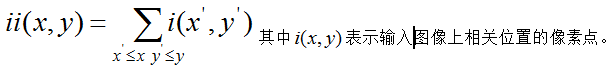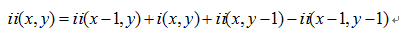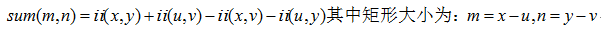影象處理之積分圖演算法
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-11
影象處理之積分圖演算法
一:積分圖來源與發展
積分影象是Crow在1984年首次提出,是為了在多尺度透視投影中提高渲染速度。隨後這種技術被應用到基於NCC的快速匹配、物件檢測和SURF變換中、基於統計學的快速濾波器等方面。積分影象是一種在影象中快速計算矩形區域和的方法,這種演算法主要優點是一旦積分影象首先被計算出來我們可以計算影象中任意大小矩形區域的和而且是在常量時間內。這樣在影象模糊、邊緣提取、物件檢測的時候極大降低計算量、提高計算速度。第一個應用積分影象技術的應用是在Viola-Jones的物件檢測框架中出現。
二:積分影象概念
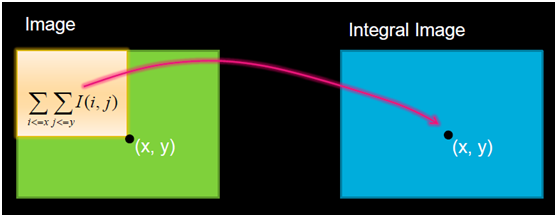
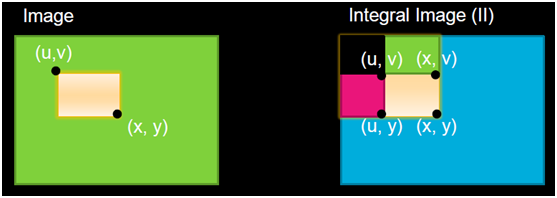
在積分影象(Integral Image - ii)上任意位置(x, y)處的ii(x, y)表示該點左上角所有畫素之和,表示如下:
從給定影象I從上到下、從左到右計算得到和的積分影象公式如下:
其中(x<0 || y<0) 時ii(x,y)=0, i(x,y)=0
得到積分影象之後,影象中任意矩形區域和通過如下公式計算:
三:程式碼實現:
積分影象演算法的Java程式碼實現如下:
-
package com.gloomyfish.ii.demo;
-
-
public
-
// sum index tables
-
private
int[] sum;
-
private
int[] squaresum;
-
// image
-
private
byte[] image;
-
private
int width;
-
private
int height;
-
-
public
byte[] getImage() {
-
return image;
-
}
-
-
public void setImage(byte[] image) {
-
this.image = image;
-
}
-
-
public int getBlockSum(int x, int y, int m, int n) {
-
int swx = x + n/
2;
-
int swy = y + m/
2;
-
int nex = x-n/
2-
1;
-
int ney = y-m/
2-
1;
-
int sum1, sum2, sum3, sum4;
-
if(swx >= width) {
-
swx = width -
1;
-
}
-
if(swy >= height) {
-
swy = height -
1;
-
}
-
if(nex <
0) {
-
nex =
0;
-
}
-
if(ney <
0) {
-
ney =
0;
-
}
-
sum1 = sum[ney*width+nex];
-
sum4 = sum[swy*width+swx];
-
sum2 = sum[swy*width+nex];
-
sum3 = sum[ney*width+swx];
-
return ((sum1 + sum4) - sum2 - sum3);
-
}
-
-
public int getBlockSquareSum(int x, int y, int m, int n) {
-
int swx = x + n/
2;
-
int swy = y + m/
2;
-
int nex = x-n/
2-
1;
-
int ney = y-m/
2-
1;
-
int sum1, sum2, sum3, sum4;
-
if(swx >= width) {
-
swx = width -
1;
-
}
-
if(swy >= height) {
-
swy = height -
1;
-
}
-
if(nex <
0) {
-
nex =
0;
-
}
-
if(ney <
0) {
-
ney =
0;
-
}
-
sum1 = squaresum[ney*width+nex];
-
sum4 = squaresum[swy*width+swx];
-
sum2 = squaresum[swy*width+nex];
-
sum3 = squaresum[ney*width+swx];
-
return ((sum1 + sum4) - sum2 - sum3);
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public void process(int width, int height) {
-
this.width = width;
-
this.height = height;
-
sum =
new
int[width*height];
-
squaresum =
new
int[width*height];
-
// rows
-
int p1=
0, p2=
0, p3=
0, p4;
-
int offset =
0, uprow=
0, leftcol=
0;
-
int s=
0;
-
for(
int row=
0; row<height; row++ ) {
-
offset = row*width;
-
uprow = row-
1;
-
for(
int col=
0; col<width; col++) {
-
leftcol=col-
1;
-
p1=image[offset]&
0xff;
// p(x, y)
-
p2=(leftcol<
0) ?
0:sum[offset-
1];
// p(x-1, y)
-
p3=(uprow<
0) ?
0:sum[offset-width];
// p(x, y-1);
-
p4=(uprow<
0||leftcol<
0) ?
0:sum[offset-width-
1];
// p(x-1, y-1);
-
s = sum[offset]= p1+p2+p3-p4;
-
squaresum[offset]=s*s;
-
// System.out.print("\t[" + offset+"]=" + s);
-
offset++;
-
}
-
// System.out.println();
-
}
-
}
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
byte[] data =
new
byte[]{
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1};
-
IntIntegralImage ii =
new IntIntegralImage();
-
ii.setImage(data);
-
ii.process(
7,
3);
-
-
int sum = ii.getBlockSum(
3,
2,
3,
3);
-
System.out.println(
"sum = " + sum);
-
}
-
}