集合的全排列(可包含重複元素)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-10-31
全排列如果按字典順序排好的話,我們知道其中的一個序列,就能推出下一個序列。比如說集合{1,2,3}的全排列按字典排序後如下:
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1
當我們知道其中一個序列為{2,3,1}時,我們是可以推出下一個序列為{3,1,2}的,但是程式應該怎麼寫呢?主要分四步來找出下一個序列:
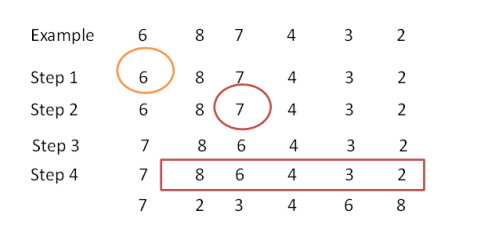
1.從右到左,找出當前序列中第一個違反遞增規則的元素(相等不違反)記為pivot
2.從右到左,找出當前序列中第一個大於pivot的元素記為change
3.交換pivot和change的位置
4.將pivot位置(是交換之前的位置)右邊的所有元素進行反轉後得到的序列就是我們要的結果。
舉個例子你應該就懂了:按上述方法求序列{6,8,7,4,3,2}的下一個序列的過程如下:
有了這個函式,我們只需要輸入最小的序列然後不斷求下一個序列,直到得到了最大的序列這樣我們就能得到這個序列的全排列。其實STL已經為我們實現了這個函式next_permutation,所以如果是筆試我們可以直接用STL給的這個函式,但是要是面試的話還是需要我們自己實現這個函式。具體程式碼如下
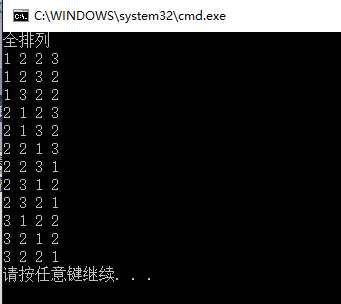
程式執行結果如下:#include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; template<typename Bidit> bool my_next_permutation(Bidit first,Bidit last) { const auto rfirst=reverse_iterator<Bidit>(last); const auto rlast=reverse_iterator<Bidit>(first); auto pivot=next(rfirst); while(pivot!=rlast && (*pivot>=*prev(pivot))) //第一步求pivot的位置 { pivot=next(pivot); } if (pivot==rlast) //判斷當前序列是否是最大序列,如果是就返回false,同時將序列變為最小序列 { reverse(rfirst,rlast); return false; } auto change=rfirst; while(change!=rlast && (*change<=*pivot)) //第二步求change位置 { change=next(change); } swap(*pivot,*change); //第三步交換pivot和change位置 reverse(rfirst,pivot); //反轉pivot右邊的所有的元素 return true; } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { //全排列 cout<<"全排列"<<endl; int inputArray[]={1,2,2,3}; vector<int> inputVec(inputArray,inputArray+4); vector<vector<int>> result; do { result.push_back(inputVec); } while (my_next_permutation(inputVec.begin(),inputVec.end())); for (int i=0;i<result.size();++i) { for (int j=0;j<result[i].size();++j) { cout<<result[i][j]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } return 0; }