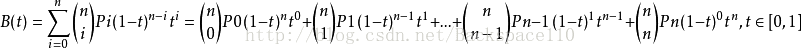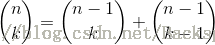n階貝塞爾曲線繪制(C/C#)
貝塞爾是很經典的東西,輪子應該有很多的。求n階貝塞爾曲線用到了?德卡斯特裏奧算法(De Casteljau’s Algorithm)
需要拷貝代碼請直接使用本文最後的例程,文章前面的大部分代碼都不是最佳實踐,是在編程過程中的摸索(走過的彎路),不過這些示範對筆者今後寫算法啟發很大。
要完成的功能是根據起點,終點和控制點,繪制n階貝塞爾曲線
首先看n階貝塞爾曲線的公式
公式中用了組合數,大數組合數計算也有算法:
簡言之就是把 ?大數乘以大數除以大數 ?這個過程?轉為單純的累加。
下面來說明一下這個組合數計算的優化過程:
100000 / 100 = ?1000
500 + 500 = 1000
上面兩個式子計算結果是相等的,但是如果編程實現,
第一個式子就必須使用至少一個Uint32 來存放100000;
但是第二個式子只需要Uint16類型就可以完成整個計算。
通過變換計算方式,可以通過計算機有限的數據大小計算盡可能大的結果。?
貝塞爾曲線也是一種插值算法,?根據起點和終點,通過中間的控制點,插值計算出整條路徑
現代的x86,硬件計算浮點都是先轉換為double的,所以用double會比float會更快,當然這裏只針對英特爾家族復雜指令集產品。
為什麽用float不用double是因為PointF是C#自帶的結構體{float X;float Y;},要改為double也是很簡單的,全局替換一下數據類型即可
C#數組自帶Length屬性,但是為了方便移植到C,這裏還是使用數組+數組長度作為入參,這樣可以很容易的改寫為C下面的數組指針+數組長度。
直接實現數學公式是比較簡單的,直接貼代碼:
public static class Bezier { /// <summary> /// 繪制n階貝塞爾曲線路徑 /// </summary> /// <param name="points">輸入點</param> /// <param name="count">點數(n+1)</param> /// <param name="step">步長,步長越小,軌跡點越密集</param> /// <returns></returns> public static PointF[] draw_bezier_curves(PointF[] points, int count, float step) { List<PointF> bezier_curves_points = new List<PointF>(); float t = 0F; do { PointF temp_point = bezier_interpolation_func(t, points, count); // 計算插值點 t += step; bezier_curves_points.Add(temp_point); } while (t <= 1 && count > 1); // 一個點的情況直接跳出. return bezier_curves_points.ToArray(); // 曲線軌跡上的所有坐標點 } /// <summary> /// n階貝塞爾曲線插值計算函數 /// 根據起點,n個控制點,終點 計算貝塞爾曲線插值 /// </summary> /// <param name="t">當前插值位置0~1 ,0為起點,1為終點</param> /// <param name="points">起點,n-1個控制點,終點</param> /// <param name="count">n+1個點</param> /// <returns></returns> private static PointF bezier_interpolation_func(float t, PointF[] points, int count) { PointF PointF = new PointF(); float[] part = new float[count]; float sum_x = 0, sum_y = 0; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { ulong tmp; int n_order = count - 1; // 階數 tmp = calc_combination_number(n_order, i); sum_x += (float)(tmp * points[i].X * Math.Pow((1 - t), n_order - i) * Math.Pow(t, i)); sum_y += (float)(tmp * points[i].Y * Math.Pow((1 - t), n_order - i) * Math.Pow(t, i)); } PointF.X = sum_x; PointF.Y = sum_y; return PointF; } /// <summary> /// 計算組合數公式 /// </summary> /// <param name="n"></param> /// <param name="k"></param> /// <returns></returns> private static ulong calc_combination_number(int n, int k) { ulong[] result = new ulong[n + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { result[i] = 1; for (int j = i - 1; j >= 1; j--) result[j] += result[j - 1]; result[0] = 1; } return result[k]; } }
使用方法:
// 第一個是起點,最後一個是終點,中間的都是控制點,貝賽爾曲線階數 = 總點數-1
PointF[] pointList = new PointF[] { new PointF(1.3F, 2.4F), new PointF(2, 3), new PointF(12.3F, 13.2F) };
PointF[] aa = Bezier.draw_bezier_curves(pointList, pointList.Length, 0.001F); // 在起點和終點之間畫1/0.001=1000個點
foreach (var item in aa)
{
? ? // 繪制曲線點
? ? // 下面是C#繪制到Panel畫板控件上的代碼
? ? // panel1.CreateGraphics().DrawEllipse(new Pen(Color.Green), new RectangleF(item, new SizeF(2, 2)));
}
可以很容易的改寫成C/C++版,
PointF只是個結構體,{float X;float Y};
C/C++中數組部分不需要new
Math.Pow()對應於C語言math.h頭文件裏的 pow()
List<PointF>在C++中可以通過vector實現
在C中可以換成malloc分配個數組,大小推薦使用 (1/step) + 1。
目前為止,只是從數學公式上實現了程序,這個程序有什麽問題呢?
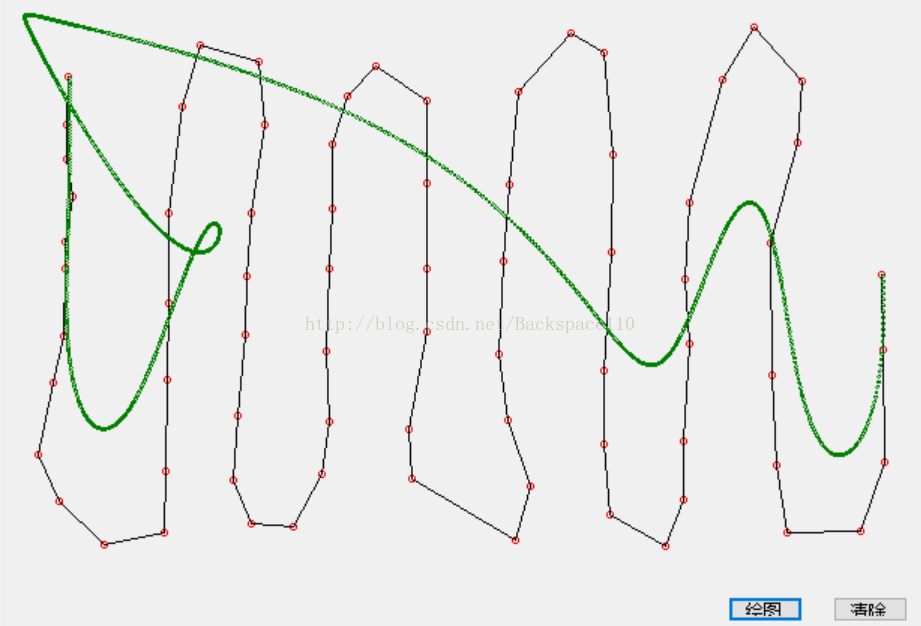
下面放兩張圖,分別是通過上面的代碼計算出來的 4階和 某n(n很大)階的巴賽爾曲線,
可以看到階數過多的時候計算出錯了,原因就在於計算組合數函數那裏,當階數過多的時候,組合數中階乘的計算結果溢出了。
其實仔細觀察會發現階乘計算結果在bezier_interpolation_func函數中又乘以 了一個小數,
這裏就是可以改進的地方,階乘的計算結果既然只是中間值,那麽就可以通過某些算法來除掉這個中間值或者通過轉化為累加的方式來解決,
就像文章開篇把組合數的 計算公式 n!/(k!*(n-k)!) 簡化為 (n-1)!/(k!*(n-k-1)!) + (n-1)!/((k-1)!*(n-k+1)!) ?的遞歸加法一樣,bezier_interpolation_func函數也可以通過遞歸的方式來優化。
使它能夠計算更高的階數而不會溢出(如果有足夠的內存空間..)。
下面來看一個改進版的程序
public static PointF bezier_interpolation_func(float t, PointF[] points, int count)
{
if (points.Length < 1) // 一個點都沒有
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException();
if (count == 1)
return points[0];
else
{
PointF[] tmp_points = new PointF[count];
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++)
{
tmp_points[i - 1].X = (float)(points[i - 1].X * t + points[i].X * (1 - t));
tmp_points[i - 1].Y = (float)(points[i - 1].Y * t + points[i].Y * (1 - t));
}
return bezier_interpolation_func(t, tmp_points, count - 1);
}
}
看一下結果
可以,實現了功能。
然後將遞歸改為循環,循環的方式有更好的兼容性和效率,特別是某些低端的嵌入式編譯器不支持遞歸方式。
/// 參考: http://blog.csdn.net/Fioman/article/details/2578895
public static PointF bezier_interpolation_func(float t, PointF[] points, int count)
{
? ? if (points.Length < 1) ?// 一個點都沒有
? ? ? ? throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException();
? ? PointF[] tmp_points = new PointF[count];
? ? for (int i = 1; i < count; ++i)
? ? {
? ? ? ? for (int j = 0; j < count - i; ++j)
? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? if (i == 1) // 計算+搬運數據,在計算的時候不要汙染源數據
? ? ? ? ? ? {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? tmp_points[j].X = (float)(points[j].X * (1 - t) + points[j + 1].X * t);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? tmp_points[j].Y = (float)(points[j].Y * (1 - t) + points[j + 1].Y * t);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? continue;
? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? tmp_points[j].X = (float)(tmp_points[j].X * (1 - t) + tmp_points[j + 1].X * t);
? ? ? ? ? ? tmp_points[j].Y = (float)(tmp_points[j].Y * (1 - t) + tmp_points[j + 1].Y * t);
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
? ? return tmp_points[0];
}下面是c語言的一個完整程序,不過是打印曲線點的坐標,不太直觀。
#include "stdio.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "assert.h"
typedef struct
{
float X;
float Y;
} PointF;
PointF bezier_interpolation_func(float t, PointF* points, int count)
{
assert(count>0);
PointF tmp_points[count];
for (int i = 1; i < count; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < count - i; ++j)
{
if (i == 1)
{
tmp_points[j].X = (float)(points[j].X * (1 - t) + points[j + 1].X * t);
tmp_points[j].Y = (float)(points[j].Y * (1 - t) + points[j + 1].Y * t);
continue;
}
tmp_points[j].X = (float)(tmp_points[j].X * (1 - t) + tmp_points[j + 1].X * t);
tmp_points[j].Y = (float)(tmp_points[j].Y * (1 - t) + tmp_points[j + 1].Y * t);
}
}
return tmp_points[0];
}
void draw_bezier_curves(PointF* points, int count, PointF* out_points,int out_count)
{
float step = 1.0 / out_count;
float t =0;
for(int i=0; i<out_count; i++)
{
PointF temp_point = bezier_interpolation_func(t, points, count); // 計算插值點
t += step;
out_points[i] = temp_point;
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
PointF in[3] = {{100,100},{200,200},{300,100}}; // 輸入點
int num = 1000; // 輸出點數
PointF out[num]; // 輸出點數組
draw_bezier_curves(in,3,out,num);// 二階貝塞爾曲線
for(int j=0; j<num; j++) // 輸出路徑點
{
printf("%d\t X=%f \t Y=%f \r\n",j,out[j].X,out[j].Y);
}
return 0;
}
參考連接http://blog.csdn.net/Fioman/article/details/2578895
簡介引用連接http://www.cs.mtu.edu/~shene/COURSES/cs3621/NOTES/spline/Bezier/de-casteljau.html
n階貝塞爾曲線繪制(C/C#)