馮志霞201771010107《面向物件程式設計(java)》第十週學習總結
實驗十 泛型程式設計技術
實驗時間 2018-11-1
1、實驗目的與要求
(1) 理解泛型概念;
(2) 掌握泛型類的定義與使用;
(3) 掌握泛型方法的宣告與使用;
(4) 掌握泛型介面的定義與實現;
(5)瞭解泛型程式設計,理解其用途。
Java中泛型類的定義也比較簡單,例如:public class Test<T>{}。這樣就定義了一個泛型類Test,在例項化該類時,必須指明泛型T的具體型別,例如:Test<Object> t = new Test<Object>();,指明泛型T的型別為Object。
泛型類,是在例項化類的時候指明泛型的具體型別;泛型方法,是在呼叫方法的時候指明泛型的具體型別。
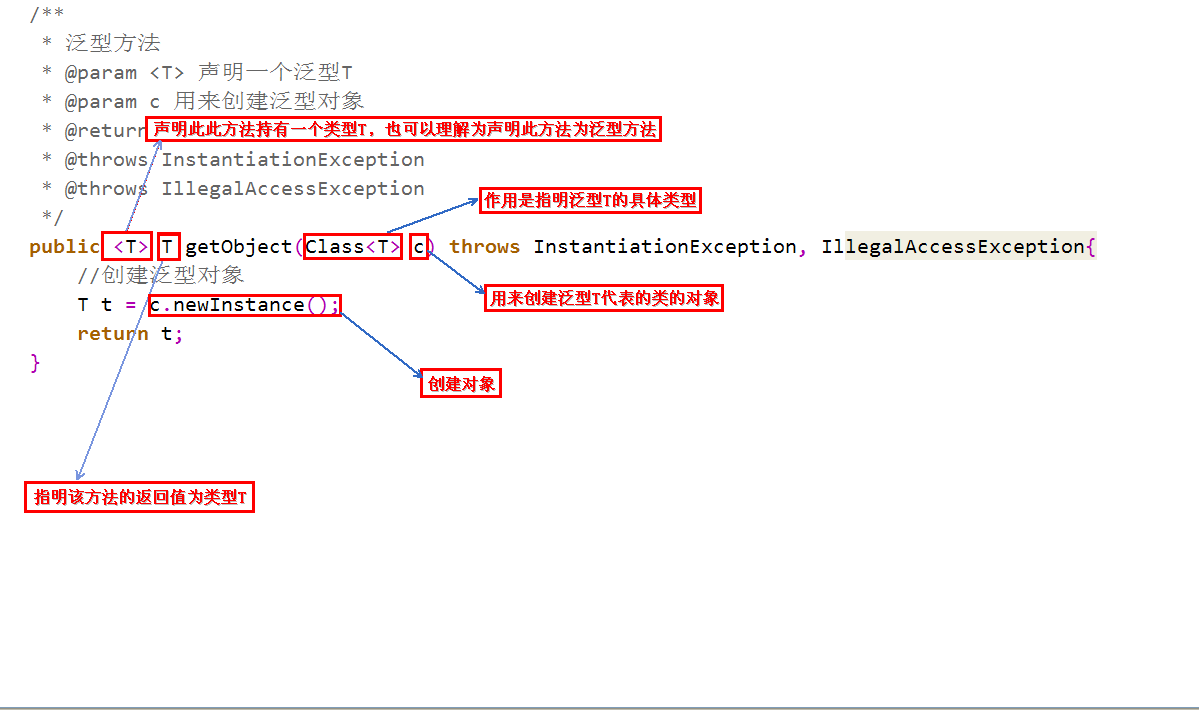
呼叫泛型方法語法格式如下:

說明一下,定義泛型方法時,必須在返回值前邊加一個<T>,來宣告這是一個泛型方法,持有一個泛型T,然後才可以用泛型T作為方法的返回值。
Class<T>的作用就是指明泛型的具體型別,而Class<T>型別的變數c,可以用來建立泛型類的物件。
為什麼要用變數c來建立物件呢?既然是泛型方法,就代表著我們不知道具體的型別是什麼,也不知道構造方法如何,因此沒有辦法去new一個物件,但可以利用變數c的newInstance方法去建立物件,也就是利用反射建立物件。
泛型方法要求的引數是Class<T>型別,而Class.forName()方法的返回值也是Class<T>,因此可以用Class.forName()作為引數。其中,forName()方法中的引數是何種型別,返回的Class<T>就是何種型別。在本例中,forName()方法中傳入的是User類的完整路徑,因此返回的是Class<User>型別的物件,因此呼叫泛型方法時,變數c的型別就是Class<User>,因此泛型方法中的泛型T就被指明為User,因此變數obj的型別為User。
當然,泛型方法不是僅僅可以有一個引數Class<T>,可以根據需要新增其他引數。
為什麼要使用泛型方法呢?因為泛型類要在例項化的時候就指明型別,如果想換一種型別,不得不重新new一次,可能不夠靈活;而泛型方法可以在呼叫的時候指明型別,更加靈活。
定義泛型方法
(1) 如果你定義了一個泛型(類、介面),那麼Java規定,你不能在所有的靜態方法、靜態初塊等所有靜態內容中使用泛型的型別引數。例如:
public class A<T> { public static void func(T t) { //報錯,編譯不通過 } }(2) 如何在靜態內容(靜態方法)中使用泛型,更一般的問題是,如果類(或者介面)沒有定義成泛型,但是就想在其中某幾個方法中運用泛型(比如接受一個泛型的引數等),該如何解決?
- 定義泛型方法就像定義泛型類或介面一樣,在定義類名(或者介面名)的時候需要指定我的作用域中誰是泛型引數。例如:
public class A<T> { ... }表明在類A的作用域中,T是泛型型別引數。 - 定義泛型方法,其格式是:修飾符 <型別引數列表> 返回型別 方法名(形參列表) { 方法體 }。例如:
public static <T, S> int func(List<T> list, Map<Integer, S> map) { ... },其中T和S是泛型型別引數。 - 泛型方法的定義和普通方法定義不同的地方在於需要在修飾符和返回型別之間加一個泛型型別引數的宣告,表明在這個方法作用域中誰才是泛型型別引數;
- 不管是普通的類/介面的泛型定義,還是方法的泛型定義都逃不出兩大要素:
- 明哪些是泛型型別引數;
- 這些型別引數在哪裡使用。
(3) 型別引數的作用域
class A<T> { ... }中T的作用域就是整個A;-
public <T> func(...) { ... }中T的作用域就是方法func; -
型別引數也存在作用域覆蓋的問題,可以在一個泛型模板類/介面中繼續定義泛型方法,例如:
class A<T> {
// A已經是一個泛型類,其型別引數是T public static <T> void func(T t) { // 再在其中定義一個泛型方法,該方法的型別引數也是T } } //當上述兩個型別引數衝突時,在方法中,方法的T會覆蓋類的T,即和普通變數的作用域一樣,內部覆蓋外部,外部的同名變數是不可見的。 //除非是一些特殊需求,一定要將區域性型別引數和外部型別引數區分開來,避免發生不必要的錯誤,因此一般正確的定義方式是這樣的: class A<T> { public static <S> void func(S s) { } } (4) 泛型方法的型別引數可以指定上限,型別上限必須在型別引數宣告的地方定義上限,不能在方法引數中定義上限。規定了上限就只能在規定範圍內指定型別實參,超出這個範圍就會直接編譯報錯。
<T extends X> void func(List<T> list){ ... },正確<T extends X> void func(T t){ ... },正確<T> void func(List<T extends X> list){ ... },編譯錯誤
2. 泛型呼叫
(1) 顯式指定方法的型別引數,型別引數要寫在尖括號中並放在方法名之前。例如:object.<String> func(...),這樣就顯式指定了泛型方法的型別引數為String,那麼所有出現型別引數T的地方都將替換成String型別。
(2) 隱式地自動推斷,不指明泛型引數,編譯器根據傳入的實參型別自動推斷型別引數。例如:<T> void func(T t){ ... }隱式呼叫object.func("name"),根據"name"的型別String推斷出型別引數T的型別是String
(3) 避免歧義,例如:<T> void func(T t1, T t2){ ... }如果這樣呼叫的話object.func("name", 15); 雖然編譯不會報錯,但是仍然會有很大隱患,T到底應該是String還是Integer存在歧義;
(4) 有些歧義Java是會直接當成編譯錯誤的,即所有和泛型引數有關的歧義,例如:<T> void func(List<T> l1, List<T> l2){...}如果這樣呼叫的話,object.func(new List<String>(), new List<Integer>()); 這裡會有歧義,編譯器無法知道T到底應該是String還是Integer,這種歧義會直接報錯的,編譯無法通過。即泛型方法中,如果型別引數剛好就是泛型引數的型別實參,那麼這個型別實參不得有歧義,否則直接編譯報錯。
3. 泛型方法/型別萬用字元
(1) 你會發現所有能用型別萬用字元(?)解決的問題都能用泛型方法解決,並且泛型方法可以解決的更好。
- 型別萬用字元:
void func(List<? extends A> list); - 完全可以用泛型方法完美解決:
<T extends A> void func(List<T> list);
(2) 兩種方法可以達到相同的效果,“?”可以代表範圍內任意型別,而T也可以傳入範圍內的任意型別實參,並且泛型方法更進一步,“?”泛型物件是隻讀的,而泛型方法裡的泛型物件是可修改的,即List<T> list中的list是可修改的。
(3) 兩者最明顯的區別
- “?”泛型物件是隻讀的,不可修改,因為“?”型別是不確定的,可以代表範圍內任意型別;
- 而泛型方法中的泛型引數物件是可修改的,因為型別引數T是確定的(在呼叫方法時確定),因為T可以用範圍內任意型別指定;
2、實驗內容和步驟
實驗1: 匯入第8章示例程式,測試程式並進行程式碼註釋。
測試程式1:
l 編輯、除錯、執行教材311、312頁 程式碼,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 在泛型類定義及使用程式碼處添加註釋;
l 掌握泛型類的定義及使用。

package pair1; /** * @version 1.01 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PairTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] words = { "Mary", "had", "a", "little", "lamb" }; Pair<String> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(words);//將Pair型別例項化 System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst()); System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond()); } } class ArrayAlg { /** * Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of strings. * @param a an array of strings * @return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is null or empty */ public static Pair<String> minmax(String[] a) { if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;//判斷a是否合法 String min = a[0]; String max = a[0];//初始化 for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i]; if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i]; } return new Pair<>(min, max); } }pairtest

package pair1; /** * @version 1.00 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Pair<T>//定義泛型類// { private T first; private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; } public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; } public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; } public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; } }Pair
測試程式2:
l 編輯、除錯執行教材315頁 PairTest2,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 在泛型程式設計程式碼處新增相關注釋;
l 掌握泛型方法、泛型變數限定的定義及用途。

package pair2; import java.time.*; /** * @version 1.02 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PairTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { LocalDate[] birthdays = { LocalDate.of(1906, 12, 9), // G. Hopper LocalDate.of(1815, 12, 10), // A. Lovelace LocalDate.of(1903, 12, 3), // J. von Neumann LocalDate.of(1910, 6, 22), // K. Zuse }; Pair<LocalDate> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(birthdays); System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst()); System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond()); } } class ArrayAlg { /** Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of objects of type T. @param a an array of objects of type T @return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is null or empty */ public static <T extends Comparable> Pair<T> minmax(T[] a) { if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null; T min = a[0]; T max = a[0]; for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i]; if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i]; } return new Pair<>(min, max); } }pairtest2

package pair2; /** * @version 1.00 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Pair<T> { private T first; private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; } public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; } public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; } public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; } }pair
測試程式3:
l 用除錯執行教材335頁 PairTest3,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 瞭解萬用字元型別的定義及用途。

package pair3; /** * @version 1.01 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PairTest3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Manager ceo = new Manager("Gus Greedy", 800000, 2003, 12, 15); Manager cfo = new Manager("Sid Sneaky", 600000, 2003, 12, 15); Pair<Manager> buddies = new Pair<>(ceo, cfo); printBuddies(buddies); ceo.setBonus(1000000); cfo.setBonus(500000); Manager[] managers = { ceo, cfo }; Pair<Employee> result = new Pair<>(); minmaxBonus(managers, result); System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName() + ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName()); maxminBonus(managers, result); System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName() + ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName()); } public static void printBuddies(Pair<? extends Employee> p) { Employee first = p.getFirst(); Employee second = p.getSecond(); System.out.println(first.getName() + " and " + second.getName() + " are buddies."); } public static void minmaxBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result) { if (a.length == 0) return; Manager min = a[0]; Manager max = a[0]; for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if (min.getBonus() > a[i].getBonus()) min = a[i]; if (max.getBonus() < a[i].getBonus()) max = a[i]; } result.setFirst(min); result.setSecond(max); } public static void maxminBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result) { minmaxBonus(a, result); PairAlg.swapHelper(result); // OK--swapHelper captures wildcard type } // Can't write public static <T super manager> ... } class PairAlg { public static boolean hasNulls(Pair<?> p) { return p.getFirst() == null || p.getSecond() == null; } public static void swap(Pair<?> p) { swapHelper(p); } public static <T> void swapHelper(Pair<T> p) { T t = p.getFirst(); p.setFirst(p.getSecond()); p.setSecond(t); } }pairtest3

package pair3; /** * @version 1.00 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Pair<T> { private T first; private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; } public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; } public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; } public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; } }pair

package pair3; import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }employee

package pair3; public class Manager extends Employee { private double bonus; /** @param name the employee's name @param salary the salary @param year the hire year @param month the hire month @param day the hire day */ public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day); bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double b) { bonus = b; } public double getBonus() { return bonus; } }manager
實驗2:程式設計練習:
程式設計練習1:實驗九程式設計題總結
l 實驗九程式設計練習1總結(從程式總體結構說明、模組說明,目前程式設計存在的困難與問題三個方面闡述)。

import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Scanner; public class B{ private static ArrayList<Test> studentlist; public static void main(String[] args) { studentlist = new ArrayList<>(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); File file = new File("D:\\身份證號.txt"); try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); String temp = null; while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" "); String name = linescanner.next(); String number = linescanner.next(); String sex = linescanner.next(); String age = linescanner.next(); String province =linescanner.nextLine(); Test student = new Test(); student.setName(name); student.setnumber(number); student.setsex(sex); int a = Integer.parseInt(age); student.setage(a); student.setprovince(province); studentlist.add(student); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("學生資訊檔案找不到"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("學生資訊檔案讀取錯誤"); e.printStackTrace(); } boolean isTrue = true; while (isTrue) { System.out.println("1:字典排序"); System.out.println("2:輸出年齡最大和年齡最小的人"); System.out.println("3:尋找老鄉"); System.out.println("4:尋找年齡相近的人"); System.out.println("5:退出"); String m = scanner.next(); switch (m) { case "1": Collections.sort(studentlist); System.out.println(studentlist.toString()); break; case "2": int max=0,min=100; int j,k1 = 0,k2=0; for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++) { j=studentlist.get(i).getage(); if(j>max) { max=j; k1=i; } if(j<min) { min=j; k2=i; } } System.out.println("年齡最大:"+studentlist.get(k1)); System.out.println("年齡最小:"+studentlist.get(k2)); break; case "3": System.out.println("province?"); String find = scanner.next(); String place=find.substring(0,3); for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++) { if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place)) System.out.println("province"+studentlist.get(i)); } break; case "4": System.out.println("年齡:"); int yourage = scanner.nextInt(); int near=agematched(yourage); int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage(); System.out.println(""+studentlist.get(near)); break; case "5": isTrue = false; System.out.println("退出程式!"); break; default: System.out.println("輸入有誤"); } } } public static int agematched(int age) { int j=0,min=53,value=0,k=0; for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++) { value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age; if(value<0) value=-value; if (value<min) { min=value; k=i; } } return k; } }B

public class Test implements Comparable<Test> { private String name; private String number ; private String sex ; private int age; private String province; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getnumber() { return number; } public void setnumber(String number) { this.number = number; } public String getsex() { return sex ; } public void setsex(String sex ) { this.sex =sex ; } public int getage() { return age; } public void setage(int age) { this.age= age; } public String getprovince() { return province; } public void setprovince(String province) { this.province=province ; } @Override public int compareTo(Test o) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.name.compareTo(o.getName()); } public String toString() { return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n"; } }test
程式總體結構與模組說明:程式分為兩個類:主類和test類(主類當中進行檔案的讀取以及操作,test類實現了comparable介面,控制其輸出形式
目前困難與問題:檔案捕獲錯誤的程式碼用的不熟悉,檔案系列的操作還不行
l 實驗九程式設計練習2總結(從程式總體結構說明、模組說明,目前程式設計存在的困難與問題三個方面闡述)。

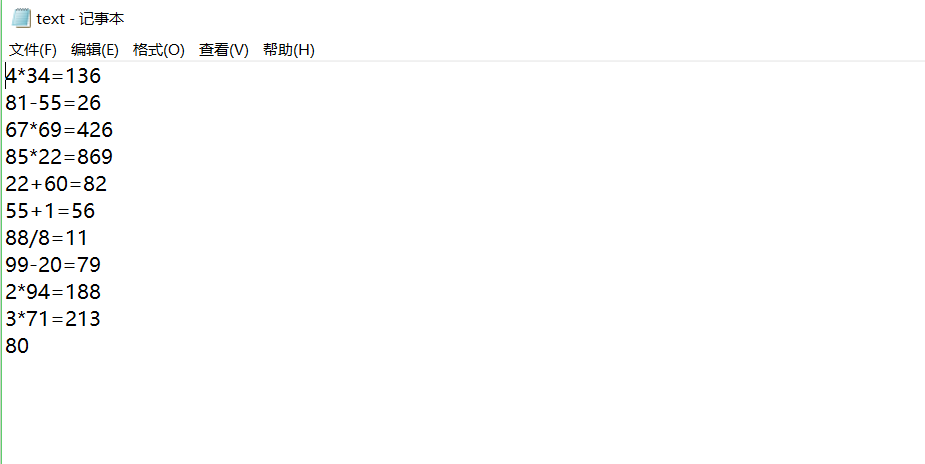
import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; public class math{ public static void main(String[] args) { yunsuan counter=new yunsuan();//與其它類建立聯絡 PrintWriter out=null; try { out=new PrintWriter("D:/text.txt"); }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } int sum=0; for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { int a=new Random().nextInt(100); int b=new Random().nextInt(100); Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); //in.close(); switch((int)(Math.random()*4)) { case 0: System.out.println( ""+a+"+"+b+"="); int c1 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c1); if (c1 == counter.add(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("答案正確"); } else { System.out.println("答案錯誤"); } break ; case 1: while((a-b)<0) { b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } System.out.println(""+a+"-"+b+"="); int c2 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c2); if (c2 == counter.reduce(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("答案正確"); } else { System.out.println("答案錯誤"); } break ; case 2: System.out.println(""+a+"*"+b+"="); int c = in.nextInt(); out.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c); if (c == counter.multiply(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("答案正確"); } else { System.out.println("答案錯誤"); } break; case 3: System.out.println(""+a+"/"+b+"="); while(b==0) { b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } int c0= in.nextInt(); out.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c0); if (c0 == counter.devision(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("答案正確"); } else { System.out.println("答案錯誤"); } break; } } System.out.println("totlescore:"+sum); out.println(sum); out.close(); } }math

//import java.util.Random; public class yunsuan{ //int a=new Random().nextInt(100); //int b=new Random().nextInt(100); public int add(int a,int b) { return a+b; } public int reduce(int a,int b) { if((a-b)>0) return a-b; else return 0; } public int multiply(int a,int b) { return a*b; } public int devision(int a,int b) { if(b!=0) return a/b; else return 0; } }yunsuan
總體結構:主類呼叫以及實現yunsuan類的功能,yunsuan類主要模組化實現各種操作
模組說明:如註釋
問題:對於switch, case字句用的時候掌握的還不太會
程式設計練習2:採用泛型程式設計技術改進實驗九程式設計練習2,使之可處理實數四則運算,其他要求不變。

import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { yunsuan counter=new yunsuan();//與其它類建立聯絡 PrintWriter out=null; try { out=new PrintWriter("D:/text.txt");//將檔案裡的內容讀入到D盤名叫text的檔案中 }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("檔案找不到"); e.printStackTrace(); } int sum=0; for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { int a=new Random().nextInt(100); int b=new Random().nextInt(100); Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); //in.close(); switch((int)(Math.random()*4)) { case 0: System.out.println( ""+a+"+"+b+"="); int c1 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c1); if (c1 == counter.plus(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("答案正確"); } else { System.out.println("答案錯誤"); } break ; case 1: if(a<b) { int temp=a; a=b; b=temp; }//為避免減數比被減數大的情況 System.out.println(""+a+"-"+b+"="); /*while((a-b)<0) { b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); }*/ int c2 = in.nextInt(); out.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c2); if (c2 == counter.minus(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("答案正確"); } else { System.out.println("答案錯誤"); } break ; case 2: System.out.println(""+a+"*"+b+"="); int c = in.nextInt(); out.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c); if (c == counter.multiply(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("答案正確"); } else { System.out.println("答案錯誤"); } break; case 3: while(b==0) { b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);//滿足分母不為0 } while(a%b!=0) { a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } System.out.println(""+a+"/"+b+"="); int c0= in.nextInt(); out.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c0); if (c0 == counter.divide(a, b)) { sum += 10; System.out.println("答案正確"); } else { System.out.println("答案錯誤"); } break; } } System.out.println("totlescore:"+sum); out.println(sum); out.close(); } }Main

public class yunsuan <T>{ private T a; private T b; public void yunsaun() { a=null; b=null; } public void yunsuan(T a,T b) { this.a=a; this.b=b; } public int plus(int a,int b) { return a+b; } public int minus(int a,int b) { return a-b; } public int multiply(int a,int b) { return a*b; } public int divide(int a,int b) { if(b!=0 && a%b==0) return a/b; else return 0; } }yunsuan