', 'font-weight': 'bold', 'font-size': '24px' }; } }通過在元件的屬性中設定多個內聯樣式物件的形式,完成對於頁面元素樣式的批量設定
NgModel:雙向資料繫結
<input type="text" id="userName" [(ngModel)]="name">
4.2.2、結構型指令
結構型指令用來操作 dom 樹,通過進行一些的邏輯判斷,從而完成對於頁面佈局的修改
NgIf:根據表示式的值(true or false)來建立或者銷燬 dom 元素
<p *ngIf="expr">NgIf 結構型指令</p>當 expr 屬性為 true 時,這個元素則會顯示在頁面上,當屬性值為 false 時,則不顯示該元素
ngIf 指令並不是通過使用 css 樣式來隱藏元素的,當值為 false 時,則這些元素會從 dom 中被銷燬,並且所有監聽該 dom 元素的事件會被取消,當重新顯示該元素時,會重新執行初始化的過程
與銷燬元素不同,對於隱藏的元素來說,所有的元素監聽事件還會執行監聽的,再次顯示時不用重新進行初始化過程
NgFor:通過定義單條資料的顯示格式,angular 以此為模板,迴圈渲染出所有的資料
<p *ngFor="let item of products; let i = index">{{i+1}} - {{item.name}} --- {{item.price}}</p>import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-product-list', templateUrl: './product-list.component.html', styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss'] }) export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit { public products = [{ 'name': 'lalala', 'price': '$200' }, { 'name': 'hehehe', 'price': '$400' }, { 'name': 'wuwuwu', 'price': '$120' }, { 'name': 'xixi', 'price': '$570' }]; constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { } }NgFor 指令上下文中的 index 屬性在每次迭代中,會獲取到條資料的索引值
當渲染的資料發生改變時 4,會導致 dom 元素的重新渲染,此時可以採用 trackBy 的方式,通過在元件中新增一個方法,指定迴圈需要跟蹤的屬性值,此時當渲染的資料發生改變時,只會重新渲染變更了指定的屬性值的資料
<p>不使用 trackBy 跟蹤屬性</p> <div> <p *ngFor="let item of products; let i = index;"> {{i+1}} - {{item.name}} --- {{item.price}} </p> </div> <p>使用 trackBy 跟蹤屬性</p> <div> <p *ngFor="let item of products; let i = index; trackBy: trackByIndex"> {{i+1}} - {{item.name}} --- {{item.price}} </p> </div> <button (click)="addProduct()">新增</button>import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-product-list', templateUrl: './product-list.component.html', styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss'] }) export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit { public products = [{ 'name': 'lalala', 'price': '$200' }, { 'name': 'hehehe', 'price': '$400' }, { 'name': 'wuwuwu', 'price': '$120' }, { 'name': 'xixi', 'price': '$570' }]; constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { } trackByIndex(index: number, item: any): string { return item.price; } addProduct() { this.products = [{ 'name': 'lalala', 'price': '$200' }, { 'name': 'hehehe', 'price': '$400' }, { 'name': 'wuwuwu', 'price': '$120' }, { 'name': 'xixi', 'price': '$570' }, { 'name': 'lululu', 'price': '$' + (Math.random() * 100).toFixed() }]; } }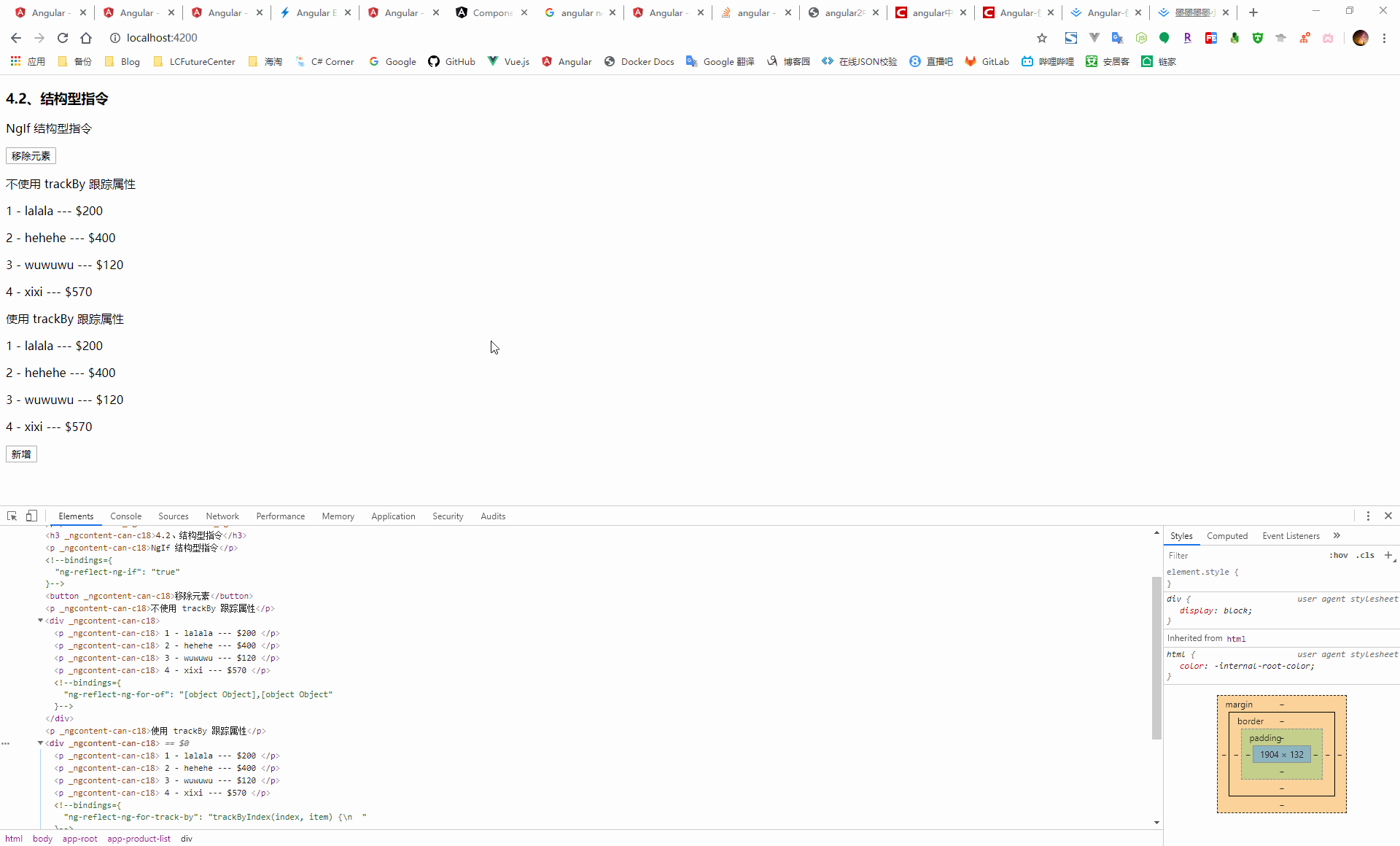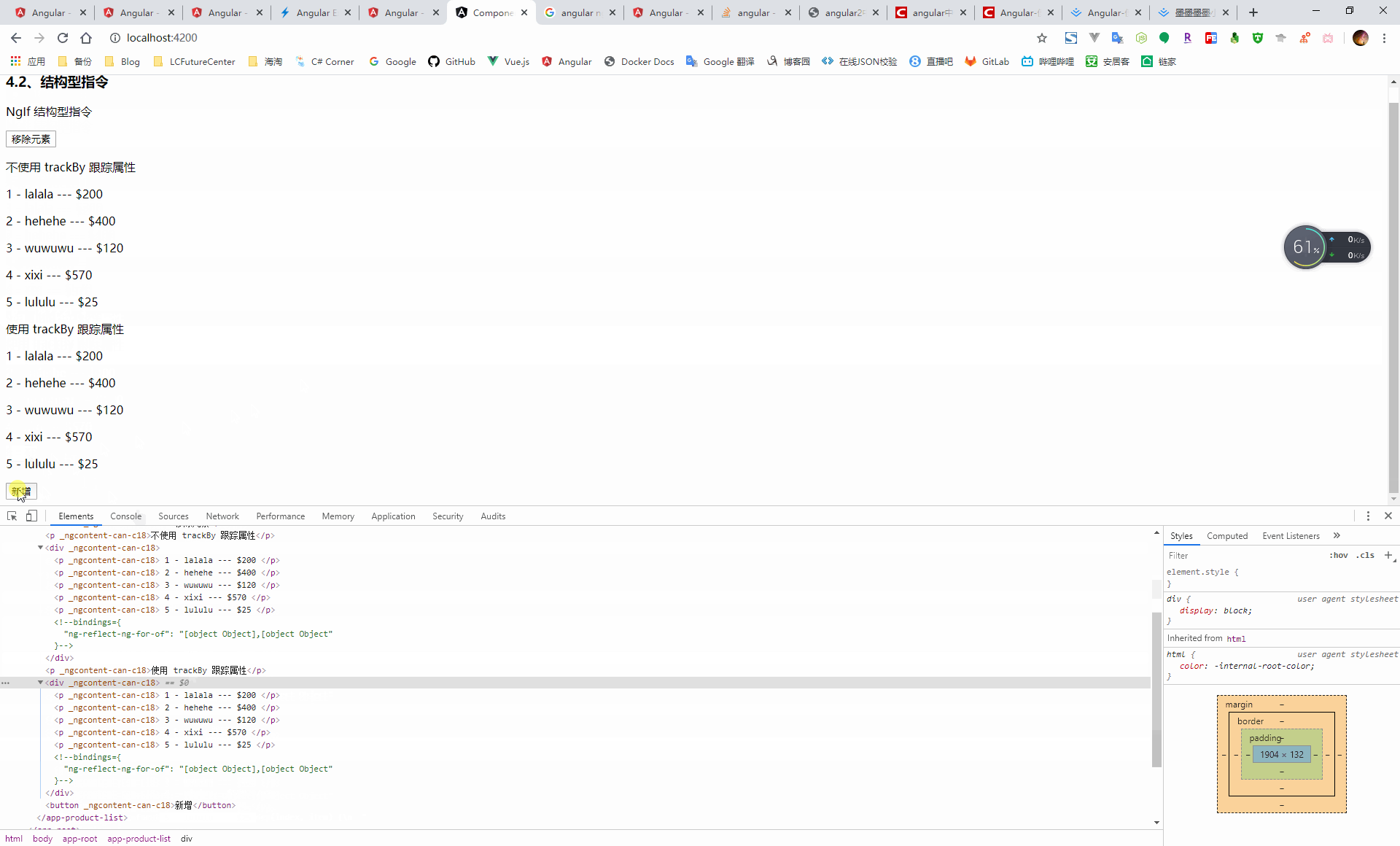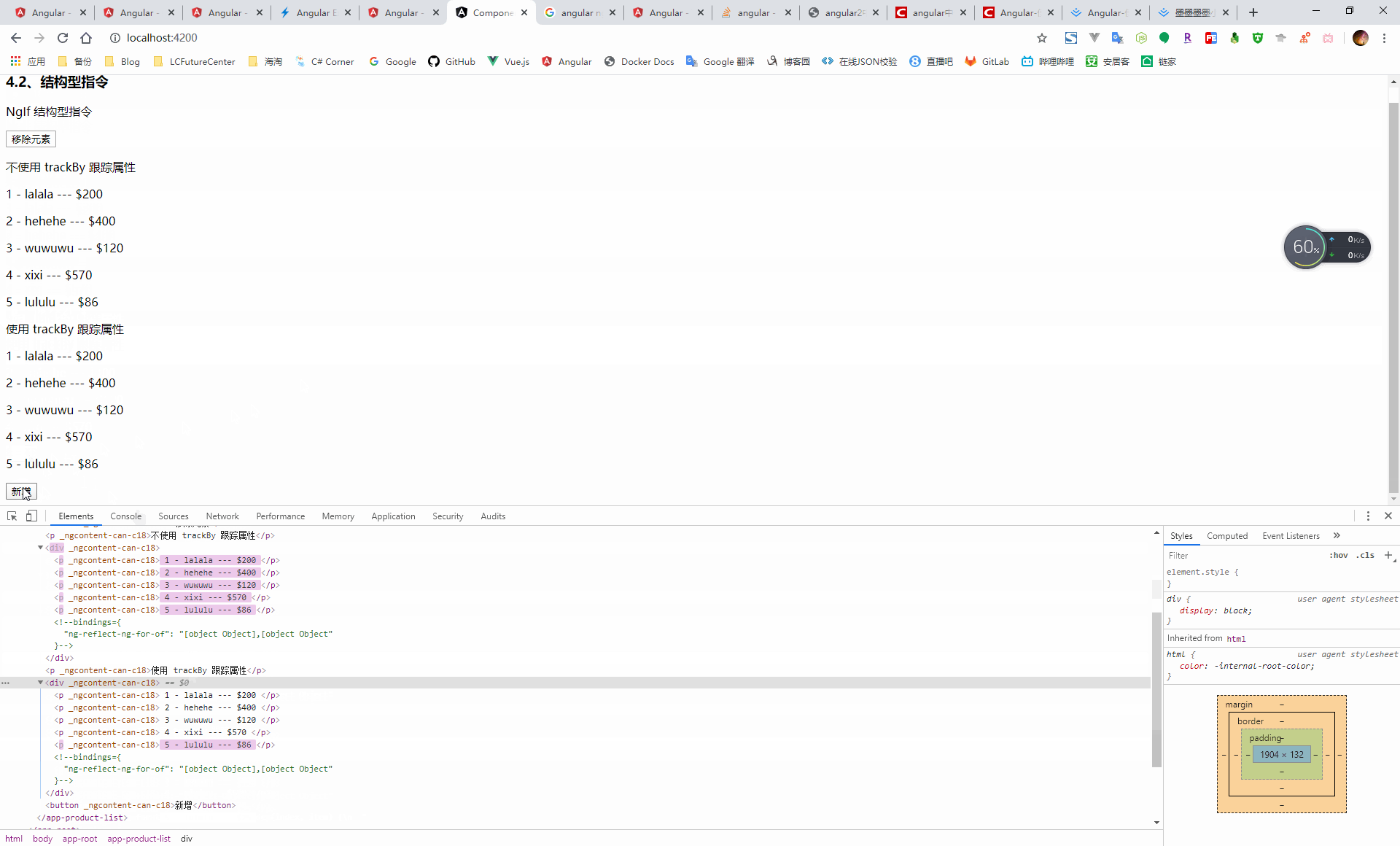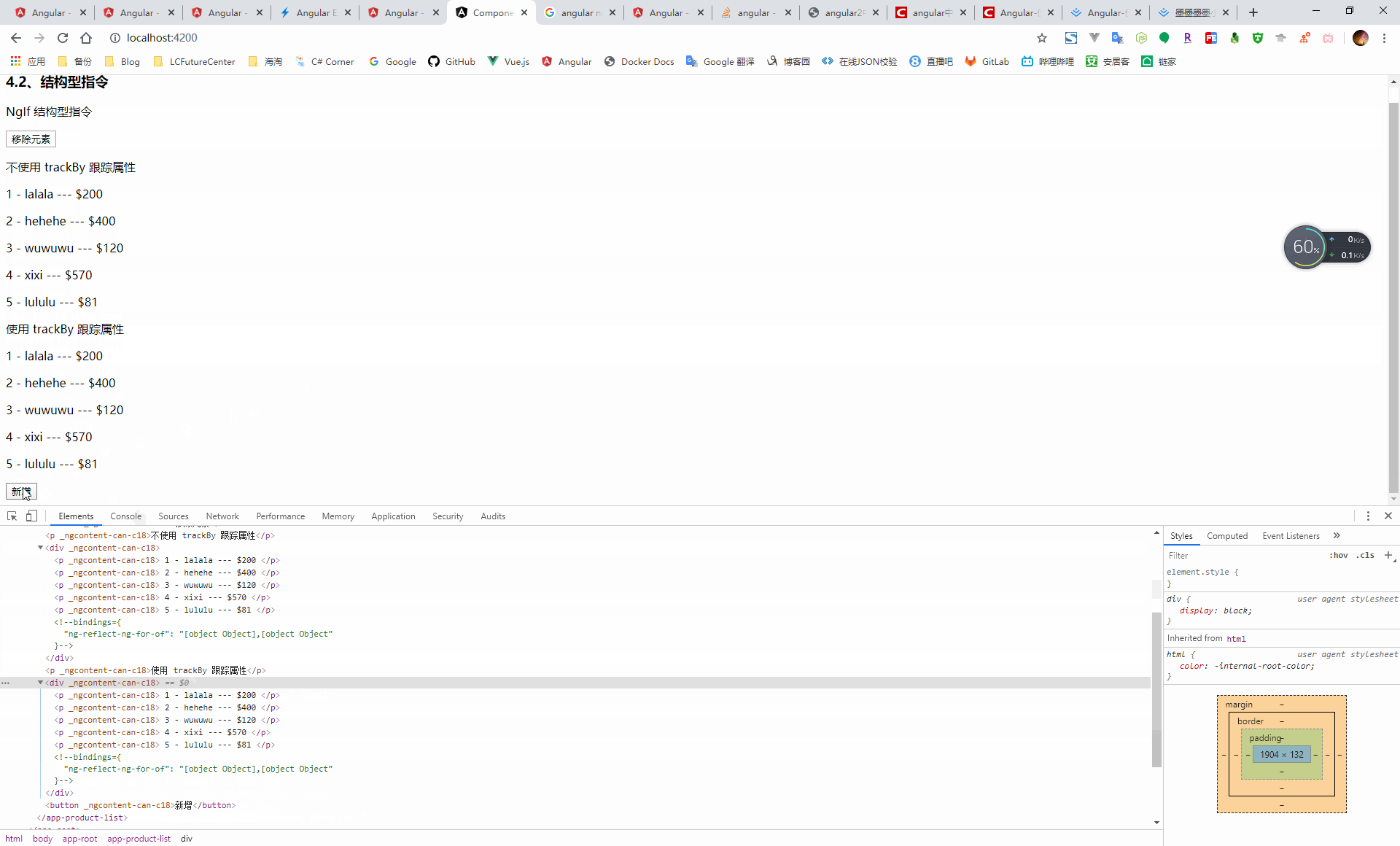
NgSwitch:根據條件切換,從候選的幾個元素中選擇匹配的,放到 dom 元素中
<p> 請選擇配置 <select [(ngModel)]="config"> <option value="">請選擇</option> <option value="r7-3700x">AMD Ryzen 7 3700X</option> <option value="i5-9400f">Intel i5 9400F</option> <option value="i5-9600kf">Intel i5 9600KF</option> </select> </p> <p> 配置描述 </p> <div [ngSwitch]="config"> <p *ngSwitchCase="'r7-3700x'"> 一個能打得都木的~~~ </p> <p *ngSwitchCase="'i5-9400f'"> 擠牙膏的。。。 </p> <p *ngSwitchCase="'i5-9600kf'"> 別看了,我不是開封菜。。。 </p> <p *ngSwitchDefault> 你選一個啊~~~ </p> </div>import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-product-list', templateUrl: './product-list.component.html', styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss'] }) export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit { public config = ''; constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { } }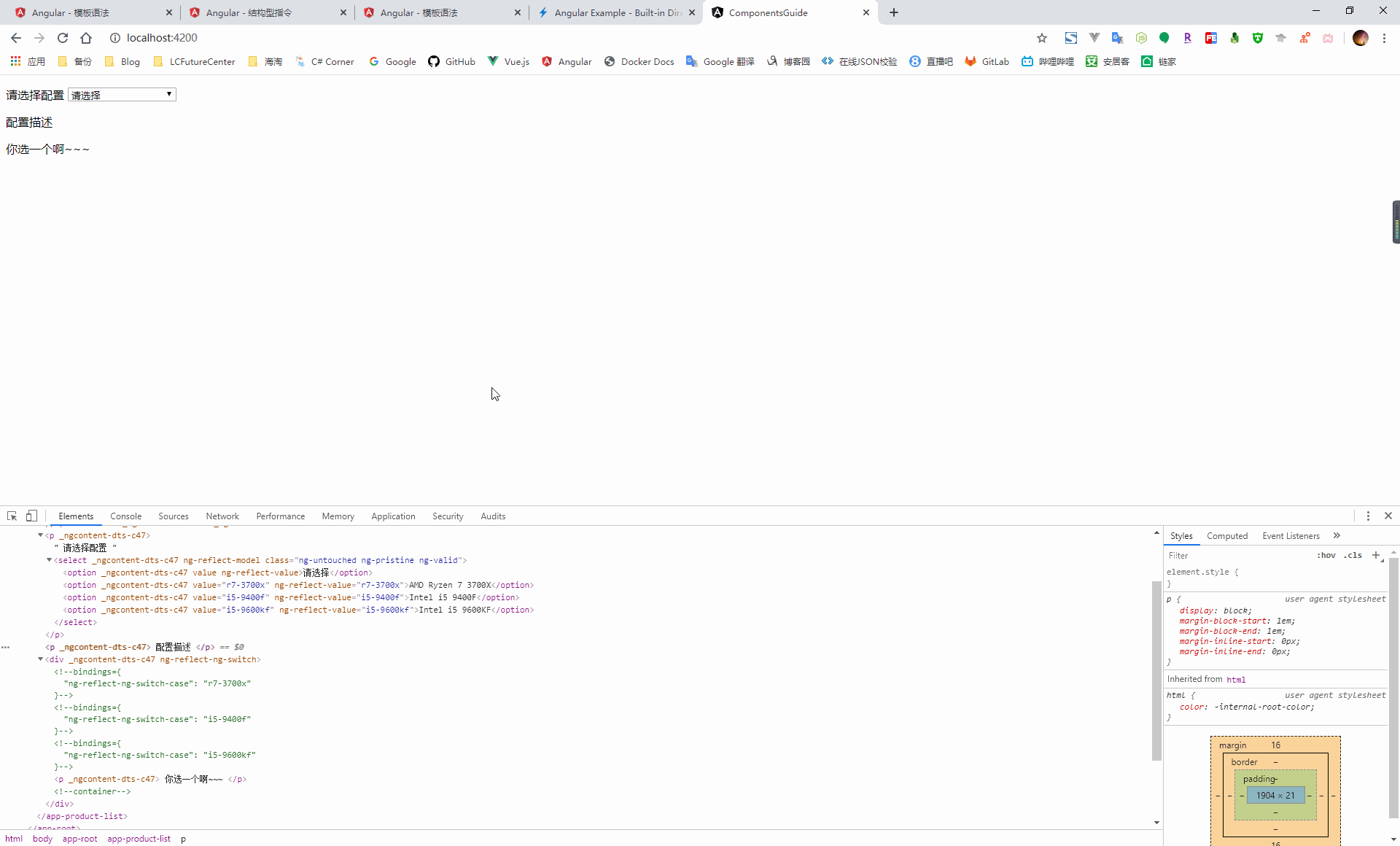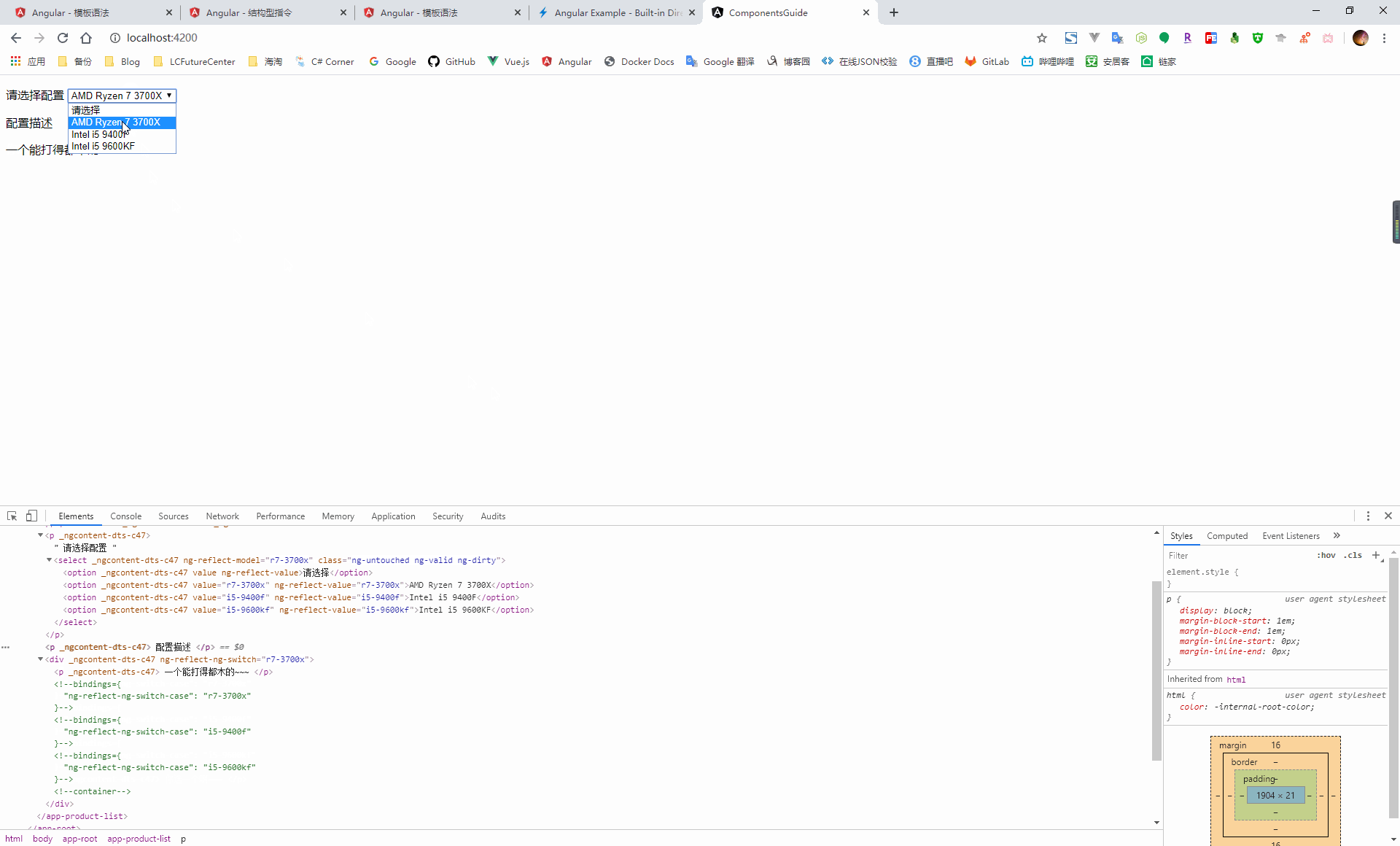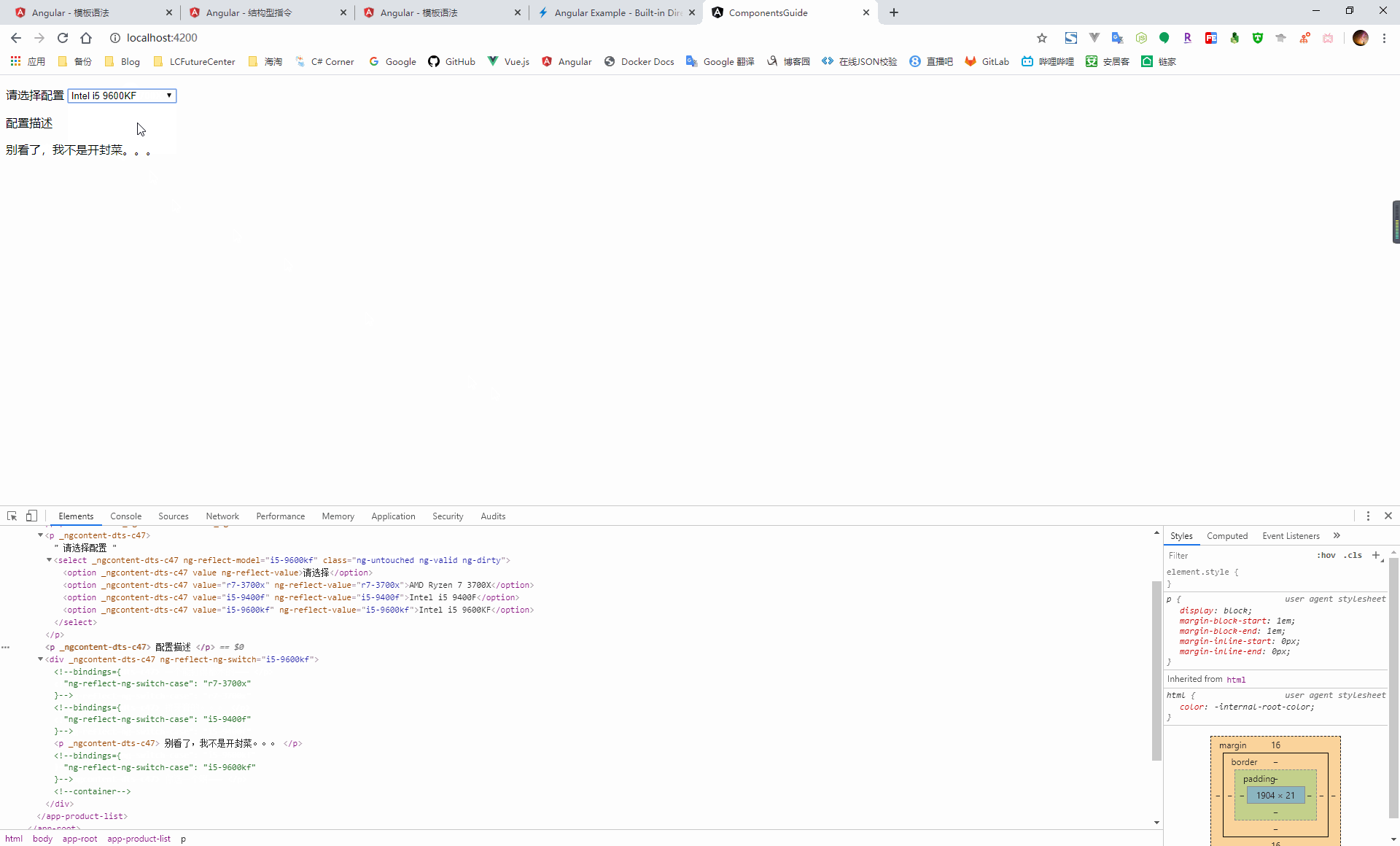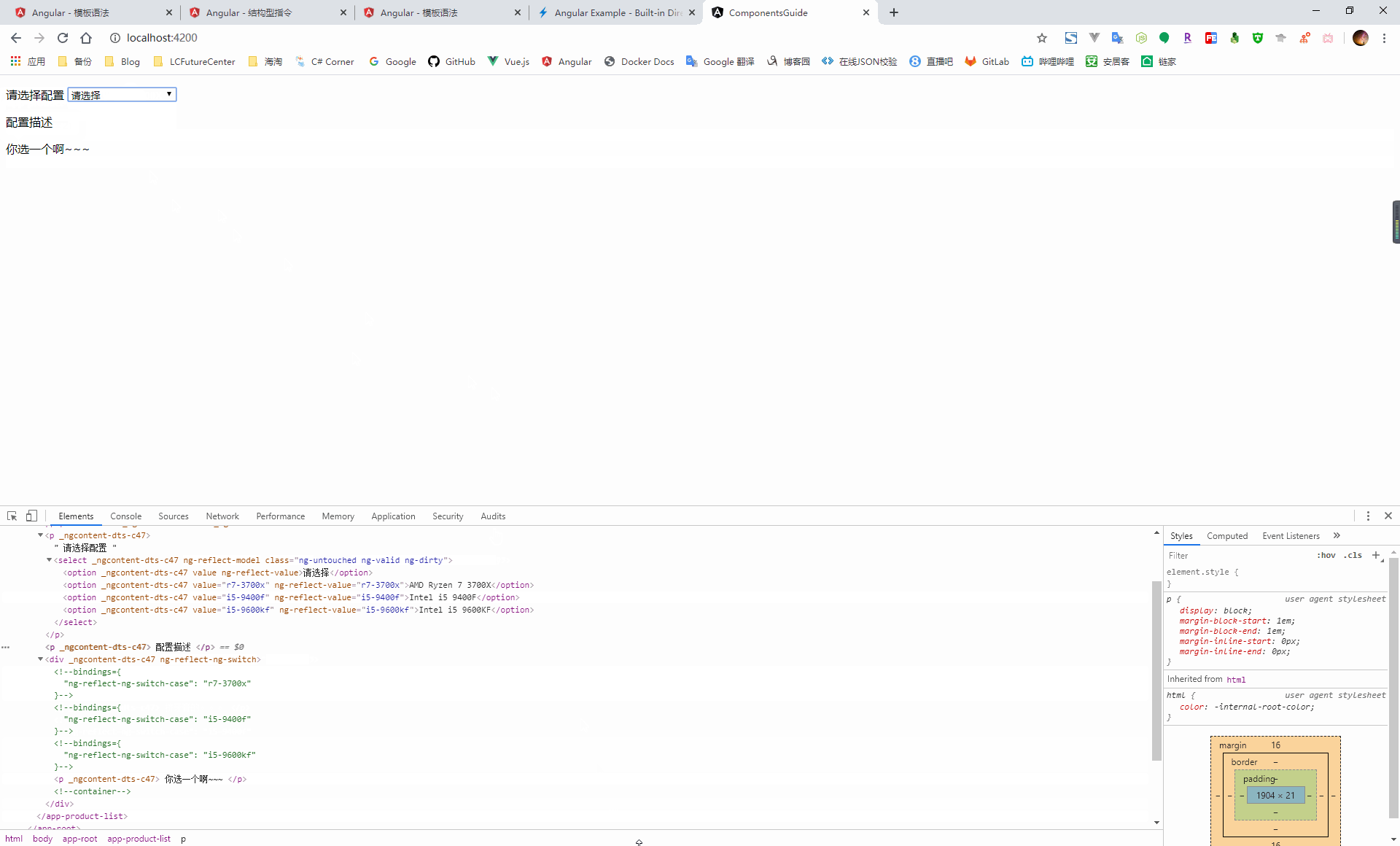
NgSwitch 本身是一個屬性型指令,它不會直接操作 dom 元素,而是通過它所控制的兩個結構型指令(NgSwitchCase、ngSwitchDefault)來操作 dom 元素
4.3、管道
在使用模板表示式繫結資料時,可以使用管道對於表示式的結果進行轉換
管道是一種簡單的函式,它們接受輸入值並返回轉換後的值。通過在模板表示式中使用管道運算子(|)則可以完成相應的結果轉換
4.3.1、模板表示式中的特殊運算子
angular 模板表示式是 javascript 的子集,相對於常見的 javascript 運算子,添加了三個特殊的運算子
管道運算子
管道是一種特殊的函式,可以把運算子(|)左邊的資料轉換成期望呈現給檢視的資料格式,例如,將時間進行格式化、將資料轉換成 json 字串的形式等等
可以針對一個數據使用多個管道進行串聯,並且管道運算子的優先順序比三元運算子( ?: )高
<h3>5.1、管道運算子</h3> <div> <p>產品資訊 json 字串</p> {{products | json}} </div>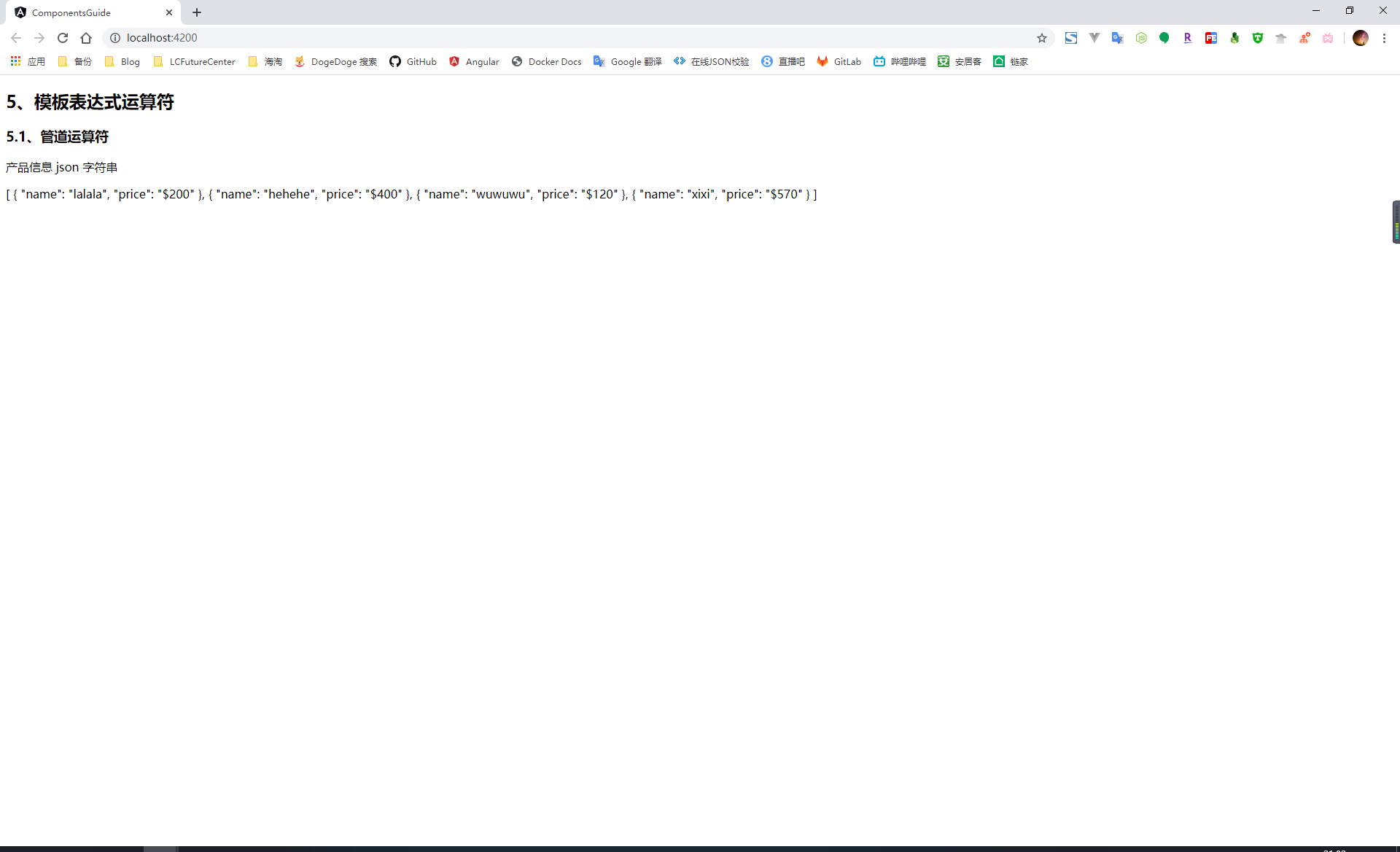
安全導航運算子
在檢視中使用的屬性值為 null or undefined 時,javascript 和 angular 會引發空指標異常並中斷檢視的渲染過程, 從而檢視會渲染失敗,而使用了安全導航運算子(?)後,檢視依然會渲染,只是顯示的值為空白
<h3>5.2、安全導航運算子</h3> <p>第五個專案的名稱為:{{products[5].name}}</p>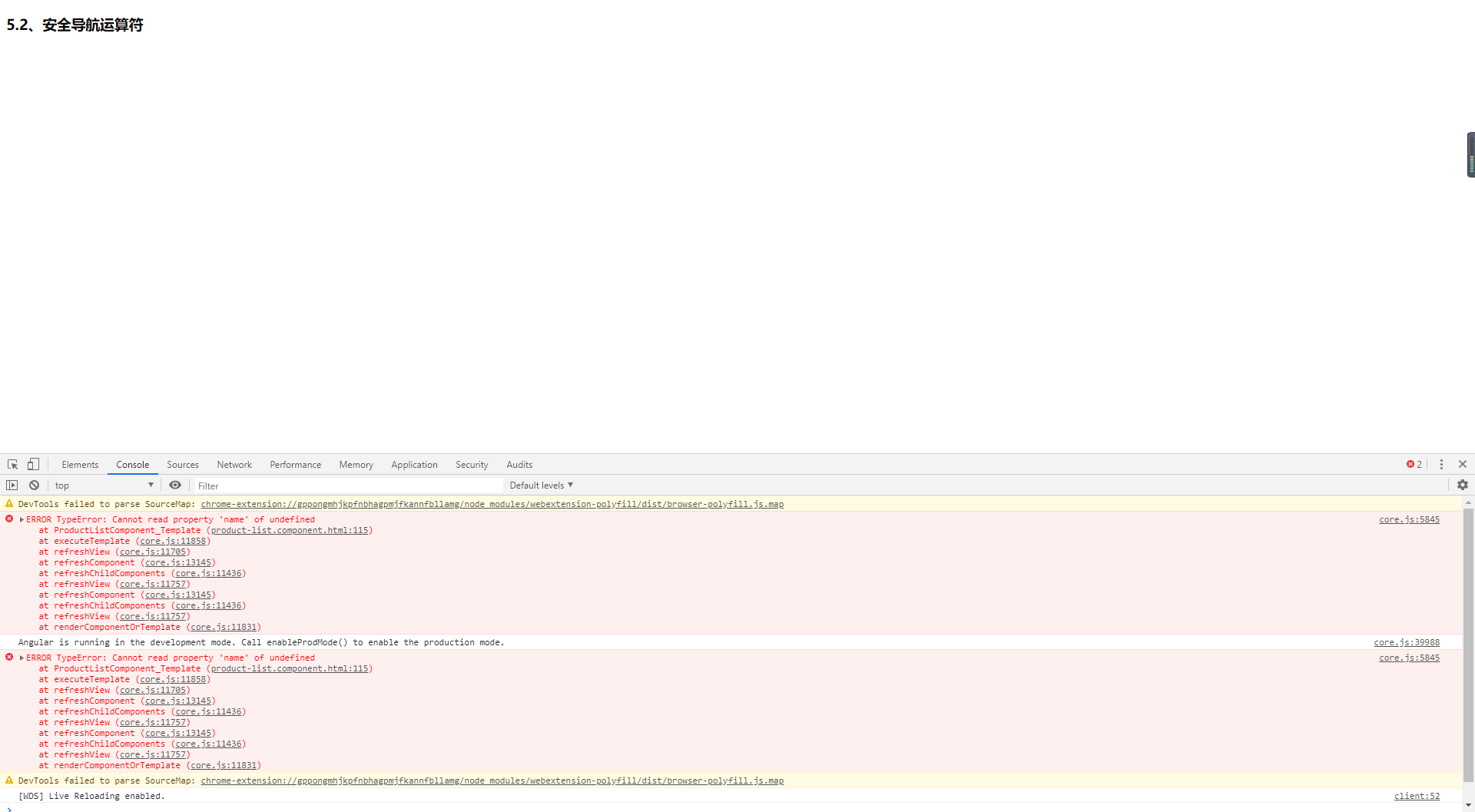
<p>第五個專案的名稱為:{{products[5]?.name}}</p>
非空斷言運算子
在 tsconfig.json 中啟用 strictNullChecks 屬性,typescript 將會強制開啟嚴格的空值檢查,在這種模式下,所有定義了型別的屬性是不允許賦值為 null 的,當將屬性賦值為 null,則會編譯報錯
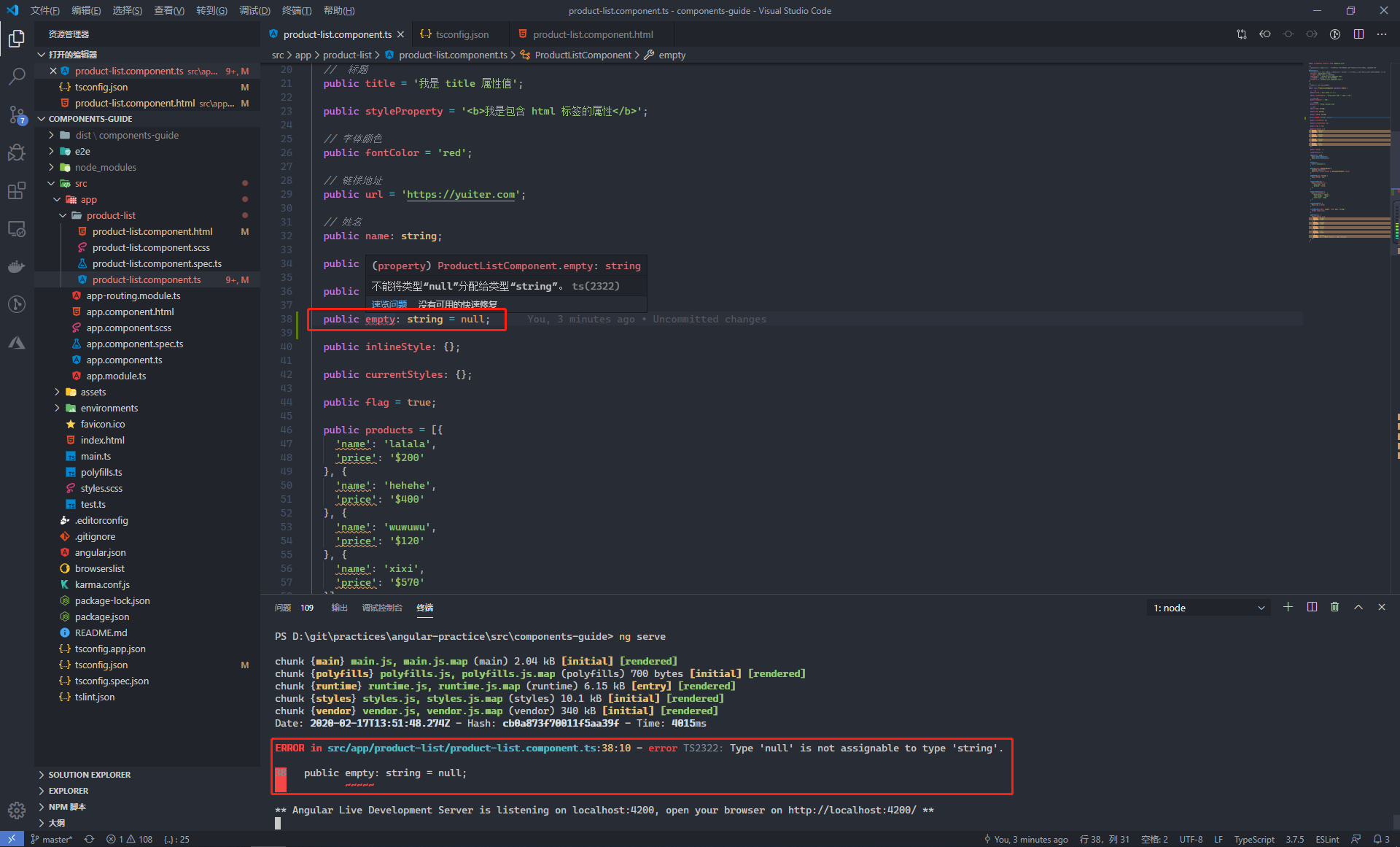
非空斷言運算子用來告訴編譯器對特定的屬性不做嚴格的空值校驗,當屬性值為 null or undefined 時,不拋錯誤。在下面的程式碼中,在判斷 obj 存在後,就不再針對 obj.name 進行校驗
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; interface Person { name: string; age: number; } @Component({ selector: 'app-product-list', templateUrl: './product-list.component.html', styleUrls: ['./product-list.component.scss'] }) export class ProductListComponent implements OnInit { public obj: Person; constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { } }<p *ngIf="obj"> <span>{{obj!.name}}</span> </p>非空斷言運算子不會防止出現 null 或 undefined,只是不提示
4.3.2、常用的管道函式
純管道
只有在它檢測到輸入值發生了純變更時才會執行,但是會忽略物件內部的變更
純變更是指對原始型別值(String、Number、Boolean、Symbol)的更改, 或者對物件引用(Date、Array、Function、Object)的更改
非純管道
每個元件的變更週期都會執行
| 管道 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| JsonPipe | 將一個值轉換成 json 字串 |
| DatePipe | 根據區域設定規則格式化日期值 |
| UpperCasePipe | 把文字轉換成全大寫形式 |
| LowerCasePipe | 把文字轉換成全小寫形式 |
<h3>6.1、json 管道</h3>
<p>{{products | json}}</p>
<h3>6.2、date 管道</h3>
<p>現在時間:{{date | date:'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss'}}</p>
<h3>6.3、upper 管道</h3>
<p>轉換成全大寫:{{url | uppercase}}</p>
<h3>6.4、lower 管道</h3>
<p>轉換成全小寫:{{url | lowercase}}</p>
4.4、元件之間的通訊
4.4.1、輸入屬性與輸出屬性
輸入屬性(@Input)和輸出屬性(@Output)用來在父子元件或指令中進行共享資料。@Input 用來獲取資料,@Output 用來向外傳送資料
4.4.2、子元件獲取父元件資訊
在父元件中,新增對於子元件的引用,並將需要傳遞的資料 or 方法繫結到子元件上
傳遞資料直接將父元件中的屬性值賦值給繫結在子元件上的屬性就可以了
傳遞方法時,繫結在子元件上的屬性是父元件方法的名稱,此處不能加 () ,否則就會直接執行該父元件的方法
在傳遞資料給子元件時,也可以通過 this 來指代父元件,從而將整個父元件作為資料繫結子元件上
<h2>父元件內容:</h2> <p> <label for="title">標題:</label> <input id="title" type="text" [(ngModel)]="title"> </p> <hr> <h2>子元件內容:</h2> <!-- 將父元件的資料繫結到子元件上 --> <app-child-component [parentTitle]="title" [parentGetMsg]='getMsg'></app-child-component>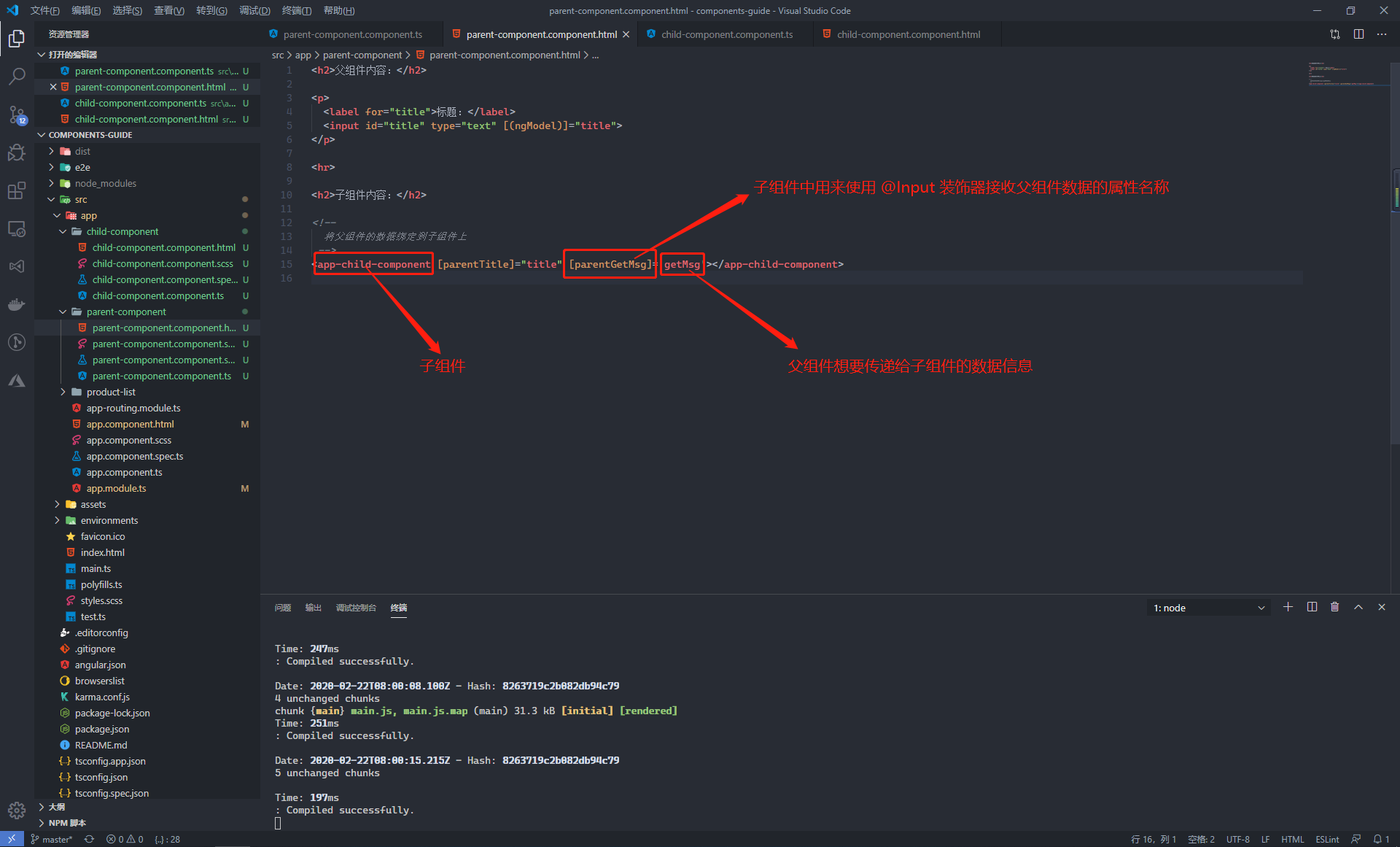
在子元件中引入 Inupt,同時使用 @Input 裝飾器來接收父元件傳遞的資料
// 引入 Input 介面 import { Component, OnInit, Input } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-child-component', templateUrl: './child-component.component.html', styleUrls: ['./child-component.component.scss'] }) export class ChildComponentComponent implements OnInit { // 獲取父元件的資料 @Input() parentGetMsg: any; // 使用 setter 對父元件的資料進行深加工 private _title: string; @Input() set parentTitle(title: string) { this._title = (title && title.trim()) || '父元件的 title 屬性值為空'; } get parentTitle(): string { return this._title; } constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { } runParentFunc() { this.parentGetMsg(); } }<p>父元件的 title 屬性值:{{parentTitle}}</p> <p> <button (click)="runParentFunc()">呼叫父元件的方法</button> </p>對於使用 @Input 裝飾器獲取到的父元件資料,可以通過輸入屬性中的 setter 方法中進行重新賦值

4.4.3、父元件獲取子元件資訊
使用 @ViewChild 裝飾器獲取
在子元件上定義一個模板引用變數
<h2>父元件內容:</h2> <h3>1、使用 @ViewChild 裝飾器獲取子元件資料</h3> <p> <button (click)="getChildMsg()">獲取子元件的 msg 資料</button> </p> <p> <button (click)="runChildFunc()">呼叫子元件的方法</button> </p> <hr> <h2>子元件內容:</h2> <!-- 在子元件上定義一個模板引用變數 --> <app-child-component #childComponent></app-child-component>在父元件中新增對於 ViewChild 的引用,然後使用 @ViewChild 裝飾器來接收子元件的 dom 資訊,從而獲取到子元件的資料或方法
// 引入 ViewChild import { Component, OnInit, ViewChild } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-parent-component', templateUrl: './parent-component.component.html', styleUrls: ['./parent-component.component.scss'] }) export class ParentComponentComponent implements OnInit { // 通過 @ViewChild 裝飾器來接收字元件的 dom 資訊 @ViewChild('childComponent') child: any; constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { } getMsg() { alert('我是父元件的 getMsg 方法'); } getChildMsg() { alert(this.child.msg); } }
使用 @Output 裝飾器配合 EventEmitter 實現
在子元件中引入 Output 和 EventEmitter,通過 @Output 裝飾器定義一個事件觸發器,然後就可以通過這個事件觸發器的 emit 方法進行事件廣播
// 引入 Output、EventEmitter import { Component, OnInit, Output, EventEmitter } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-child-component', templateUrl: './child-component.component.html', styleUrls: ['./child-component.component.scss'] }) export class ChildComponentComponent implements OnInit { public msg = 'child title'; // 定義一個事件觸發器 @Output() childEmitter = new EventEmitter<string>(); constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { } runParentFunc() { this.parentGetMsg(); } sendMsg() { this.childEmitter.emit(this.msg); } }當子元件進行事件廣播時,就可以通過在子元件上使用事件繫結的方式繫結到一個父元件事件,通過 $event 獲取到子元件傳遞的資料值
<h2>父元件內容:</h2> <h3>2、使用 @Output 裝飾器配合 EventEmitter 獲取子元件資料</h3> <p>{{childMsg}}</p> <hr> <h2>子元件內容:</h2> <!-- 將子元件的事件廣播繫結到父元件事件上 --> <app-child-component (childEmitter)='childEmitMsg($event)'></app-child-component>import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-parent-component', templateUrl: './parent-component.component.html', styleUrls: ['./parent-component.component.scss'] }) export class ParentComponentComponent implements OnInit { public childMsg: string; constructor() { } ngOnInit(): void { } childEmitMsg(event) { this.childMsg = event; } }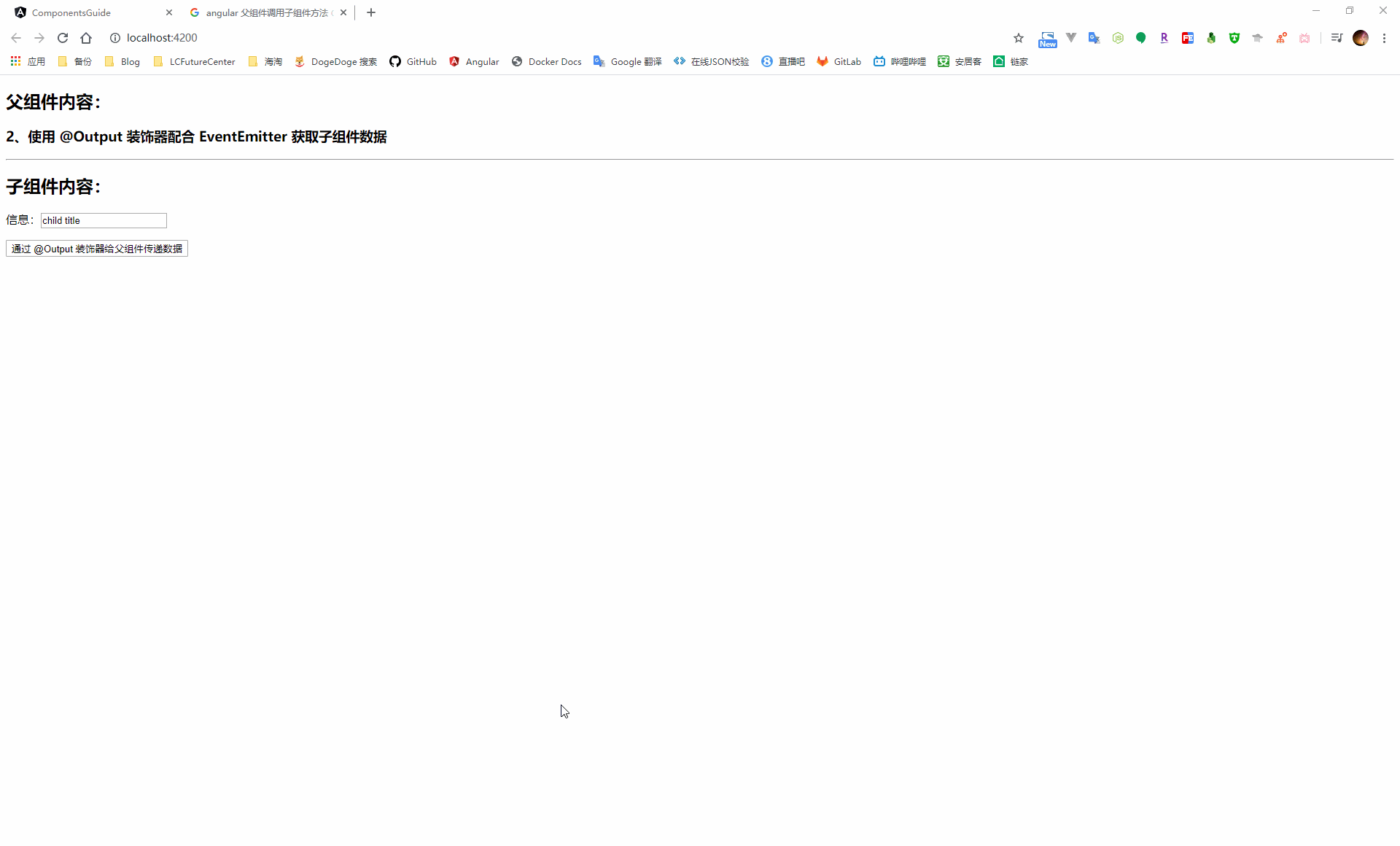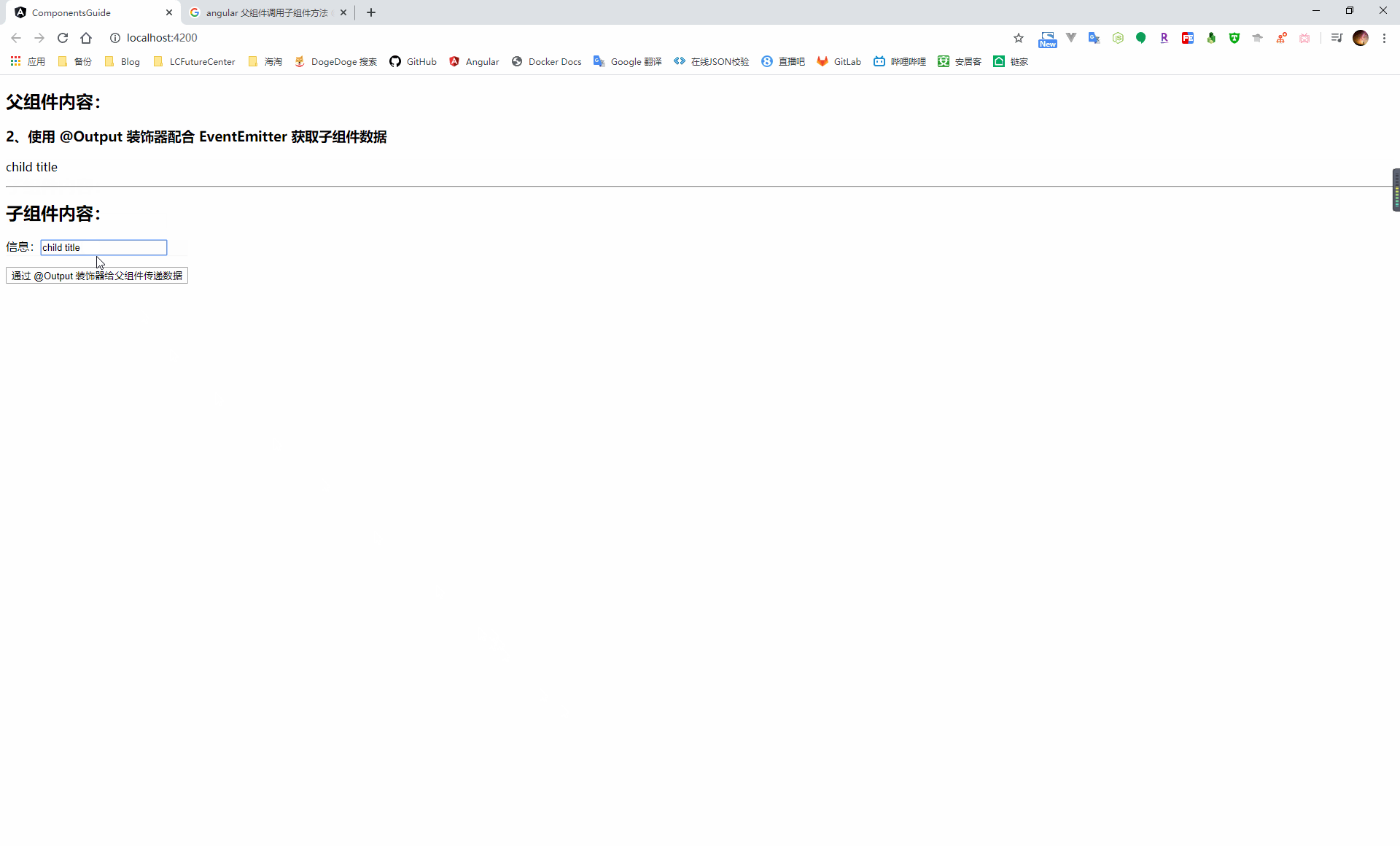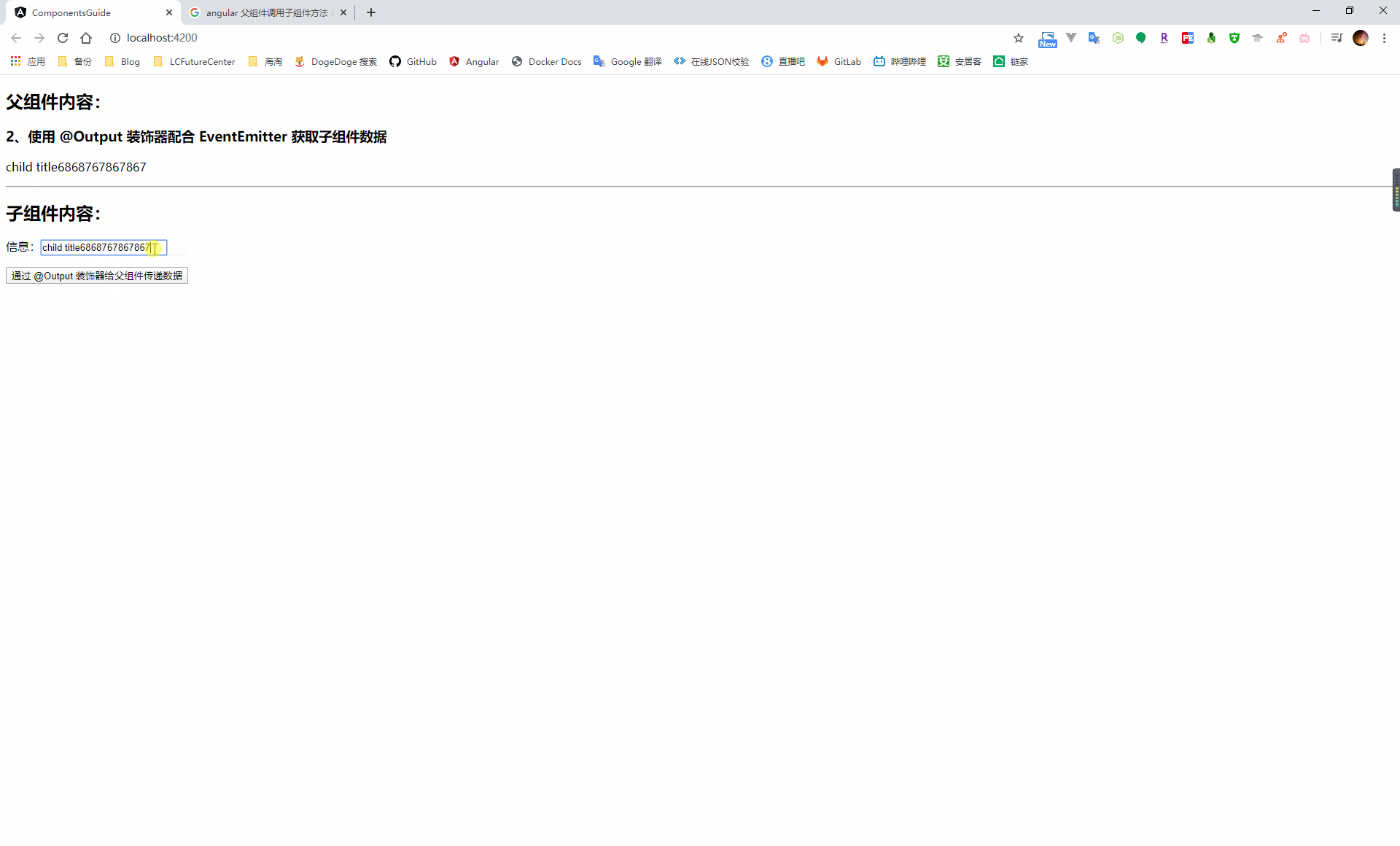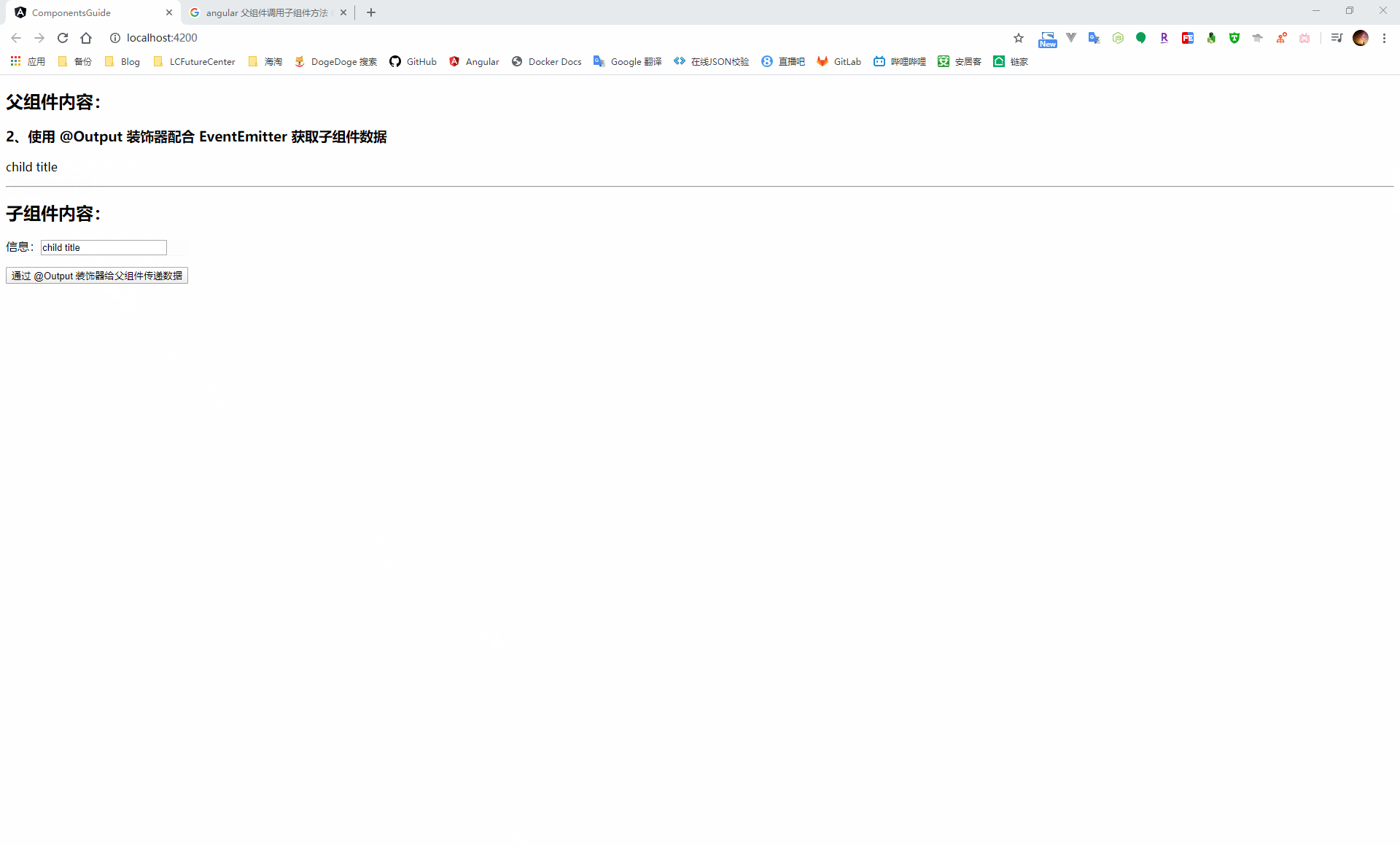
4.4.4、非父子元件之間的通訊
不管元件之間是否具有關聯關係,都可以通過共享一個服務的方式來進行資料互動,也可以將需要進行共享的資料儲存到一些儲存介質中,通過直接讀取這個儲存介質中的資料進行通訊
建立一個服務,並新增到模組中
## 在 services/storage 路徑下建立一個 storage 服務 ng g service services/storage/storageimport { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module'; import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; import { ProductListComponent } from './product-list/product-list.component'; import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; import { ParentComponentComponent } from './parent-component/parent-component.component'; import { ChildComponentComponent } from './child-component/child-component.component'; // 引入自定義的服務 import { StorageService } from './services/storage/storage.service'; @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent, ProductListComponent, ParentComponentComponent, ChildComponentComponent ], imports: [ BrowserModule, AppRoutingModule, FormsModule ], // 配置自定義的服務 providers: [StorageService], bootstrap: [AppComponent] }) export class AppModule { }
在元件中使用服務
在需要使用的元件中引入服務,然後在元件的建構函式中通過依賴注入的方式注入這個服務,就可以在元件中完成對於這個服務的使用
在父元件中對資料進行賦值,然後呼叫服務的方法改變資料資訊
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; // 引入服務 import { StorageService } from '../services/storage/storage.service'; @Component({ selector: 'app-parent-component', templateUrl: './parent-component.component.html', styleUrls: ['./parent-component.component.scss'] }) export class ParentComponentComponent implements OnInit { public msg = 'this is a service default value writen in parent component'; constructor(private storage: StorageService) { this.storage.setMsg(this.msg); } ngOnInit(): void { } submit() { this.storage.setMsg(this.msg); } }<h2>父元件內容:</h2> <h3>3、通過服務在屬性中共享資料</h3> <p> 修改服務中的資料值 <input type="text" [(ngModel)]="msg"> <button (click)="submit()">提交</button> </p> <p>服務中的資料:{{msg}}</p> <hr> <h2>子元件內容:</h2> <app-child-component></app-child-component>在子元件中引入服務,從而同步獲取到父元件修改後的服務中的資料資訊
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; // 引入服務 import { StorageService } from '../services/storage/storage.service'; @Component({ selector: 'app-child-component', templateUrl: './child-component.component.html', styleUrls: ['./child-component.component.scss'] }) export class ChildComponentComponent implements OnInit { public storageMsg: string; constructor(private storage: StorageService) { } ngOnInit(): void { } getServiceMsg() { this.storageMsg = this.storage.getMsg(); } }<button (click)="getServiceMsg()">獲取服務中的資料值</button> <p> 服務中 msg 屬性值:{{storageMsg}} </p>
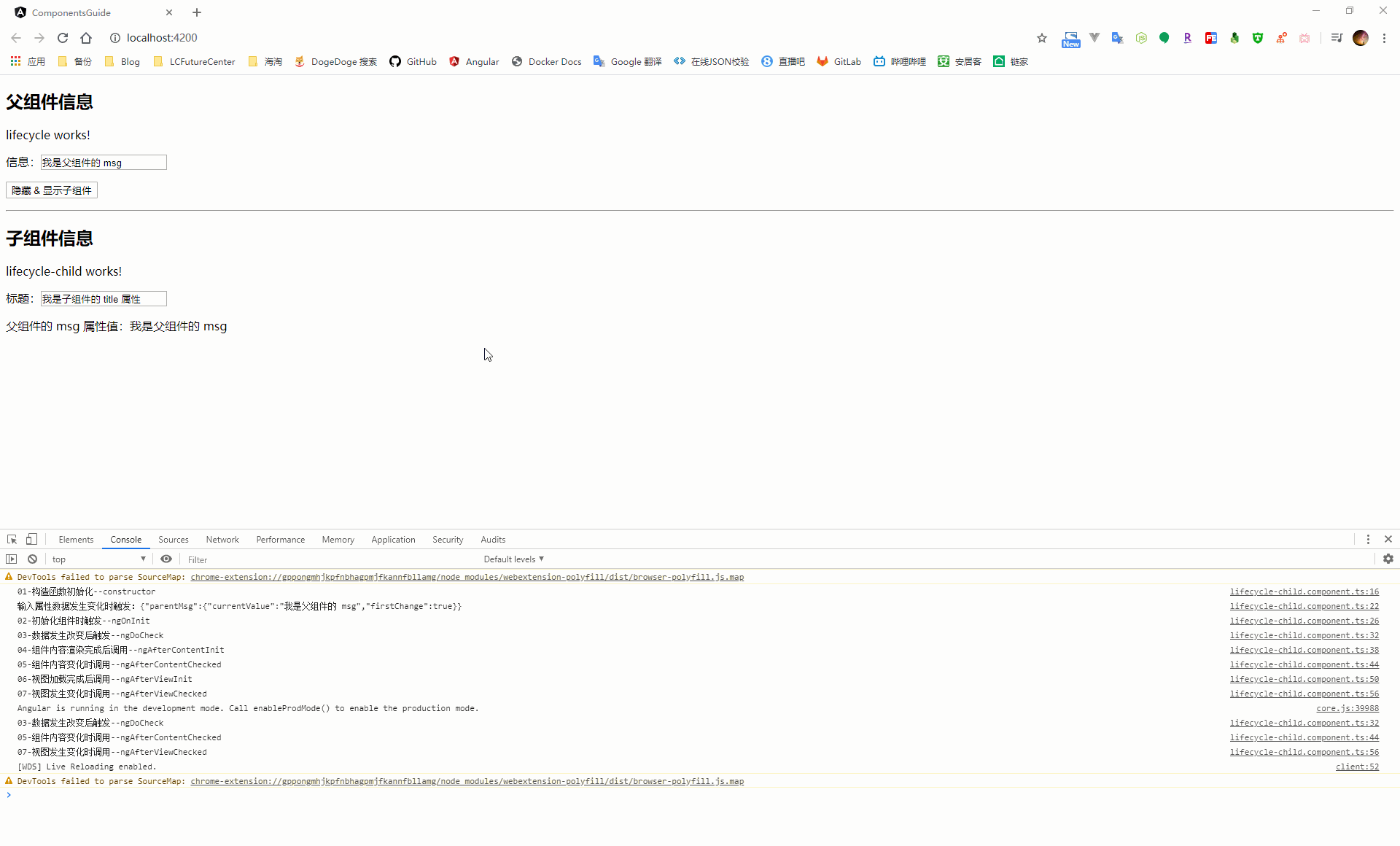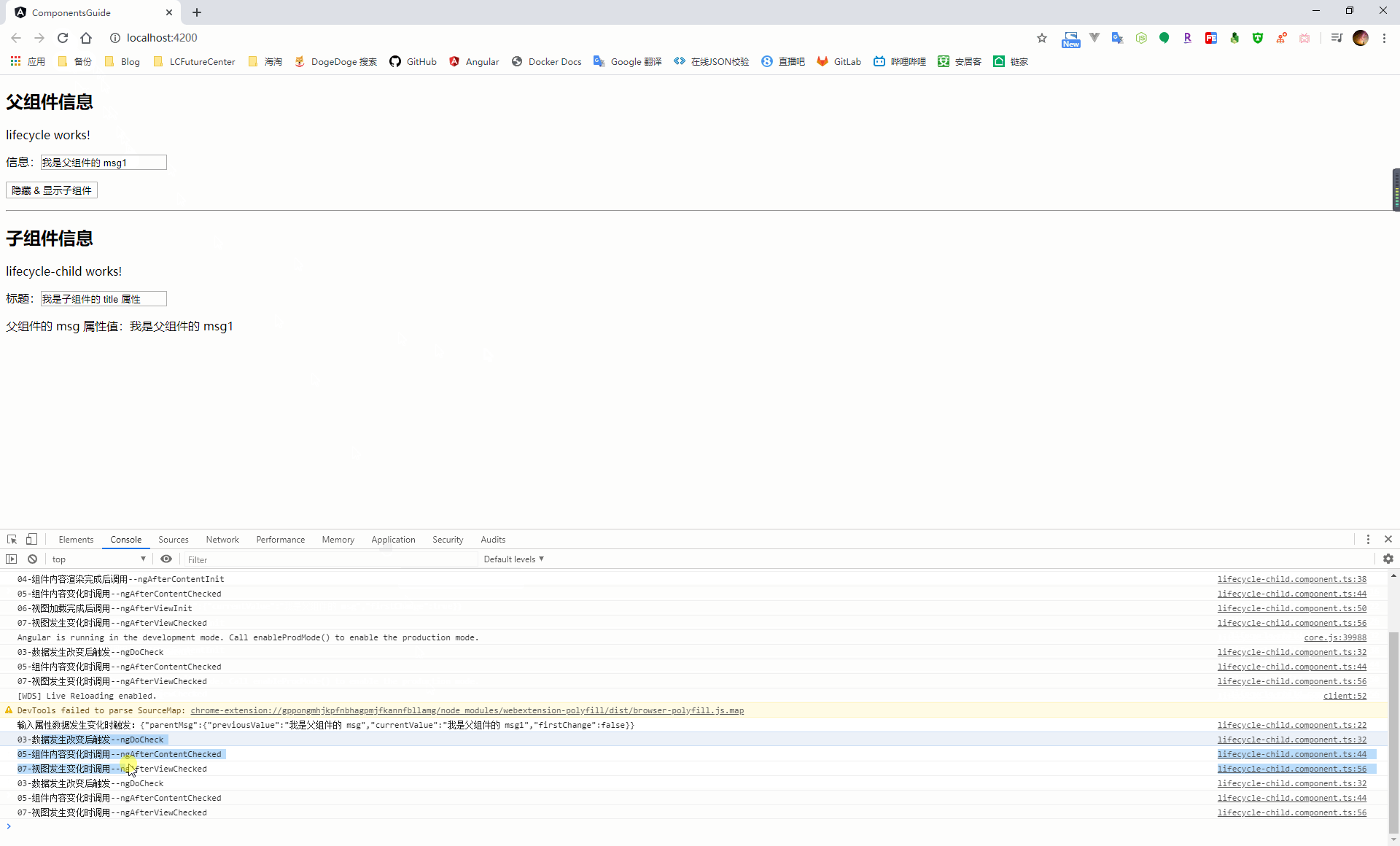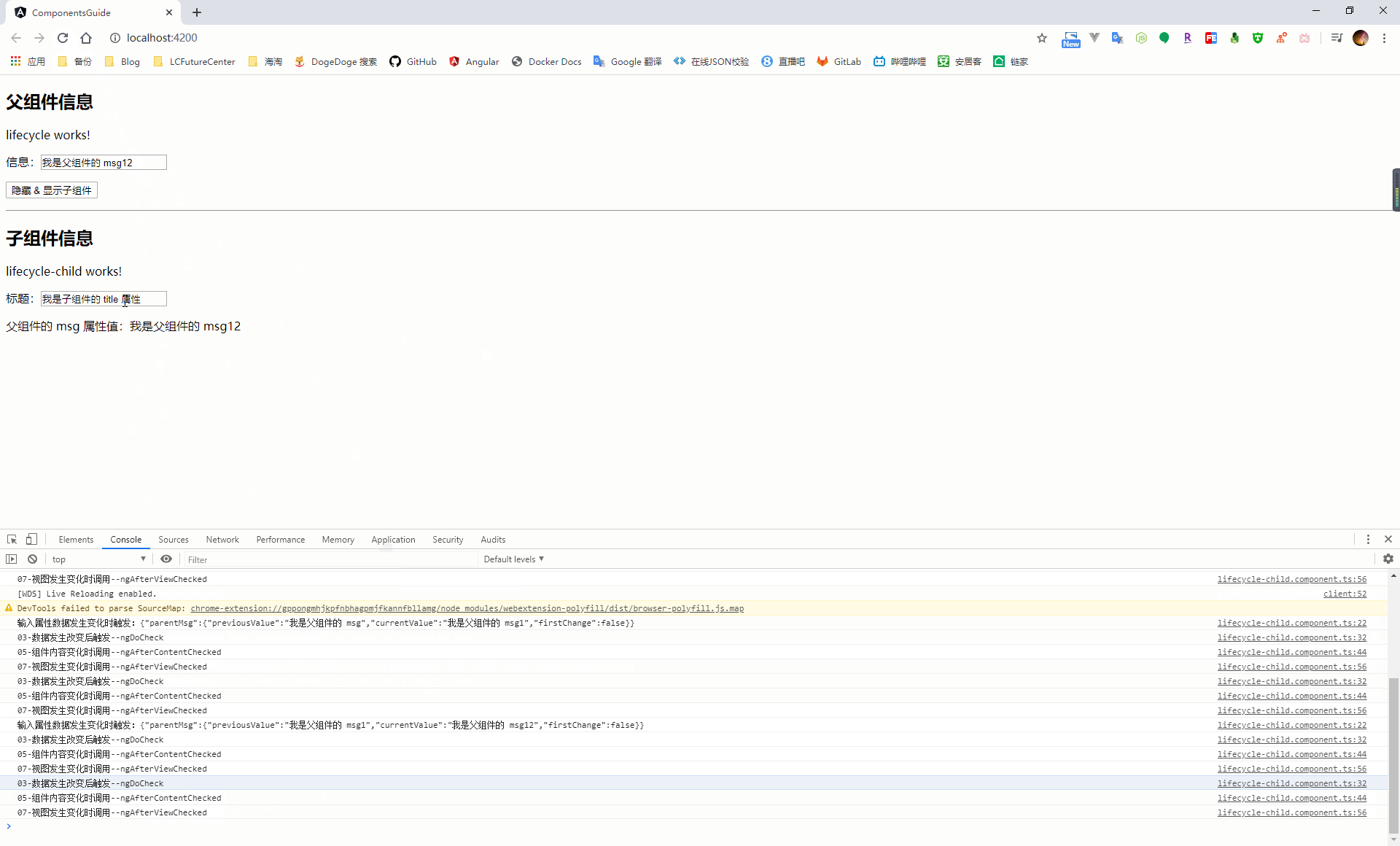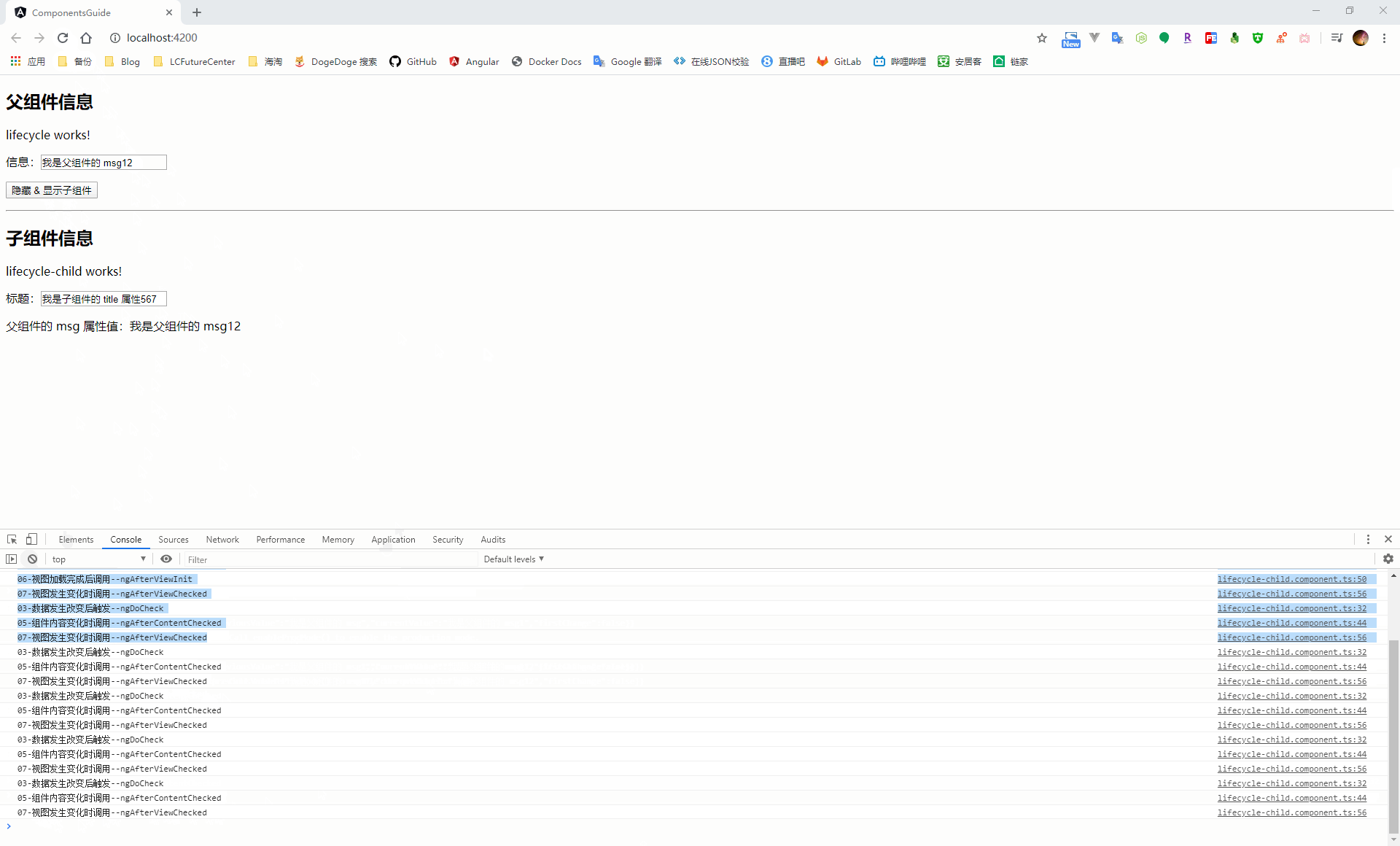
五、元件的生命週期鉤子函式
當 angular 在建立、更新、銷燬元件時都會觸發元件的生命週期鉤子函式,通過在元件中實現這些生命週期函式,從而介入到這些關鍵時刻
| 鉤子函式 | 觸發時機 |
|---|---|
| ngOnChanges | 被繫結的輸入屬性值發生變化時觸發,會呼叫多次;如果沒有使用到父子元件傳值,則不會觸發 |
| ngOnInit | 初始化元件時會呼叫一次,一般是用來在建構函式之後執行元件複雜的初始化邏輯 |
| ngDoCheck | 只要資料發生改變就會被呼叫 |
| ngAfterContentInit | 元件內容渲染完成後呼叫一次 |
| ngAfterContentChecked | 只要元件的內容發生改變就會被呼叫 |
| ngAfterViewInit | 檢視載入完成後觸發一次,一般用來對檢視的 dom 元素進行操作 |
| ngAfterViewChecked | 檢視發生變化時呼叫,在元件的生命週期中會呼叫多次 |
| ngOnDestroy | 只在銷燬元件時呼叫一次,一般用來在元件銷燬前執行某些操作 |
在元件載入過程中,會按照上面列出的鉤子函式順序,在元件的建構函式執行之後依次執行,在頁面載入過程中會涉及繫結資料的操作,因此會再次出發 ngDoCheck、ngAfterContentChecked、ngAfterViewChecked 這三個生命週期鉤子函式。後續只要頁面資料有發生改變,都會觸發這幾個事件
裝飾器是一種特殊型別的宣告,它能夠被附加到類宣告,方法, 訪問符,屬性或引數上,就像是 C# 中的特性↩
元資料是用來描述資料的資料項,例如這裡的 selector 是為了描述 Component 這個資料資訊資源中抽取出來用於說明其特徵的一個結構化的資料↩
property 是 dom 元素預設的基本屬性,在 dom 初始化時會被全部建立,而 attribute 是 html 標籤上定義的屬性和值 =》DOM 中 Property 和 Attribute 的區別↩
這裡的資料改變指的是會將原來的資料物件重新銷燬然後重建的過程,因此像 push、unshift 這樣的方法即使不新增 trackBy 也不會重新渲染整個 DOM,只會重新渲染改變的資料↩
