SpringMVC原始碼學習:容器初始化+MVC初始化+請求分發處理+引數解析+返回值解析+檢視解析
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-05-09
[toc]
# 一、前言
> 版本:
>
> springMVC 5.0.2RELEASE
>
> JDK1.8
前端控制器的配置:
web.xml
```xml
dispatcherServlet
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
classpath:springmvc.xml
1
dispatcherServlet /
```
springmvc.xml配置
```xml
```
# 二、初始化
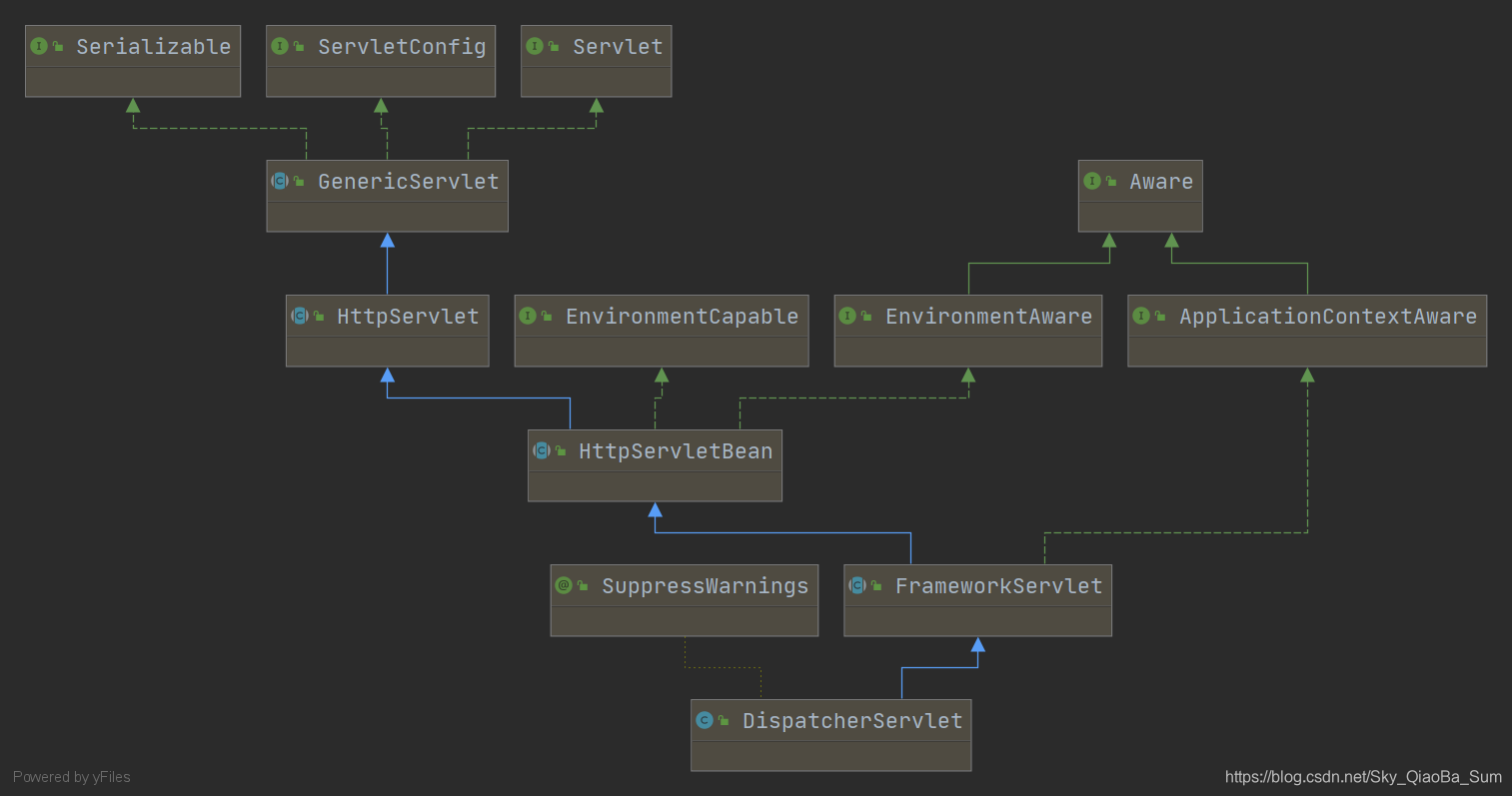
DispatcherServlet的啟動與Servlet的啟動過程緊密聯絡,我們通過以上繼承圖就可以發現。
## 1. 容器初始化
Servlet中定義的init()方法就是其生命週期的初始化方法,接著往下走,GenericServlet並沒有給出具體實現,在HttpServletBean中的init()方法給出了具體的實現:
`HttpServletBean.init()`方法(忽略日誌)
```java
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
//根據初始化引數設定bean屬性(我們設定了contextConfigLocation,故可以獲取)
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
//包裝DispatcherServlet
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
//獲取資源載入器,用以載入springMVC的配置檔案
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
//註冊一個ResourceEditor
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
//該方法為空實現,可以重寫,初始化BeanWrapper
initBeanWrapper(bw);
//最終將init-param讀取的值spirng-mvc.xml存入contextConfigLocation中
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
}
// 讓子類實現初始化
initServletBean();
}
```
那就來看看`FrameworfServlet.initServletBean()`幹了啥(基本都是日誌記錄,還有計時,省略了這些部分):
```java
/**
* Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties
* have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
//WebApplicationContext的初始化
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
//也是空實現,允許子類自定義
initFrameworkServlet();
}
```
所以重頭戲就在initWebApplicationContext方法上,我們可以先來看看執行後的效果:
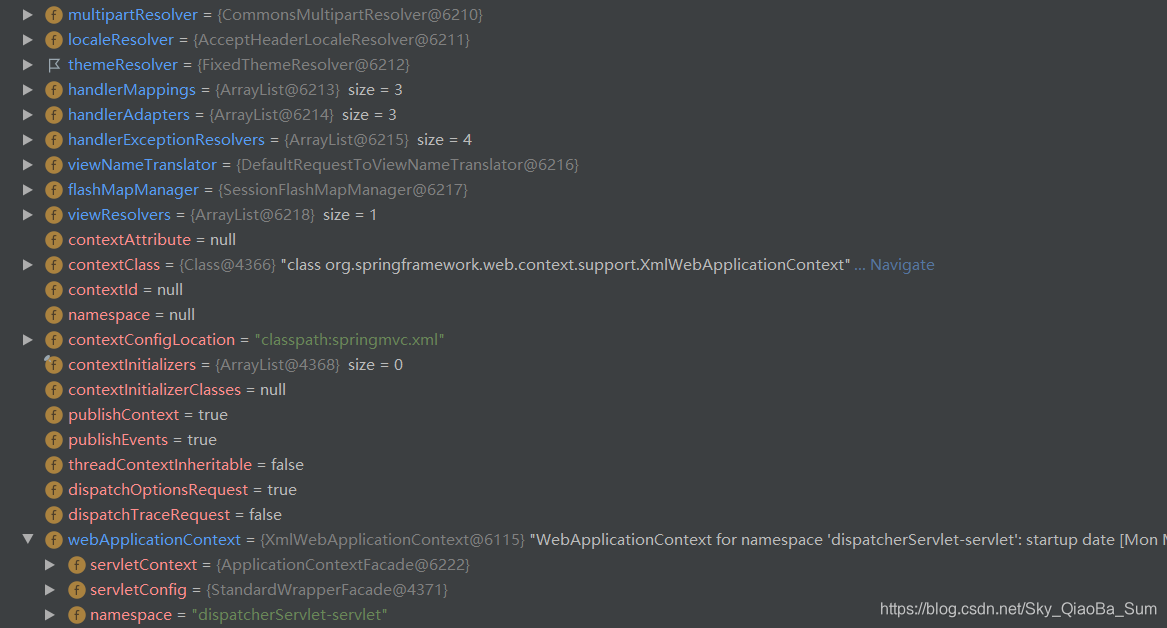
可以看到springMVC九大元件被賦值,除此之外webApplicationContext也已被賦值。
我們再來看看原始碼,看看其內部具體實現:`FrameworkServlet.initWebApplicationContext()`
```java
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//根容器查詢
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
//在構建時注入了DispatcherServlet並且webApplicationContext已經存在-> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
//嘗試從容器中獲取
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
//保證至少有一個handlerMapping
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
}
}
```
接下來幾個操作都差不多,就不贅述了。
總的來說,MVC初始化的過程建立在IoC容器初始化之後,畢竟要從容器中取出這些元件物件。
## 3. HandlerMapping的實現原理
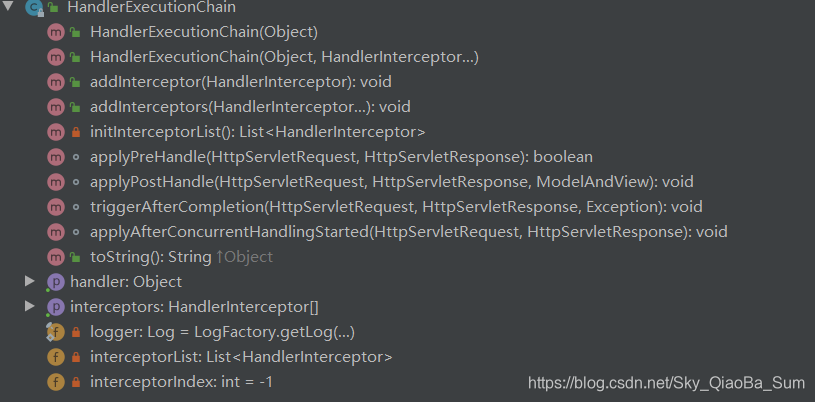
### HandlerExecutionChain
HandlerMapping在SpringMVC扮演著相當重要的角色,我們說,它可以為HTTP請求找到 對應的Controller控制器,於是,我們來好好研究一下,這裡面到底藏著什麼玩意。

HandlerMapping是一個介面,其中包含一個getHandler方法,能夠通過該方法獲得與HTTP請求對應的handlerExecutionChain,而這個handlerExecutionChain物件中持有handler和interceptorList,以及和設定攔截器相關的方法。可以判斷是同通過這些配置的攔截器對handler物件提供的功能進行了一波增強。
### RequestMappingHandlerMapping
我們以其中一個HandlerMapping作為例子解析一下,我們關注一下:
```java
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
//獲取所有上下文中的beanName
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class beanType = null;
//得到對應beanName的Class
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
//判斷是否為控制器類
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
//對控制器中的方法進行處理
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
```
isHandler方法:判斷該類是否存在@Controller註解或者@RequestMapping註解
```java
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
```
detectHandlerMethods方法:
```java
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
//獲取到控制器的型別
Class handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
//對型別再次進行處理,主要是針對cglib
final Class userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
//遍歷方法,對註解中的資訊進行處理,得到RequestMappingInfo物件,得到methods陣列
Map methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup) method -> {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
});
//遍歷methods[Method,{path}]
for (Map.Entry entry : methods.entrySet()) {
//對方法的可訪問性進行校驗,如private,static,SpringProxy
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
//獲取最終請求路徑
T mapping = entry.getValue();
//註冊
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
}
}
}
```
mapping物件的屬性:
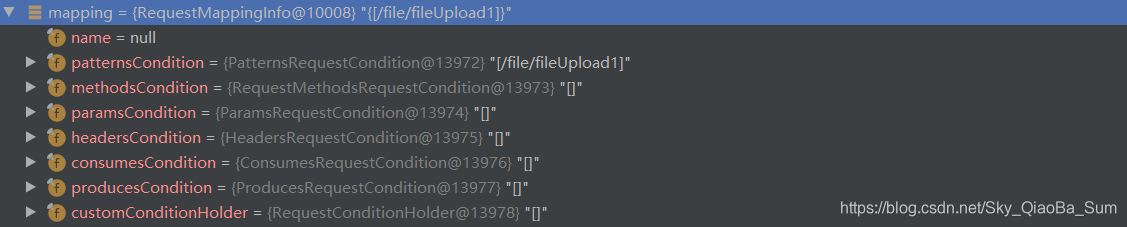
methods物件中儲存的元素:
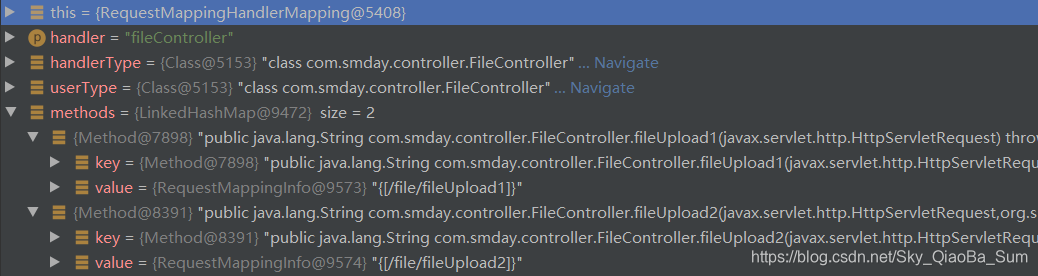
註冊方法在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中實現:
```java
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
//處理方法的物件
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
//判斷對映的唯一性
assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
//將mapping資訊和控制器方法對應
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
//將path與處理器對映(一個方法可能可以處理多個url)
List directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
//控制器名的大寫英文縮寫#方法名
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
//跨域請求相關配置
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
//將所有配置統一註冊到registry中
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
```
至此,所有的Controller,以及其中標註了@RequestMapping註解的方法,都被一一解析,註冊進HashMap中,於是,對應請求路徑與處理方法就一一匹配,此時HandlerMapping也初始化完成。
# 三、請求響應處理
## 1. 請求分發
我們需要明確的一個點是,請求過來的時候,最先執行的地方在哪,是Servlet的service方法,我們只需要看看該方法在子類中的一個實現即可:
FrameworkServlet重寫的service方法:
```java
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//獲取請求方法
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
//攔截PATCH請求
if (HttpMethod.PATCH == httpMethod || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
```
其實最後都是呼叫了processRequest方法,該方法中又呼叫了真正的doService()方法,其中細節先不探討,我們直奔,看看DispatcherServlet的這個doService幹了哪些事情(DispatcherServlet這個類確實是核心中的核心,既建立了IoC容器,又負責請求分發):
```java
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
//忽略一大串前期準備,使其能夠處理view 物件
//接著進入真正的分發
doDispatch(request, response);
}
```
doService:
```java
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//如果是檔案上傳請求,對request進行包裝,如果不是就原樣返回
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
//檔案上傳請求識別符號
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
//為當前的request請求尋找合適的handler
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
//如果沒有handler可以處理該請求,就跳轉到錯誤頁面
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//為當前的request請求尋找合適的adapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
//判斷是否支援getLastModified,如果不支援,返回-1
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//執行註冊攔截器的preHandle方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 真正處理請求的方法
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//如果mv!=null&&mv物件沒有View,則為mv物件設定一個預設的ViewName
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//執行註冊攔截器的applyPostHandle方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
//進行檢視解析和渲染
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
```
需要注意的是,mappedHandler和HandlerAdapter都是從對應的集合中遍歷查詢,一旦找到可以執行的目標,就會停止查詢,我們也可以人為定義優先順序,決定他們之間的次序。
## 2. 請求處理
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的handleInternal方法,含有真正處理請求的邏輯。
```java
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
//定義返回值變數
ModelAndView mav;
//對請求進行檢查 supportedMethods和requireSession
checkRequest(request);
// 看看synchronizeOnSession是否開啟,預設為false
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
//Httpsession可用
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
//加鎖,所有請求序列化
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// 沒有可用的Httpsession -> 沒必要上鎖
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// 正常呼叫處理方法
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
//檢查響應頭是否包含Cache-Control
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
```
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的invokeHandlerMethod方法,真正返回mv。
```java
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
//對HttpServletRequest進行包裝,產生ServletWebRequest處理web的request物件
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
//建立WebDataBinder物件的工廠
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
//建立Model物件的工廠
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
//將handlerMethod物件進行包裝,建立ServletInvocableHandlerMethod物件
//向invocableMethod設定相關屬性(最後是由invocableMethod物件呼叫invokeAndHandle方法
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
//建立ModelAndViewContainer物件,裡面存放有向域中存入資料的map
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
//省略非同步處理
//正常呼叫
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
//獲取ModelAndView物件
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
```
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod的invokeAndHandle方法:反射呼叫方法,得到返回值。
```java
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
//獲取引數,通過反射得到返回值
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
//設定響應狀態
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
//處理返回值
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(getReturnValueHandlingErrorMessage("Error handling return value", returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
```
### 引數解析過程
我們可以知道的是,傳遞引數時,可以傳遞Map,基本型別,POJO,ModelMap等引數,解析之後的結果又如何呢?我們以一個具體的例子舉例比較容易分析:
```java
@RequestMapping("/handle03/{id}")
public String handle03(@PathVariable("id") String sid,
Map map){
System.out.println(sid);
map.put("msg","你好!");
return "success";
}
```
```java
/**
* 獲取當前請求的方法引數值。
*/
private Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
//獲取引數物件
MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters();
//建立一個同等大小的陣列儲存引數值
Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i];
parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
args[i] = resolveProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs);
if (args[i] != null) {
continue;
}
if (this.argumentResolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
//引數處理器處理引數(針對不同型別的引數有不同型別的處理引數的策略)
args[i] = this.argumentResolvers.resolveArgument(
parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);
continue;
}
if (args[i] == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
return args;
}
```
resolveArgument方法:
```java
@Override
@Nullable
public final Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
//獲取註解的資訊
NamedValueInfo namedValueInfo = getNamedValueInfo(parameter);
//包裝parameter物件
MethodParameter nestedParameter = parameter.nestedIfOptional();
//獲取@PathVariable指定的屬性名
Object resolvedName = resolveStringValue(namedValueInfo.name);
//
if (resolvedName == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Specified name must not resolve to null: [" + namedValueInfo.name + "]");
}
//根據name從url中尋找並獲取引數值
Object arg = resolveName(resolvedName.toString(), nestedParameter, webRequest);
//沒有匹配
if (arg == null) {
//如果有default值,則根據該值查詢
if (namedValueInfo.defaultValue != null) {
arg = resolveStringValue(namedValueInfo.defaultValue);
}
//如果required為false,則可以不指定name,但預設為true。
else if (namedValueInfo.required && !nestedParameter.isOptional()) {
handleMissingValue(namedValueInfo.name, nestedParameter, webRequest);
}
arg = handleNullValue(namedValueInfo.name, arg, nestedParameter.getNestedParameterType());
}
//雖然匹配,路徑中傳入的引數如果是“ ”,且有預設的name,則按照預設處理
else if ("".equals(arg) && namedValueInfo.defaultValue != null) {
arg = resolveStringValue(namedValueInfo.defaultValue);
}
if (binderFactory != null) {
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, null, namedValueInfo.name);
arg = binder.convertIfNecessary(arg, parameter.getParameterType(), parameter);
}
handleResolvedValue(arg, namedValueInfo.name, parameter, mavContainer, webRequest);
return arg;
}
```
getNameValueInfo方法:
```java
private NamedValueInfo getNamedValueInfo(MethodParameter parameter) {
//從快取中獲取
NamedValueInfo namedValueInfo = this.namedValueInfoCache.get(parameter);
if (namedValueInfo == null) {
//建立一個namedValueInfo物件
namedValueInfo = createNamedValueInfo(parameter);
//如果沒有在註解中指定屬性名,預設為引數名
namedValueInfo = updateNamedValueInfo(parameter, namedValueInfo);
//更新快取
this.namedValueInfoCache.put(parameter, namedValueInfo);
}
return namedValueInfo;
}
```
createNamedValueInfo:獲取@PathVariable註解的資訊,封裝成NamedValueInfo物件
```java
@Override
protected NamedValueInfo createNamedValueInfo(MethodParameter parameter) {
PathVariable ann = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(PathVariable.class);
Assert.state(ann != null, "No PathVariable annotation");
return new PathVariableNamedValueInfo(ann);
}
```
updateNamedValueInfo:
```java
private NamedValueInfo updateNamedValueInfo(MethodParameter parameter, NamedValueInfo info) {
String name = info.name;
if (info.name.isEmpty()) {
//如果註解中沒有指定name,則為引數名
name = parameter.getParameterName();
if (name == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Name for argument type [" + parameter.getNestedParameterType().getName() +
"] not available, and parameter name information not found in class file either.");
}
}
String defaultValue = (ValueConstants.DEFAULT_NONE.equals(info.defaultValue) ? null : info.defaultValue);
return new NamedValueInfo(name, info.required, defaultValue);
}
```
resolveName方法:
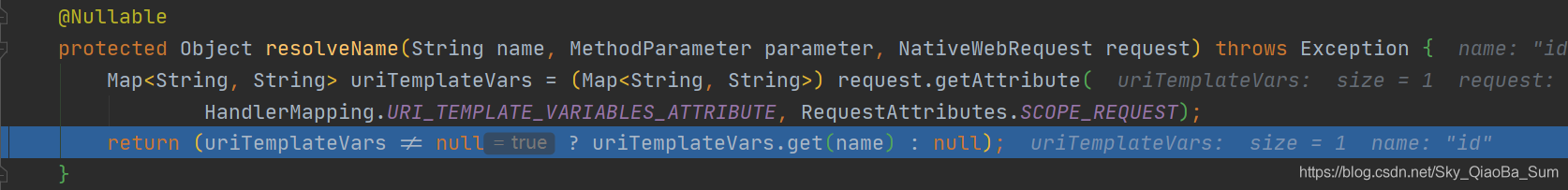
引數解析的過程:
- 根據方法物件,獲取引數物件陣列,並建立儲存引數的陣列。
- 遍歷引數物件陣列,並根據引數解析器argumentResolver解析。
- 如果沒有引數解析器,報錯。
- 引數解析時,先嚐試獲取註解的資訊,以@PathVariable為例。
- 根據指定的name從url中獲取引數值,如果沒有指定,則預設為自己傳入的引數名。
### 傳遞頁面引數
我們可能會通過Map、Model、ModelMap等向域中存入鍵值對,這部分包含在請求處理中。
我們要關注的是ModelAndViewContainer這個類,它裡面預設包含著BindingAwareModelMap。
在解析引數的時候,就已經通過MapMethodProcessor引數處理器初始化了一個BindingAwareModelMap。
當然其實這裡重點還是引數解析,至於資料為什麼封裝進map,就很簡單了,無非是反射執行方法的時候,通過put將資料存入,當然最後的資料也就存在於ModelAndViewContainer中。
### 返回值解析
省略尋找返回值解析器的過程,因為返回值為檢視名,所以解析器為:ViewNameMethodReturnValueHandler。
```java
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
if (returnValue instanceof CharSequence) {
//獲取檢視名
String viewName = returnValue.toString();
//向mavContainer中設定
mavContainer.setViewName(viewName);
//是否是isRedirectViewName
if (isRedirectViewName(viewName)) {
mavContainer.setRedirectModelScenario(true);
}
}
else if (returnValue != null){
// should not happen
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unexpected return type: " +
returnType.getParameterType().getName() + " in method: " + returnType.getMethod());
}
}
```
isRedirectViewName方法
```java
protected boolean isRedirectViewName(String viewName) {
//是否符合自定義的redirectPatterns,或者滿足redirect:開頭的名字
return (PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(this.redirectPatterns, viewName) || viewName.startsWith("redirect:"));
}
```
最後通過getModelAndView獲取mv物件,我們來詳細解析一下:
```java
@Nullable
private ModelAndView getModelAndView(ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,ModelFactory modelFactory, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
//Promote model attributes listed as @SessionAttributes to the session
modelFactory.updateModel(webRequest, mavContainer);
//如果請求已經處理完成
if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
return null;
}
//從mavContainer中獲取我們存入的資料map
ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel();
//通過檢視名、modelmap、和status建立一個ModelAndView物件
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, mavContainer.getStatus());
if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) {
mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView());
}
if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes) {
Map flashAttributes = ((RedirectAttributes) model).getFlashAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = webRequest.getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class);
if (request != null) {
RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes);
}
}
return mav;
}
```
最後返回的都是ModelAndView物件,包含了邏輯名和模型物件的檢視。
返回值解析的過程相對比較簡單:
- 根據返回的引數,獲取對應的返回值解析器。
- 獲取檢視名,如果是需要redirect,則`mavContainer.setRedirectModelScenario(true);`
- 其他情況下,直接給mvcContainer中的ViewName檢視名屬性設定上即可。
- 最後將mvcContainer的model、status、viewName取出,建立mv物件返回。
【總結】
引數解析、返回值解析兩個過程都包含大量的解決策略,其中尋找合適的解析器的過程都是先遍歷初始化的解析器表,然後判斷是否需要非同步處理,判斷是否可以處理返回值型別,如果可以的話,就使用該解析器進行解析,如果不行,就一直向下遍歷,直到表中沒有解析器為止。
## 3. 檢視解析
```java
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
// 保證渲染一次,cleared作為標記
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
//渲染過程!!!
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
}
```
DispatcherServlet的render方法
```java
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
//獲取檢視名
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
//通過檢視解析器viewResolvers對檢視名進行處理,建立view物件
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
}
else {
view = mv.getView();
}
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
```
獲取檢視解析器,解析檢視名:
```java
@Nullable
protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, @Nullable Map model,
Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//這裡我們註冊的是InternalResourceViewResolver
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
}
return null;
}
```
UrlBasedViewResolver的createView方法:
```java
@Override
protected View createView(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
//如果解析器不能處理所給的view,就返回null,讓下一個解析器看看能否執行
if (!canHandle(viewName, locale)) {
return null;
}
// Check for special "redirect:" prefix.
if (viewName.startsWith(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX)) {
//判斷是否需要重定向
}
// Check for special "forward:" prefix.
if (viewName.startsWith(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX)) {
//判斷是否需要轉發
}
//呼叫父類的loadView方法
return super.createView(viewName, locale);
}
```
最後返回的檢視物件:
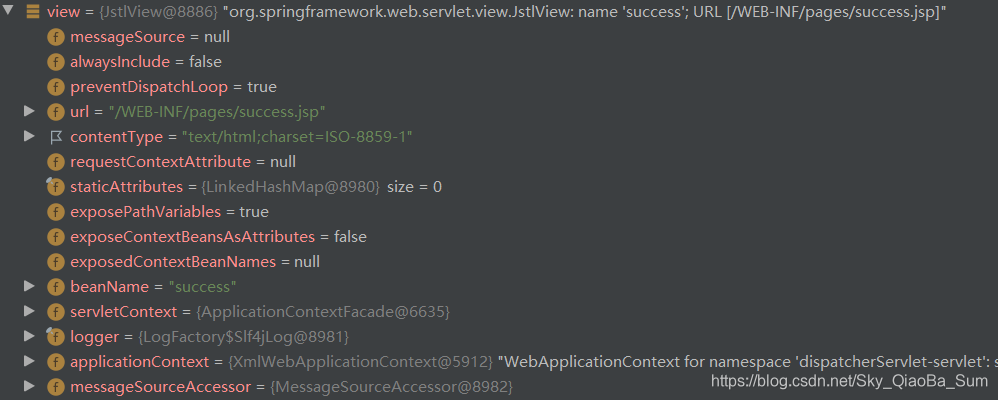
> 檢視解析器 viewResolver --例項化 --> view(無狀態的,不會有執行緒安全問題)
AbstractView的render方法
```java
@Override
public void render(@Nullable Map model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
//獲取合併後的map,有我們存入域中的map,還有PathVariable對應的鍵值等
Map mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
//根據給定的model渲染內部資源,如將model設定為request的屬性
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
}
```
InternalResourceView的renderMergedOutputModel
```java
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
//將model中的值設定到request域中
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);
// 如果有的話,給request設定helpers
exposeHelpers(request);
// 將目標地址設定到request中
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response);
// 獲取目標資源(通常是JSP)的RequestDispatcher。
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath);
// 如果已經包含或響應已經提交,則執行包含,否則轉發。
if (useInclude(request, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
rd.include(request, response);
}
else {
// Note: 轉發的資源應該確定內容型別本身。
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
```
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes
```java
protected void exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(Map model,HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//遍歷model
model.forEach((modelName, modelValue) -> {
if (modelValue != null) {
//向request中設定值
request.setAttribute(modelName, modelValue);
}
else {
//value為null的話,移除該name
request.removeAttribute(modelName);
}
});
}
```
### 檢視解析器
檢視解析器(實現ViewResolver介面):將邏輯檢視解析為具體的檢視物件。
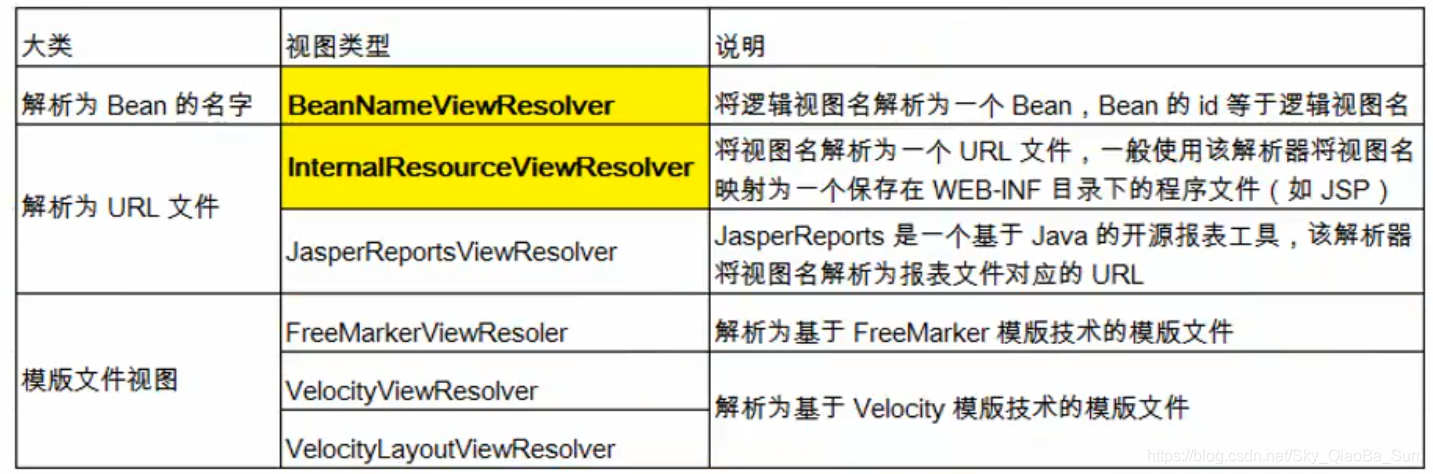
每個檢視解析器都實現了Ordered介面,並開放order屬性,order越小優先順序越高。
按照檢視解析器的優先順序對邏輯檢視名進行解析,直到解析成功並返回檢視物件,否則丟擲異常。
### 檢視
檢視(實現View介面):渲染模型資料,將模型資料以某種形式展現給使用者。
最終採取的檢視物件對模型資料進行渲染render,處理器並不關心,處理器關心生產模型的資料,實現解耦。
