hdu 6161--Big binary tree(思維--壓縮空間)
阿新 • • 發佈:2017-09-01
style ons desc stream 我們 value chan 向上 while 
You are given a complete binary tree with n nodes. The root node is numbered 1, and node x‘s father node is ⌊x/2⌋. At the beginning, node x has a value of exactly x. We define the value of a path as the sum of all nodes it passes(including two ends, or one if the path only has one node). Now there are two kinds of operations:
2. query u Query the max value of all paths which passes node u.
For each case:
The first line contains two integers n,m(1≤n≤10^8,1≤m≤10^5), which represent the size of the tree and the number of operations, respectively.
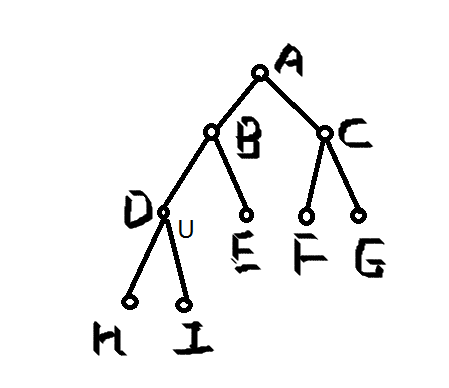 如求經過D的最大路徑權值和。有以下的路徑:1、起始為從D的葉子節點經D到D的另一個葉子節點。 2、從D的葉子節點經D B 到B的一個葉子節點。 3、從D的一個葉子節點經B D A 到A的一個葉子節點。所以求經過D的最大路徑權值和時就是由D開始向上搜索D的祖先節點,進行計算。
代碼如下:
如求經過D的最大路徑權值和。有以下的路徑:1、起始為從D的葉子節點經D到D的另一個葉子節點。 2、從D的葉子節點經D B 到B的一個葉子節點。 3、從D的一個葉子節點經B D A 到A的一個葉子節點。所以求經過D的最大路徑權值和時就是由D開始向上搜索D的祖先節點,進行計算。
代碼如下:
題目鏈接
Problem Description

You are given a complete binary tree with n nodes. The root node is numbered 1, and node x‘s father node is ⌊x/2⌋. At the beginning, node x has a value of exactly x. We define the value of a path as the sum of all nodes it passes(including two ends, or one if the path only has one node). Now there are two kinds of operations:
2. query u Query the max value of all paths which passes node u.
Input There are multiple cases.
For each case:
The first line contains two integers n,m(1≤n≤10^8,1≤m≤10^5), which represent the size of the tree and the number of operations, respectively.
Output For each query operation, output an integer in one line, indicating the max value of all paths which passes the specific node.
Sample Input 6 13 query 1 query 2 query 3 query 4 query 5 query 6 change 6 1 query 1 query 2 query 3 query 4 query 5 query 6
 如求經過D的最大路徑權值和。有以下的路徑:1、起始為從D的葉子節點經D到D的另一個葉子節點。 2、從D的葉子節點經D B 到B的一個葉子節點。 3、從D的一個葉子節點經B D A 到A的一個葉子節點。所以求經過D的最大路徑權值和時就是由D開始向上搜索D的祖先節點,進行計算。
代碼如下:
如求經過D的最大路徑權值和。有以下的路徑:1、起始為從D的葉子節點經D到D的另一個葉子節點。 2、從D的葉子節點經D B 到B的一個葉子節點。 3、從D的一個葉子節點經B D A 到A的一個葉子節點。所以求經過D的最大路徑權值和時就是由D開始向上搜索D的祖先節點,進行計算。
代碼如下:
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <map> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; map<int,LL>mp; map<int,LL>mx; LL ans; int n,m; int pos[100]; void init() { int tmp=n; int deep=(int)log2(n)+1; for(int i=deep;i>=1;i--) { pos[i]=tmp; tmp>>=1; } } void cal(int x) { if(mp.count(x)) return ; if(x>n) { mp[x]=0; return ; } int deep=(int)log2(x)+1; LL tmp=0; for(int i=x;i<=n;i=(i<<1|1)) tmp+=i; if(pos[deep]==x){ LL sum=0; for(int i=deep;;i++) { sum+=pos[i]; if(pos[i]==n) break; } tmp=max(tmp,sum); } mp[x]=tmp; } void update(int x) { if(!x) return ; LL y; if(mx.count(x)==0) y=x; else y=mx[x]; cal(x<<1); cal(x<<1|1); mp[x]=max(mp[x<<1],mp[x<<1|1])+y; update(x>>1); } void query(LL sum,int x,int son) { if(!x) return ; cal(x<<1); cal(x<<1|1); if(!mx.count(x)) mx[x]=x; ans=max(ans,sum+mp[son^1]+mx[x]); sum+=mx[x]; query(sum,x>>1,x); } int main() { char s[10]; while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { init(); mp.clear(); mx.clear(); scanf("%d",&m); while(m--) { scanf("%s",s); if(s[0]==‘q‘) { int x; scanf("%d",&x); cal(x<<1); cal(x<<1|1); if(!mx.count(x)) mx[x]=x; ans=mp[x<<1]+mp[x<<1|1]+mx[x]; cal(x); query(mp[x],x>>1,x); printf("%lld\n",ans); } else { int x; LL y; scanf("%d%lld",&x,&y); mx[x]=y; update(x); } } } return 0; }
hdu 6161--Big binary tree(思維--壓縮空間)
