12.深入k8s:kubelet建立pod流程原始碼分析
阿新 • • 發佈:2020-09-26

> 轉載請宣告出處哦~,本篇文章釋出於luozhiyun的部落格:https://www.luozhiyun.com
>
> 原始碼版本是[1.19](https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/tree/release-1.19)
在上一篇中,我們知道在kubelet中,工作核心就是圍繞著整個syncLoop來完成不同的工作的。syncLoop會根據不同的上報資訊管理pod的生命週期,這些操作都是通過HandlePods來實現的。
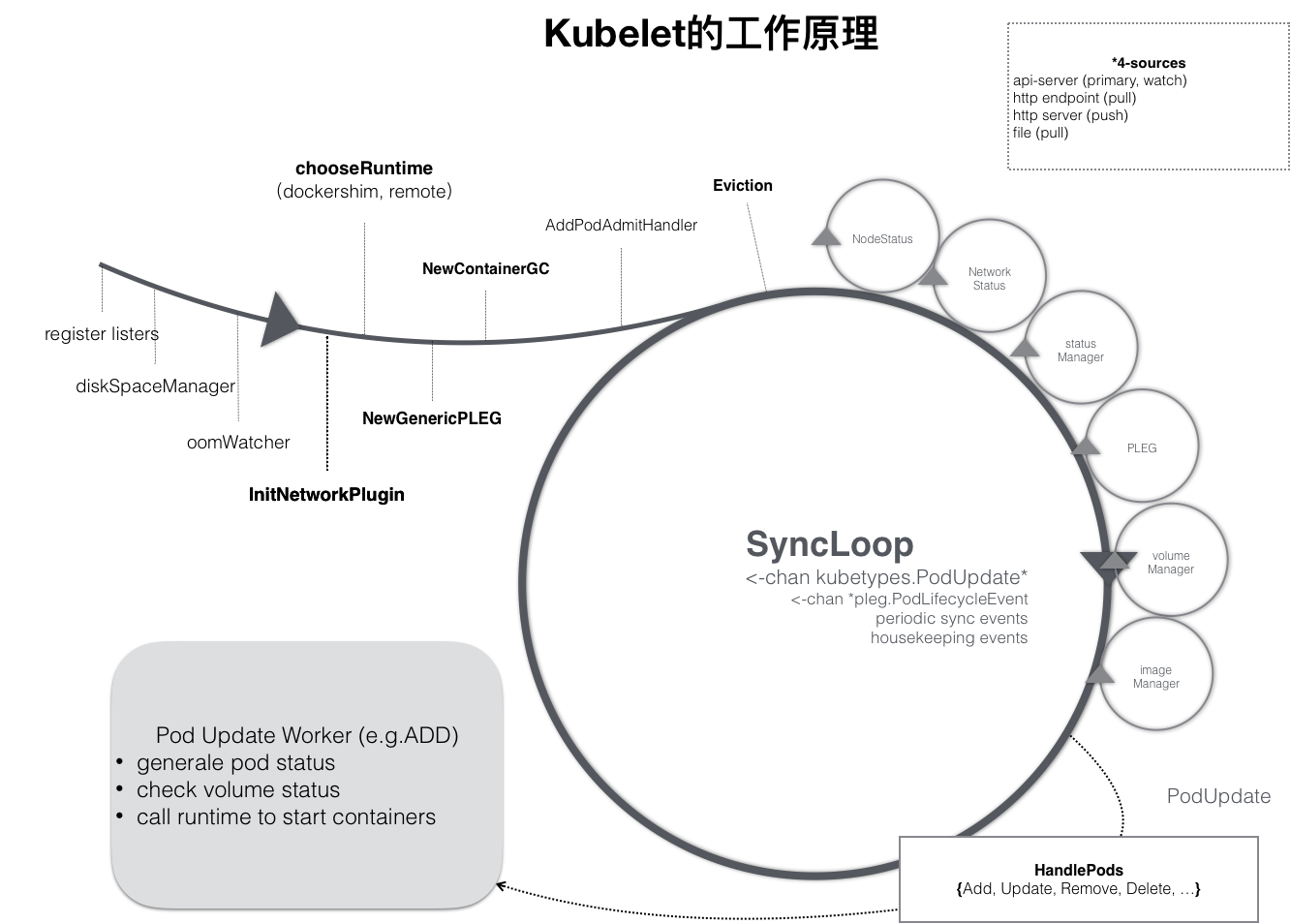
整個事件迴圈的程式碼在Kubelet呼叫run方法最後會通過呼叫kl.syncLoop方法啟動事件迴圈。
## kubelet建立pod流程
### syncLoop迴圈監聽管道資訊
檔案位置:pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
```go
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoop(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler) {
...
syncTicker := time.NewTicker(time.Second)
defer syncTicker.Stop()
housekeepingTicker := time.NewTicker(housekeepingPeriod)
defer housekeepingTicker.Stop()
plegCh := kl.pleg.Watch()
for {
...
kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now())
if !kl.syncLoopIteration(updates, handler, syncTicker.C, housekeepingTicker.C, plegCh) {
break
}
kl.syncLoopMonitor.Store(kl.clock.Now())
}
}
```
syncLoop的主要邏輯是在syncLoopIteration中實現,由於本文主要探討的是pod建立相關程式碼,所以我們只需要看處理configCh管道部分的程式碼就好了。
### syncLoopIteration處理事件迴圈中的邏輯
```go
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoopIteration(configCh <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler,
//方法會監聽多個 channel,當發現任何一個 channel 有資料就交給 handler 去處理,在 handler 中通過呼叫 dispatchWork 分發任務
syncCh <-chan time.Time, housekeepingCh <-chan time.Time, plegCh <-chan *pleg.PodLifecycleEvent) bool {
select {
//該模組將同時 watch 3 個不同來源的 pod 資訊的變化(file,http,apiserver),
//一旦某個來源的 pod 資訊發生了更新(建立/更新/刪除),這個 channel 中就會出現被更新的 pod 資訊和更新的具體操作;
case u, open := <-configCh:
if !open {
klog.Errorf("Update channel is closed. Exiting the sync loop.")
return false
}
switch u.Op {
case kubetypes.ADD:
klog.V(2).Infof("SyncLoop (ADD, %q): %q", u.Source, format.Pods(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodAdditions(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.UPDATE:
klog.V(2).Infof("SyncLoop (UPDATE, %q): %q", u.Source, format.PodsWithDeletionTimestamps(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodUpdates(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.REMOVE:
klog.V(2).Infof("SyncLoop (REMOVE, %q): %q", u.Source, format.Pods(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodRemoves(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.RECONCILE:
klog.V(4).Infof("SyncLoop (RECONCILE, %q): %q", u.Source, format.Pods(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodReconcile(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.DELETE:
klog.V(2).Infof("SyncLoop (DELETE, %q): %q", u.Source, format.Pods(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodUpdates(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.SET:
klog.Errorf("Kubelet does not support snapshot update")
default:
klog.Errorf("Invalid event type received: %d.", u.Op)
}
kl.sourcesReady.AddSource(u.Source)
...
}
```
該模組將同時 watch 3 個不同來源的 pod 資訊的變化(file,http,apiserver),一旦某個來源的 pod 資訊發生了更新(建立/更新/刪除),這個 channel 中就會出現被更新的 pod 資訊和更新的具體操作。
### HandlePodAdditions執行建立pod
```go
func (kl *Kubelet) HandlePodAdditions(pods []*v1.Pod) {
start := kl.clock.Now()
sort.Sort(sliceutils.PodsByCreationTime(pods))
for _, pod := range pods {
existingPods := kl.podManager.GetPods()
//將pod新增到pod管理器中,如果有pod不存在在pod管理器中,那麼這個pod表示已經被刪除了
kl.podManager.AddPod(pod)
if kubetypes.IsMirrorPod(pod) {
kl.handleMirrorPod(pod, start)
continue
}
//如果該pod沒有被Terminate
if !kl.podIsTerminated(pod) {
// 獲取目前還在active狀態的pod
activePods := kl.filterOutTerminatedPods(existingPods)
//驗證 pod 是否能在該節點執行,如果不可以直接拒絕
if ok, reason, message := kl.canAdmitPod(activePods, pod); !ok {
kl.rejectPod(pod, reason, message)
continue
}
}
mirrorPod, _ := kl.podManager.GetMirrorPodByPod(pod)
//把 pod 分配給給 worker 做非同步處理,建立pod
kl.dispatchWork(pod, kubetypes.SyncPodCreate, mirrorPod, start)
//在 probeManager 中新增 pod,如果 pod 中定義了 readiness 和 liveness 健康檢查,啟動 goroutine 定期進行檢測
kl.probeManager.AddPod(pod)
}
}
```
HandlePodAdditions主要任務是:
1. 按照建立時間給pods進行排序;
2. 將pod新增到pod管理器中,如果有pod不存在在pod管理器中,那麼這個pod表示已經被刪除了;
3. 校驗pod 是否能在該節點執行,如果不可以直接拒絕;
4. 呼叫dispatchWork把 pod 分配給給 worker 做非同步處理,建立pod;
5. 將pod新增到probeManager中,如果 pod 中定義了 readiness 和 liveness 健康檢查,啟動 goroutine 定期進行檢測;
#### dispatchWork
```go
func (kl *Kubelet) dispatchWork(pod *v1.Pod, syncType kubetypes.SyncPodType, mirrorPod *v1.Pod, start time.Time) {
...
kl.podWorkers.UpdatePod(&UpdatePodOptions{
Pod: pod,
MirrorPod: mirrorPod,
UpdateType: syncType,
OnCompleteFunc: func(err error) {
if err != nil {
metrics.PodWorkerDuration.WithLabelValues(syncType.String()).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(start))
}
},
})
...
}
```
dispatchWork會封裝一個UpdatePodOptions結構體丟給podWorkers.UpdatePod去執行。
#### UpdatePod
檔案位置:pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go
```go
func (p *podWorkers) UpdatePod(options *UpdatePodOptions) {
pod := options.Pod
uid := pod.UID
var podUpdates chan UpdatePodOptions
var exists bool
p.podLock.Lock()
defer p.podLock.Unlock()
//如果該pod在podUpdates數組裡面找不到,那麼就建立channel,並啟動非同步執行緒
if podUpdates, exists = p.podUpdates[uid]; !exists {
podUpdates = make(chan UpdatePodOptions, 1)
p.podUpdates[uid] = podUpdates
go func() {
defer runtime.HandleCrash()
p.managePodLoop(podUpdates)
}()
}
// 下發更新事件
if !p.isWorking[pod.UID] {
p.isWorking[pod.UID] = true
podUpdates <- *options
} else {
update, found := p.lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate[pod.UID]
if !found || update.UpdateType != kubetypes.SyncPodKill {
p.lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate[pod.UID] = *options
}
}
}
```
這個方法會加鎖之後獲取podUpdates數組裡面數據,如果不存在那麼會建立一個channel然後執行一個非同步協程。
#### managePodLoop
```go
func (p *podWorkers) managePodLoop(podUpdates <-chan UpdatePodOptions) {
var lastSyncTime time.Time
//遍歷channel
for update := range podUpdates {
err := func() error {
podUID := update.Pod.UID
// 直到cache裡面有新資料之前這段程式碼會阻塞,這保證worker在cache裡面有新的資料之前不會提前開始。
status, err := p.podCache.GetNewerThan(podUID, lastSyncTime)
if err != nil {
p.recorder.Eventf(update.Pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedSync, "error determining status: %v", err)
return err
}
//syncPodFn會在kubelet初始化的時候設定,呼叫的是kubelet的syncPod方法
err = p.syncPodFn(syncPodOptions{
mirrorPod: update.MirrorPod,
pod: update.Pod,
podStatus: status,
killPodOptions: update.KillPodOptions,
updateType: update.UpdateType,
})
lastSyncTime = time.Now()
return err
}()
if update.OnCompleteFunc != nil {
update.OnCompleteFunc(err)
}
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Error syncing pod %s (%q), skipping: %v", update.Pod.UID, format.Pod(update.Pod), err)
}
p.wrapUp(update.Pod.UID, err)
}
}
```
這個方法會遍歷channel裡面的資料,然後呼叫syncPodFn方法並傳入一個syncPodOptions,kubelet會在執行NewMainKubelet方法的時候呼叫newPodWorkers方法設定syncPodFn為Kubelet的syncPod方法。
如下:
```go
func NewMainKubelet(...){
...
klet := &Kubelet{...}
...
klet.podWorkers = newPodWorkers(klet.syncPod, kubeDeps.Recorder, klet.workQueue, klet.resyncInterval, backOffPeriod, klet.podCache)
...
}
```
#### syncPod
檔案位置:pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
```go
func (kl *Kubelet) syncPod(o syncPodOptions) error {
// pull out the required options
pod := o.pod
mirrorPod := o.mirrorPod
podStatus := o.podStatus
updateType := o.updateType
...
apiPodStatus := kl.generateAPIPodStatus(pod, podStatus)
// 校驗該pod能否執行
runnable := kl.canRunPod(pod)
//如果不能執行,那麼回寫container的等待原因
if !runnable.Admit {
// Pod is not runnable; update the Pod and Container statuses to why.
apiPodStatus.Reason = runnable.Reason
apiPodStatus.Message = runnable.Message
// Waiting containers are not creating.
const waitingReason = "Blocked"
for _, cs := range apiPodStatus.InitContainerStatuses {
if cs.State.Waiting != nil {
cs.State.Waiting.Reason = waitingReason
}
}
for _, cs := range apiPodStatus.ContainerStatuses {
if cs.State.Waiting != nil {
cs.State.Waiting.Reason = waitingReason
}
}
}
// 更新狀態管理器中的狀態
kl.statusManager.SetPodStatus(pod, apiPodStatus)
// 如果校驗沒通過或pod已被刪除或pod跑失敗了,那麼kill掉pod
if !runnable.Admit || pod.DeletionTimestamp != nil || apiPodStatus.Phase == v1.PodFailed {
var syncErr error
...
kl.killPod(pod, nil, podStatus, nil)
....
return syncErr
}
//校驗網路外掛是否已準備好
if err := kl.runtimeState.networkErrors(); err != nil && !kubecontainer.IsHostNetworkPod(pod) {
kl.recorder.Eventf(pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.NetworkNotReady, "%s: %v", NetworkNotReadyErrorMsg, err)
return fmt.Errorf("%s: %v", NetworkNotReadyErrorMsg, err)
}
// 建立
pcm := kl.containerManager.NewPodContainerManager()
// 校驗該pod是否已被Terminate
if !kl.podIsTerminated(pod) {
firstSync := true
// 校驗該pod是否首次建立
for _, containerStatus := range apiPodStatus.ContainerStatuses {
if containerStatus.State.Running != nil {
firstSync = false
break
}
}
podKilled := false
// 如果該pod 的cgroups不存在,並且不是首次啟動,那麼kill掉
if !pcm.Exists(pod) && !firstSync {
if err := kl.killPod(pod, nil, podStatus, nil); err == nil {
podKilled = true
}
}
// 如果該pod在上面沒有被kill掉,或重啟策略不是永不重啟
if !(podKilled && pod.Spec.RestartPolicy == v1.RestartPolicyNever) {
// 如果該pod的cgroups不存在,那麼就建立cgroups
if !pcm.Exists(pod) {
if err := kl.containerManager.UpdateQOSCgroups(); err != nil {
klog.V(2).Infof("Failed to update QoS cgroups while syncing pod: %v", err)
}
if err := pcm.EnsureExists(pod); err != nil {
kl.recorder.Eventf(pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToCreatePodContainer, "unable to ensure pod container exists: %v", err)
return fmt.Errorf("failed to ensure that the pod: %v cgroups exist and are correctly applied: %v", pod.UID, err)
}
}
}
}
//為靜態pod 建立 映象
if kubetypes.IsStaticPod(pod) {
...
}
// 建立pod的檔案目錄
if err := kl.makePodDataDirs(pod); err != nil {
kl.recorder.Eventf(pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToMakePodDataDirectories, "error making pod data directories: %v", err)
klog.Errorf("Unable to make pod data directories for pod %q: %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
return err
}
// 如果該pod沒有被終止,那麼需要等待attach/mount volumes
if !kl.podIsTerminated(pod) {
// Wait for volumes to attach/mount
if err := kl.volumeManager.WaitForAttachAndMount(pod); err != nil {
kl.recorder.Eventf(pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedMountVolume, "Unable to attach or mount volumes: %v", err)
klog.Errorf("Unable to attach or mount volumes for pod %q: %v; skipping pod", format.Pod(pod), err)
return err
}
}
// 如果有 image secrets,去 apiserver 獲取對應的 secrets 資料
pullSecrets := kl.getPullSecretsForPod(pod)
// 真正的容器建立邏輯
result := kl.containerRuntime.SyncPod(pod, podStatus, pullSecrets, kl.backOff)
kl.reasonCache.Update(pod.UID, result)
if err := result.Error(); err != nil {
for _, r := range result.SyncResults {
if r.Error != kubecontainer.ErrCrashLoopBackOff && r.Error != images.ErrImagePullBackOff {
return err
}
}
return nil
}
return nil
}
```
該方法主要是為建立pod前做一些準備工作。主要準備工作如下:
1. 校驗該pod能否執行,如果不能執行,那麼回寫container的等待原因,然後更新狀態管理器中的狀態;
2. 如果校驗沒通過或pod已被刪除或pod跑失敗了,那麼kill掉pod,然後返回;
3. 校驗網路外掛是否已準備好,如果沒有,直接返回;
4. 如果該pod的cgroups不存在,那麼就建立cgroups;
5. 為靜態pod建立映象;
6. 建立pod的檔案目錄,等待volumes attach/mount;
7. 拉取這個pod的Secret;
8. 呼叫containerRuntime.SyncPod真正建立pod;
#### syncPod
檔案位置:pkg/kubelet/kuberuntime/kuberuntime_manager.go
```go
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) SyncPod(pod *v1.Pod, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus, pullSecrets []v1.Secret, backOff *flowcontrol.Backoff) (result kubecontainer.PodSyncResult) {
// 計算一下有哪些pod中container有沒有變化,有哪些container需要建立,有哪些container需要kill掉
podContainerChanges := m.computePodActions(pod, podStatus)
...
// kill掉 sandbox 已經改變的 pod
if podContainerChanges.KillPod {
...
//kill容器操作
killResult := m.killPodWithSyncResult(pod, kubecontainer.ConvertPodStatusToRunningPod(m.runtimeName, podStatus), nil)
result.AddPodSyncResult(killResult)
...
} else {
// kill掉ContainersToKill列表中的container
for containerID, containerInfo := range podContainerChanges.ContainersToKill {
...
if err := m.killContainer(pod, containerID, containerInfo.name, containerInfo.message, nil); err != nil {
killContainerResult.Fail(kubecontainer.ErrKillContainer, err.Error())
klog.Errorf("killContainer %q(id=%q) for pod %q failed: %v", containerInfo.name, containerID, format.Pod(pod), err)
return
}
}
}
//清理同名的 Init Container
m.pruneInitContainersBeforeStart(pod, podStatus)
var podIPs []string
if podStatus != nil {
podIPs = podStatus.IPs
}
podSandboxID := podContainerChanges.SandboxID
if podContainerChanges.CreateSandbox {
var msg string
var err error
...
//為pod建立sandbox
podSandboxID, msg, err = m.createPodSandbox(pod, podContainerChanges.Attempt)
if err != nil {
...
return
}
...
}
podIP := ""
if len(podIPs) != 0 {
podIP = podIPs[0]
}
...
//生成Sandbox的config配置,如pod的DNS、hostName、埠對映
podSandboxConfig, err := m.generatePodSandboxConfig(pod, podContainerChanges.Attempt)
if err != nil {
...
return
}
start := func(typeName string, spec *startSpec) error {
...
// 啟動容器
if msg, err := m.startContainer(podSandboxID, podSandboxConfig, spec, pod, podStatus, pullSecrets, podIP, podIPs); err != nil {
...
}
return nil
}
// 臨時容器相關
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.EphemeralContainers) {
for _, idx := range podContainerChanges.EphemeralContainersToStart {
start("ephemeral container", ephemeralContainerStartSpec(&pod.Spec.EphemeralContainers[idx]))
}
}
// 啟動init container
if container := podContainerChanges.NextInitContainerToStart; container != nil {
if err := start("init container", containerStartSpec(container)); err != nil {
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Completed init container %q for pod %q", container.Name, format.Pod(pod))
}
// 啟動containers列表
for _, idx := range podContainerChanges.ContainersToStart {
start("container", containerStartSpec(&pod.Spec.Containers[idx]))
}
return
}
```
1. 首先會呼叫computePodActions計算一下有哪些pod中container有沒有變化,有哪些container需要建立,有哪些container需要kill掉;
2. kill掉 sandbox 已經改變的 pod;
3. 如果有container已改變,那麼需要呼叫killContainer方法kill掉ContainersToKill列表中的container;
4. 呼叫pruneInitContainersBeforeStart方法清理同名的 Init Container;
5. 呼叫createPodSandbox方法,建立需要被建立的Sandbox,關於Sandbox我們再下面說到;
6. 如果開啟了臨時容器Ephemeral Container,那麼需要建立相應的臨時容器,臨時容器可以看這篇:https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/ephemeral-containers/;
7. 獲取NextInitContainerToStart中的container,呼叫startContainer啟動init container;
8. 獲取ContainersToStart列表中的container,呼叫startContainer啟動containers列表;
#### computePodActions
檔案路徑:pkg/kubelet/kuberuntime/kuberuntime_manager.go
```go
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) computePodActions(pod *v1.Pod, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus) podActions {
klog.V(5).Infof("Syncing Pod %q: %+v", format.Pod(pod), pod)
//判斷哪些pod的Sandbox已經改變,如果改變需要重新建立
createPodSandbox, attempt, sandboxID := m.podSandboxChanged(pod, podStatus)
changes := podActions{
KillPod: createPodSandbox,
CreateSandbox: createPodSandbox,
SandboxID: sandboxID,
Attempt: attempt,
ContainersToStart: []int{},
ContainersToKill: make(map[kubecontainer.ContainerID]containerToKillInfo),
}
//需要新建sandbox
if createPodSandbox {
if !shouldRestartOnFailure(pod) && attempt != 0 && len(podStatus.ContainerStatuses) != 0 {
// 如果pod已經存在了,那麼不應該建立sandbox
// 如果所有的containers 都已完成,那麼也不應該建立一個新的sandbox
// 如果ContainerStatuses是空的,那麼我們可以認定,我們從沒有成功建立過containers,所以我們應該重試建立sandbox
changes.CreateSandbox = false
return changes
}
//如果InitContainers 不為空,那麼將InitContainers的第一個設定成第一個建立的container
if len(pod.Spec.InitContainers) != 0 {
changes.NextInitContainerToStart = &pod.Spec.InitContainers[0]
return changes
}
// 將所有container加入到需要啟動的佇列中,除了已啟動,並且重啟策略為RestartPolicyOnFailure的pod
for idx, c := range pod.Spec.Containers {
if containerSucceeded(&c, podStatus) && pod.Spec.RestartPolicy == v1.RestartPolicyOnFailure {
continue
}
changes.ContainersToStart = append(changes.ContainersToStart, idx)
}
return changes
}
//臨時容器相關:https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/ephemeral-containers/
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.EphemeralContainers) {
for i := range pod.Spec.EphemeralContainers {
c := (*v1.Container)(&pod.Spec.EphemeralContainers[i].EphemeralContainerCommon)
// Ephemeral Containers are never restarted
if podStatus.FindContainerStatusByName(c.Name) == nil {
changes.EphemeralContainersToStart = append(changes.EphemeralContainersToStart, i)
}
}
}
// 檢查Init Container執行狀態
initLastStatus, next, done := findNextInitContainerToRun(pod, podStatus)
if !done {
if next != nil {
initFailed := initLastStatus != nil && isInitContainerFailed(initLastStatus)
if initFailed && !shouldRestartOnFailure(pod) {
changes.KillPod = true
} else {
// Always try to stop containers in unknown state first.
if initLastStatus != nil && initLastStatus.State == kubecontainer.ContainerStateUnknown {
changes.ContainersToKill[initLastStatus.ID] = containerToKillInfo{
name: next.Name,
container: next,
message: fmt.Sprintf("Init container is in %q state, try killing it before restart",
initLastStatus.State),
}
}
changes.NextInitContainerToStart = next
}
}
// 若init未完成,直接返回
return changes
}
// init已完成,計算需要kill&start的工作container
keepCount := 0
// 校驗containers列表的狀態
for idx, container := range pod.Spec.Containers {
containerStatus := podStatus.FindContainerStatusByName(container.Name)
//呼叫post-stop生命週期鉤子,這樣如果container重啟了,那麼可以馬上分配資源
if containerStatus != nil && containerStatus.State != kubecontainer.ContainerStateRunning {
if err := m.internalLifecycle.PostStopContainer(containerStatus.ID.ID); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("internal container post-stop lifecycle hook failed for container %v in pod %v with error %v",
container.Name, pod.Name, err)
}
}
// 如果container不存在或沒有在執行,那麼根據RestartPolicy決定是否需要重啟
if containerStatus == nil || containerStatus.State != kubecontainer.ContainerStateRunning {
if kubecontainer.ShouldContainerBeRestarted(&container, pod, podStatus) {
message := fmt.Sprintf("Container %+v is dead, but RestartPolicy says that we should restart it.", container)
klog.V(3).Infof(message)
changes.ContainersToStart = append(changes.ContainersToStart, idx)
// 如果container 狀態是unknown,那麼我們不知道是否它在啟動,所以我們先kill掉,再啟動,避免同時有兩個一樣的container
if containerStatus != nil && containerStatus.State == kubecontainer.ContainerStateUnknown {
changes.ContainersToKill[containerStatus.ID] = containerToKillInfo{
name: containerStatus.Name,
container: &pod.Spec.Containers[idx],
message: fmt.Sprintf("Container is in %q state, try killing it before restart",
containerStatus.State),
}
}
}
continue
}
var message string
//到這裡,說明container處於running狀態,那麼當滿足下面條件時需要kill掉重啟
restart := shouldRestartOnFailure(pod)
// 如果container的 spec已經改變了,那麼直接重啟
if _, _, changed := containerChanged(&container, containerStatus); changed {
message = fmt.Sprintf("Container %s definition changed", container.Name)
// Restart regardless of the restart policy because the container
// spec changed.
restart = true
// 如果liveness探針檢測失敗,那麼需要kill掉container,並且不需要重啟
} else if liveness, found := m.livenessManager.Get(containerStatus.ID); found && liveness == proberesults.Failure {
// If the container failed the liveness probe, we should kill it.
message = fmt.Sprintf("Container %s failed liveness probe", container.Name)
// 如果startup 探針檢測失敗,那麼需要kill掉container,並且不需要重啟
} else if startup, found := m.startupManager.Get(containerStatus.ID); found && startup == proberesults.Failure {
// If the container failed the startup probe, we should kill it.
message = fmt.Sprintf("Container %s failed startup probe", container.Name)
// 到這裡,如果探針檢測又沒問題,container又沒改變,那麼不需要重啟
} else {
// Keep the container.
keepCount++
continue
}
// 如果需要重啟,那麼加入佇列
if restart {
message = fmt.Sprintf("%s, will be restarted", message)
changes.ContainersToStart = append(changes.ContainersToStart, idx)
}
//這裡時設定需要kill掉的container的列表
changes.ContainersToKill[containerStatus.ID] = containerToKillInfo{
name: containerStatus.Name,
container: &pod.Spec.Containers[idx],
message: message,
}
klog.V(2).Infof("Container %q (%q) of pod %s: %s", container.Name, containerStatus.ID, format.Pod(pod), message)
}
if keepCount == 0 && len(changes.ContainersToStart) == 0 {
changes.KillPod = true
}
return changes
}
```
computePodActions方法主要做這麼幾件事:
1. 檢查PodSandbox有沒有改變,如果改變了,那麼需要建立PodSandbox;
2. 找到需要執行的Init Container設定到NextInitContainerToStart欄位中;
3. 找到需要被kill掉的Container列表ContainersToKill;
4. 找到需要被啟動的Container列表ContainersToStart;
#### Sandbox
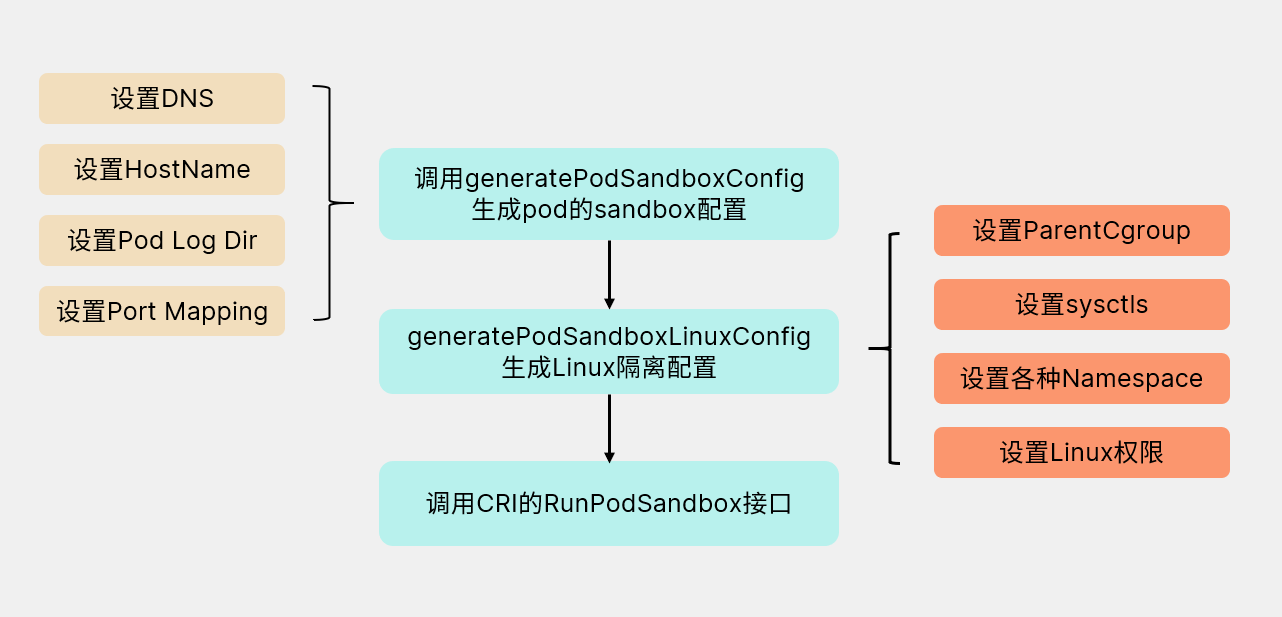
Sandbox沙箱是一種程式的隔離執行機制,其目的是限制不可信程序的許可權。k8s 中每個 pod 共享一個 sandbox定義了其 cgroup 及各種 namespace,所以同一個 pod 的所有容器才能夠互通,且與外界隔離。我們在呼叫createPodSandbox方法建立sandbox的時候分為如下幾步:
#### startContainer
檔案位置:pkg/kubelet/kuberuntime/kuberuntime_container.go
```go
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) startContainer(podSandboxID string, podSandboxConfig *runtimeapi.PodSandboxConfig, spec *startSpec, pod *v1.Pod, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus, pullSecrets []v1.Secret, podIP string, podIPs []string) (string, error) {
container := spec.container
// 拉取映象
imageRef, msg, err := m.imagePuller.EnsureImageExists(pod, container, pullSecrets, podSandboxConfig)
if err != nil {
...
return msg, err
}
//如果是個新的container,那麼restartCount應該為0
restartCount := 0
containerStatus := podStatus.FindContainerStatusByName(container.Name)
if containerStatus != nil {
restartCount = containerStatus.RestartCount + 1
}
target, err := spec.getTargetID(podStatus)
if err != nil {
...
return s.Message(), ErrCreateContainerConfig
}
//生成Container config
containerConfig, cleanupAction, err := m.generateContainerConfig(container, pod, restartCount, podIP, imageRef, podIPs, target)
if cleanupAction != nil {
defer cleanupAction()
}
if err != nil {
...
return s.Message(), ErrCreateContainerConfig
}
//呼叫CRI介面建立Container
containerID, err := m.runtimeService.CreateContainer(podSandboxID, containerConfig, podSandboxConfig)
if err != nil {
...
return s.Message(), ErrCreateContainer
}
//呼叫生命週期的鉤子,預啟動Pre Start Container
err = m.internalLifecycle.PreStartContainer(pod, container, containerID)
if err != nil {
...
return s.Message(), ErrPreStartHook
}
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, containerID, v1.EventTypeNormal, events.CreatedContainer, fmt.Sprintf("Created container %s", container.Name))
// Step 3: start the container.
// 呼叫CRI介面啟動container
err = m.runtimeService.StartContainer(containerID)
if err != nil {
...
return s.Message(), kubecontainer.ErrRunContainer
}
...
// Step 4: execute the post start hook.
//依然是呼叫生命週期中設定的鉤子 post start
if container.Lifecycle != nil && container.Lifecycle.PostStart != nil {
kubeContainerID := kubecontainer.ContainerID{
Type: m.runtimeName,
ID: containerID,
}
//執行預處理工作
msg, handlerErr := m.runner.Run(kubeContainerID, pod, container, container.Lifecycle.PostStart)
if handlerErr != nil {
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, kubeContainerID.ID, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedPostStartHook, msg)
// 如果預處理失敗,那麼需要kill掉Container
if err := m.killContainer(pod, kubeContainerID, container.Name, "FailedPostStartHook", nil); err != nil {
...
}
return msg, fmt.Errorf("%s: %v", ErrPostStartHook, handlerErr)
}
}
return "", nil
}
```
這個方法是比較清晰的:
1. 拉取映象;
2. 計算一下Container重啟次數,如果是首次建立,那麼應該是0;
3. 生成Container config,用於建立container;
4. 呼叫CRI介面CreateContainer建立Container;
5. 在啟動之前呼叫PreStartContainer做預處理工作;
6. 呼叫CRI介面StartContainer啟動container;
7. 呼叫生命週期中設定的鉤子 post start;
上面涉及了很多pod生命週期相關的操作,具體可以看:[Attach Handlers to Container Lifecycle Events](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/attach-handler-lifecycle-event/)。
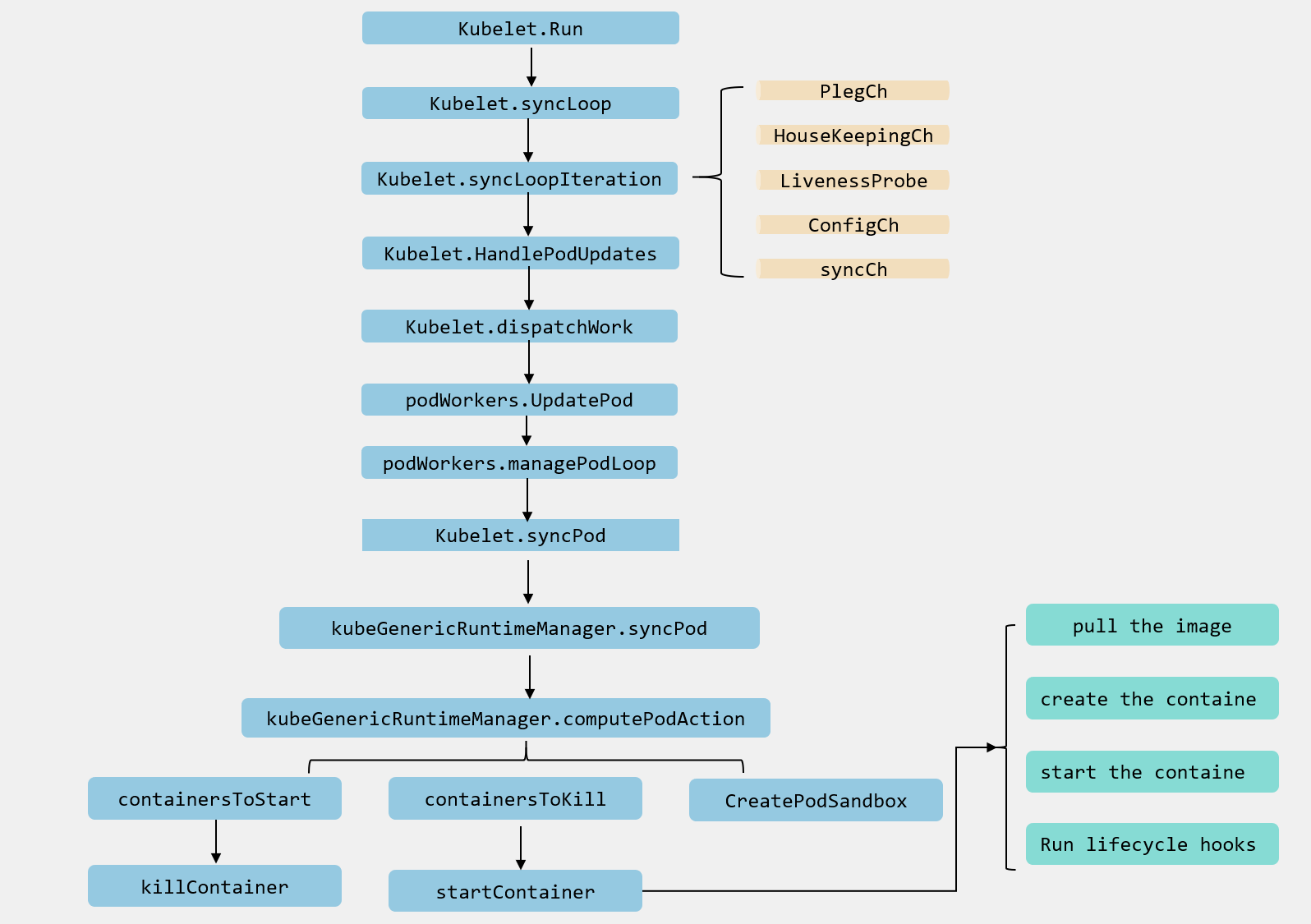
## 總結
這裡我直接放上一個流程圖來作為這一篇的結尾。
## Reference
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/
https://draveness.me/kubernetes-pod/
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/attach-handler-lifecycle-event/
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/ephemeral-con
