BZOJ1117: [POI2009]救火站Gas
看到這道題感覺跟 BZOJ2525 和 BZOJ1217 很像
其實他真的很像
不過這題有了對於個數的限制,或許要用 dp ?
看一眼資料範圍,n <= 1e5, k <= 20
所以用陣列完全可以記錄下完整的資訊
那到底是 dp 還是貪心呢?
參考 BZOJ2525 的 check 函式 或 BZOJ1217 整道題的演算法流程,感覺是可以貪心的
就是 dfs 貪心,每個節點 O(k) 的轉移一下資訊,O(nk) 的複雜度可以接受
但多了個數的限制貪心還合理嗎?
答案是肯定的,我們嘗試找一種貪心策略
以下稱每個救火站的 s 個貢獻為 “貢獻”
顯然,貪心策略一定是要基於 "當前子樹中有即將超過距離限制的點時就加一個救火站" 的
那麼接下來要考慮的是如果加多了怎麼辦
如果畫圖,可能會有助於理解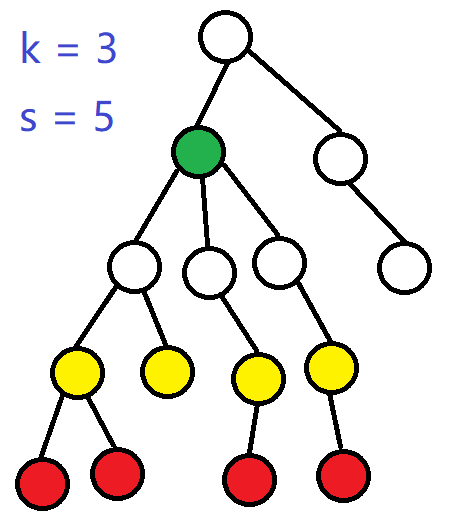
上面的情況只要 s > 4 即可
當前 dfs 回溯到了綠點,則紅點必須在這一層 dfs 中被完全覆蓋
那麼多出的 (s - sumred) 個貢獻就是我們要決策的那剩餘貢獻
考慮向上回溯一層後,黃點會變為紅點,
而對於回溯後到達的點來說,綠點的貢獻已經不能到達新的紅點
那麼這時候就應該在上一層 dfs 中更新一些黃點
同時,有一個顯然的性質:綠點的貢獻越向上回溯作用越小
所以如果在剛才的一層 dfs 中不去覆蓋黃點的話,
在當前的 dfs 會不得不新設一些綠點,
而如果剛才覆蓋了黃點,那現在這一層不一定會多設立綠點
那現在貪心的策略就很顯然了,
對於每一堆 管轄距離dst 相同的貢獻,我們只更新未覆蓋點中距離為 dfs 和 dst - 1 的
之後就可以做這道題了
胡亂 yy 一發覺得會有類似菊花圖一樣的東西來使某子樹中的總剩餘貢獻爆 int
所以開 long long
如果對於根節點寫了特判注意中間變數的 long long
我怕出一些奇怪的鍋所以寫了特判,所以一直WA...
特判的流程就是用根節點的剩餘可用貢獻的字尾和去更新未覆蓋節點
其實和 dfs 中的操作是一樣的,所以也可以不寫特判改一下 dfs
寫特判的程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 100005, MAXD = 25;
struct EDGE{
int nxt, to;
EDGE(int NXT = 0, int TO = 0) {nxt = NXT; to = TO;}
}edge[MAXN << 1];
int n, s, k, totedge;
int head[MAXN], fur[MAXN][MAXD];
ll ans, rem[MAXN][MAXD];
inline int rd() {
register int x = 0;
register char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = x * 10 + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
inline void add(int x, int y) {
edge[++totedge] = EDGE(head[x], y);
head[x] = totedge;
edge[++totedge] = EDGE(head[y], x);
head[y] = totedge;
return;
}
void dfs(int x, int frm) {
fur[x][0] = 1;
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) if (edge[i].to != frm) {
int y = edge[i].to;
dfs(y, x);
for (int j = 1; j <= k; ++j) {
fur[x][j] += fur[y][j - 1];
rem[x][j - 1] += rem[y][j];
}
}
int tmp = 0;
if (fur[x][k]) {
tmp = (fur[x][k] + s - 1) / s;
ans += tmp;
rem[x][k] += tmp * s - fur[x][k];
fur[x][k] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) if (rem[x][i]) {
for (int j = i; j >= max(i - 1, 0); --j) if (fur[x][j]) {
if (rem[x][i] >= fur[x][j]) {
rem[x][i] -= fur[x][j];
fur[x][j] = 0;
} else {
fur[x][j] -= rem[x][i];
rem[x][i] = 0;
}
}
}
return;
}
int main() {
n = rd(); s = rd(); k = rd();
register int xx, yy;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
xx = rd(); yy = rd();
add(xx, yy);
}
dfs(1, 0);
ll tot = 0ll;
for (int i = k; i >= 0; --i) {
tot += rem[1][i];
if (tot >= fur[1][i]) {
tot -= fur[1][i];
fur[1][i] = 0;
} else {
fur[1][i] -= tot;
tot = 0;
}
}
tot = 0ll;
for (int i = k; i >= 0; --i) tot += fur[1][i];
ans += (tot + s - 1) / s;
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
不寫特判的程式碼:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 100005, MAXD = 25;
struct EDGE{
int nxt, to;
EDGE(int NXT = 0, int TO = 0) {nxt = NXT; to = TO;}
}edge[MAXN << 1];
int n, s, k, totedge;
int head[MAXN], fur[MAXN][MAXD];
ll ans, rem[MAXN][MAXD];
inline int rd() {
register int x = 0;
register char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) c = getchar();
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = x * 10 + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return x;
}
inline void add(int x, int y) {
edge[++totedge] = EDGE(head[x], y);
head[x] = totedge;
edge[++totedge] = EDGE(head[y], x);
head[y] = totedge;
return;
}
void dfs(int x, int frm) {
fur[x][0] = 1;
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) if (edge[i].to != frm) {
int y = edge[i].to;
dfs(y, x);
for (int j = 1; j <= k; ++j) {
fur[x][j] += fur[y][j - 1];
rem[x][j - 1] += rem[y][j];
}
}
int tmp = 0;
if (fur[x][k]) {
tmp = (fur[x][k] + s - 1) / s;
ans += tmp;
rem[x][k] += tmp * s - fur[x][k];
fur[x][k] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) if (rem[x][i]) {
for (int j = i; j >= 0 && (j >= i - 1 || x == 1); --j) if (fur[x][j]) {
if (rem[x][i] >= fur[x][j]) {
rem[x][i] -= fur[x][j];
fur[x][j] = 0;
} else {
fur[x][j] -= rem[x][i];
rem[x][i] = 0;
}
}
}
return;
}
int main() {
n = rd(); s = rd(); k = rd();
register int xx, yy;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
xx = rd(); yy = rd();
add(xx, yy);
}
dfs(1, 0);
ll tot = 0ll;
for (int i = k; i >= 0; --i) tot += fur[1][i];
ans += (tot + s - 1) / s;
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
