mask_rcnn keras原始碼跟讀2)資料部分
資料生成部分主要用了keras_model.fit_generator介面,具體函式在model.py的1626行,其函式說明如下:
def data_generator(dataset, config, shuffle=True, augment=False, augmentation=None,
random_rois=0, batch_size=1, detection_targets=False):
"""A generator that returns images and corresponding target class ids,
bounding box deltas, and masks.
dataset: The Dataset object to pick data from
config: The model config object
shuffle: If True, shuffles the samples before every epoch
augment: (Depricated. Use augmentation instead). If true, apply random
image augmentation. Currently, only horizontal flipping is offered.
augmentation: Optional. An imgaug (https://github.com/aleju/imgaug) augmentation.
For example, passing imgaug.augmenters.Fliplr(0.5) flips images
right/left 50% of the time.
random_rois: If > 0 then generate proposals to be used to train the
network classifier and mask heads. Useful if training
the Mask RCNN part without the RPN.
batch_size: How many images to return in each call
detection_targets: If True, generate detection targets (class IDs, bbox
deltas, and masks). Typically for debugging or visualizations because
in trainig detection targets are generated by DetectionTargetLayer.
Returns a Python generator. Upon calling next() on it, the
generator returns two lists, inputs and outputs. The containtes
of the lists differs depending on the received arguments:
inputs list:
- images: [batch, H, W, C]
- image_meta: [batch, (meta data)] Image details. See compose_image_meta()
- rpn_match: [batch, N] Integer (1=positive anchor, -1=negative, 0=neutral)
- rpn_bbox: [batch, N, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] Anchor bbox deltas.
- gt_class_ids: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES] Integer class IDs
- gt_boxes: [batch, MAX_GT_INSTANCES, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
- gt_masks: [batch, height, width, MAX_GT_INSTANCES]. The height and width
are those of the image unless use_mini_mask is True, in which
case they are defined in MINI_MASK_SHAPE.
outputs list: Usually empty in regular training. But if detection_targets
is True then the outputs list contains target class_ids, bbox deltas,
and masks.
""" 1.Anchor生成
# Anchors
# [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
#compute_backbone_shapes:獲得P2-P5對應特徵圖大小
backbone_shapes = compute_backbone_shapes(config, config.IMAGE_SHAPE)
anchors = utils.generate_pyramid_anchors(config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS,
backbone_shapes,
config.BACKBONE_STRIDES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE) 接下來看generate_pyramid_anchors函式,這裡依次生成P2-P5對應的anchor
def generate_pyramid_anchors(scales, ratios, feature_shapes, feature_strides,
anchor_stride):
"""Generate anchors at different levels of a feature pyramid. Each scale
is associated with a level of the pyramid, but each ratio is used in
all levels of the pyramid.
Returns:
anchors: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]. All generated anchors in one array. Sorted
with the same order of the given scales. So, anchors of scale[0] come
first, then anchors of scale[1], and so on.
""" 然後進入generate_anchors函式,這裡使用np.meshgrid來生成對應的網格,把scales和ratios組合在一起,注意這裡的scales(anchor預設大小)其實是標量。假如輸入的圖片大小為512*512,對於P2來說,其anchor_number=feature_map_size*feature_map_size*3=512/4*512/4*3=49152
(3為橫縱比,4為stride,anchor_stride預設為1)
def generate_anchors(scales, ratios, shape, feature_stride, anchor_stride):
"""
scales: 1D array of anchor sizes in pixels. Example: [32, 64, 128]
ratios: 1D array of anchor ratios of width/height. Example: [0.5, 1, 2]
shape: [height, width] spatial shape of the feature map over which
to generate anchors.
feature_stride: Stride of the feature map relative to the image in pixels.
anchor_stride: Stride of anchors on the feature map. For example, if the
value is 2 then generate anchors for every other feature map pixel.
"""
# Get all combinations of scales and ratios
scales, ratios = np.meshgrid(np.array(scales), np.array(ratios))
scales = scales.flatten()
ratios = ratios.flatten()
# Enumerate heights and widths from scales and ratios
heights = scales / np.sqrt(ratios)
widths = scales * np.sqrt(ratios)
# Enumerate shifts in feature space
shifts_y = np.arange(0, shape[0], anchor_stride) * feature_stride
shifts_x = np.arange(0, shape[1], anchor_stride) * feature_stride
shifts_x, shifts_y = np.meshgrid(shifts_x, shifts_y)
# Enumerate combinations of shifts, widths, and heights
box_widths, box_centers_x = np.meshgrid(widths, shifts_x)
box_heights, box_centers_y = np.meshgrid(heights, shifts_y)
# Reshape to get a list of (y, x) and a list of (h, w)
box_centers = np.stack(
[box_centers_y, box_centers_x], axis=2).reshape([-1, 2])
box_sizes = np.stack([box_heights, box_widths], axis=2).reshape([-1, 2])
# Convert to corner coordinates (y1, x1, y2, x2)
boxes = np.concatenate([box_centers - 0.5 * box_sizes,
box_centers + 0.5 * box_sizes], axis=1)
return boxes2.獲得gt_box和mask
load_image_gt函式會返回當前影象,影象原資料,標籤類別,gt_boxs和gt_max
# Get GT bounding boxes and masks for image.
image_id = image_ids[image_index]
image, image_meta, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, gt_masks = \
load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=augment,
augmentation=augmentation,
use_mini_mask=config.USE_MINI_MASK)比較核心的函式load_image_gt
def load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id, augment=False, augmentation=None,
use_mini_mask=False):
"""Load and return ground truth data for an image (image, mask, bounding boxes).
augment: (Depricated. Use augmentation instead). If true, apply random
image augmentation. Currently, only horizontal flipping is offered.
augmentation: Optional. An imgaug (https://github.com/aleju/imgaug) augmentation.
For example, passing imgaug.augmenters.Fliplr(0.5) flips images
right/left 50% of the time.
use_mini_mask: If False, returns full-size masks that are the same height
and width as the original image. These can be big, for example
1024x1024x100 (for 100 instances). Mini masks are smaller, typically,
224x224 and are generated by extracting the bounding box of the
object and resizing it to MINI_MASK_SHAPE.
Returns:
image: [height, width, 3]
shape: the original shape of the image before resizing and cropping.
class_ids: [instance_count] Integer class IDs
bbox: [instance_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
mask: [height, width, instance_count]. The height and width are those
of the image unless use_mini_mask is True, in which case they are
defined in MINI_MASK_SHAPE.
"""
# Load image and mask
#load_image就是繼承超類utils.Dataset需要實現的函式
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
#load_mask同樣是需要重寫的超類函式
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
original_shape = image.shape
#根據配置檔案中的引數,對圖片進行預處理 *這裡可以瞭解到配置檔案中引數的具體含義
image, window, scale, padding, crop = utils.resize_image(
image,
min_dim=config.IMAGE_MIN_DIM,
min_scale=config.IMAGE_MIN_SCALE,
max_dim=config.IMAGE_MAX_DIM,
mode=config.IMAGE_RESIZE_MODE)
#若對原始圖片進行了預處理,該處理同步於mask上
mask = utils.resize_mask(mask, scale, padding, crop)
# Random horizontal flips.
# TODO: will be removed in a future update in favor of augmentation
if augment:
logging.warning("'augment' is depricated. Use 'augmentation' instead.")
if random.randint(0, 1):
image = np.fliplr(image)
mask = np.fliplr(mask)
# Augmentation 資料增強部分
# This requires the imgaug lib (https://github.com/aleju/imgaug)
if augmentation:
import imgaug
# Augmentors that are safe to apply to masks
# Some, such as Affine, have settings that make them unsafe, so always
# test your augmentation on masks
MASK_AUGMENTERS = ["Sequential", "SomeOf", "OneOf", "Sometimes",
"Fliplr", "Flipud", "CropAndPad",
"Affine", "PiecewiseAffine"]
def hook(images, augmenter, parents, default):
"""Determines which augmenters to apply to masks."""
return (augmenter.__class__.__name__ in MASK_AUGMENTERS)
# Store shapes before augmentation to compare
image_shape = image.shape
mask_shape = mask.shape
# Make augmenters deterministic to apply similarly to images and masks
det = augmentation.to_deterministic()
image = det.augment_image(image)
# Change mask to np.uint8 because imgaug doesn't support np.bool
mask = det.augment_image(mask.astype(np.uint8),
hooks=imgaug.HooksImages(activator=hook))
# Verify that shapes didn't change
assert image.shape == image_shape, "Augmentation shouldn't change image size"
assert mask.shape == mask_shape, "Augmentation shouldn't change mask size"
# Change mask back to bool
mask = mask.astype(np.bool)
# Note that some boxes might be all zeros if the corresponding mask got cropped out.
# and here is to filter them out
_idx = np.sum(mask, axis=(0, 1)) > 0
mask = mask[:, :, _idx]
class_ids = class_ids[_idx]
# Bounding boxes. Note that some boxes might be all zeros
# if the corresponding mask got cropped out.
# bbox: [num_instances, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
#mask->bbox 邊緣寬體,mask_rcnn->faster_rncc 可以修改這裡
bbox = utils.extract_bboxes(mask)
# Active classes
# Different datasets have different classes, so track the
# classes supported in the dataset of this image.
active_class_ids = np.zeros([dataset.num_classes], dtype=np.int32)
source_class_ids = dataset.source_class_ids[dataset.image_info[image_id]["source"]]
active_class_ids[source_class_ids] = 1
# Resize masks to smaller size to reduce memory usage
#若在指定了MINI_MASK_SHAPE,則把包含mask的box,resize成MINI_MASK_SHAPE*MINI_MASK_SHAPE
if use_mini_mask:
mask = utils.minimize_mask(bbox, mask, config.MINI_MASK_SHAPE)
# Image meta data
image_meta = compose_image_meta(image_id, original_shape, image.shape,
window, scale, active_class_ids)
return image, image_meta, class_ids, bbox, mask在看看裡面的函式,便於理解配置檔案中引數的含義
utils.resize_image()
若指定了min_dim,則會讓原始圖片的較小邊image_min縮放到min_dim,並獲得縮放比例scale。
若指定了max_dim(square模式下),先判斷通過min_dim獲得的scale得到的較長邊image_max*scale是否大於了max_dim,若大於了,則重新獲得scale=max_dim / image_max
通過scale通比例縮放圖片後,width和height可能不一致,則使用mode來調整
若mode為square:
對width和height同時進行padding_0操作,直至等於max_dim
若mode為pad64:
對width和height向上就近padding_0至64的倍數,比如width=112,則padding_0至128
若mode為crop:
則先按min_dim進行縮放,然後隨機裁剪獲得min_dim*min_dim的新圖
def resize_image(image, min_dim=None, max_dim=None, min_scale=None, mode="square"):
"""Resizes an image keeping the aspect ratio unchanged.
min_dim: if provided, resizes the image such that it's smaller
dimension == min_dim
max_dim: if provided, ensures that the image longest side doesn't
exceed this value.
min_scale: if provided, ensure that the image is scaled up by at least
this percent even if min_dim doesn't require it.
mode: Resizing mode.
none: No resizing. Return the image unchanged.
square: Resize and pad with zeros to get a square image
of size [max_dim, max_dim].
pad64: Pads width and height with zeros to make them multiples of 64.
If min_dim or min_scale are provided, it scales the image up
before padding. max_dim is ignored in this mode.
The multiple of 64 is needed to ensure smooth scaling of feature
maps up and down the 6 levels of the FPN pyramid (2**6=64).
crop: Picks random crops from the image. First, scales the image based
on min_dim and min_scale, then picks a random crop of
size min_dim x min_dim. Can be used in training only.
max_dim is not used in this mode.
Returns:
image: the resized image
window: (y1, x1, y2, x2). If max_dim is provided, padding might
be inserted in the returned image. If so, this window is the
coordinates of the image part of the full image (excluding
the padding). The x2, y2 pixels are not included.
scale: The scale factor used to resize the image
padding: Padding added to the image [(top, bottom), (left, right), (0, 0)]
"""minimize_mask()
把包含mask的box插值縮放到mini_shape*mini_shape,首先由bbox座標先把包含mask的box扣出來,然後在進行插值縮放,expand_masks則是它的逆操作。(這裡和最後的fcn有一定的聯絡)
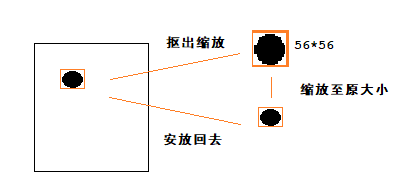
def minimize_mask(bbox, mask, mini_shape):
"""Resize masks to a smaller version to reduce memory load.
Mini-masks can be resized back to image scale using expand_masks()
See inspect_data.ipynb notebook for more details.
"""
mini_mask = np.zeros(mini_shape + (mask.shape[-1],), dtype=bool)
for i in range(mask.shape[-1]):
# Pick slice and cast to bool in case load_mask() returned wrong dtype
m = mask[:, :, i].astype(bool)
y1, x1, y2, x2 = bbox[i][:4]
m = m[y1:y2, x1:x2]
if m.size == 0:
raise Exception("Invalid bounding box with area of zero")
# Resize with bilinear interpolation
m = skimage.transform.resize(m, mini_shape, order=1, mode="constant")
mini_mask[:, :, i] = np.around(m).astype(np.bool)
return mini_mask3.build_rpn_targets
通過 anchors and GT boxes獲得rpn_match(anchor的型別)和rpn_bbox(positive_anchor和gt_box的偏移)
def build_rpn_targets(image_shape, anchors, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes, config):
"""Given the anchors and GT boxes, compute overlaps and identify positive
anchors and deltas to refine them to match their corresponding GT boxes.
anchors: [num_anchors, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
gt_class_ids: [num_gt_boxes] Integer class IDs.
gt_boxes: [num_gt_boxes, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
Returns:
rpn_match: [N] (int32) matches between anchors and GT boxes.
1 = positive anchor, -1 = negative anchor, 0 = neutral
rpn_bbox: [N, (dy, dx, log(dh), log(dw))] Anchor bbox deltas.
"""區分 1 = positive anchor, -1 = negative anchor, 0 = neutral的規則如下:
# Match anchors to GT Boxes
# If an anchor overlaps a GT box with IoU >= 0.7 then it's positive.
# If an anchor overlaps a GT box with IoU < 0.3 then it's negative.
# Neutral anchors are those that don't match the conditions above,
# and they don't influence the loss function.
# However, don't keep any GT box unmatched (rare, but happens). Instead,
# match it to the closest anchor (even if its max IoU is < 0.3).