PAT-A1053:Path of Equal Weight(普通樹的遍歷和非遞減路徑的輸出)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-12
目錄
多看多做,才能更加熟悉樹方面的知識!Very important!!
1053 Path of Equal Weight (30 分)
題目地址:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805424153280512
題目解釋:
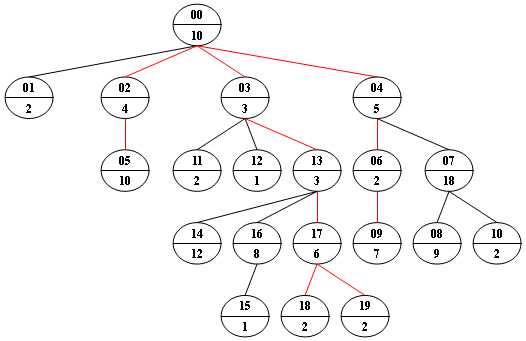
對於每個結點,上面是結點的編號,用二位數字表示(two-digit),下面是該結點的權值,先尋找所有的路徑,使路徑上所有結點的權值之和是給定的s,並按非遞減順序輸出這些路徑上經過的權值。
如果對於兩條路徑,A1=B1,.....Ai-1=B i-1,Ai>Bi那麼A路徑比B路徑大.
解題思路:
1)用path[i]存路徑上第i個結點的編號,最後在一次輸出編號對應的weight,即node[path[i]].weight
2)對於某個結點的子孩子,要先對這些子孩子的weight排序,即現遍歷weight大的子孩子,最後也先輸出weight大的子孩子,即實現了非遞減得輸出路徑
3)dfs遍歷樹
ac程式碼:
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <vector> #define maxn 110 using namespace std; struct NODE{ int weight; vector<int> child; }node[maxn];//結點陣列 bool cmp(int a,int b)//weight從大到小輸出,先排序 { return node[a].weight>node[b].weight; } int n,m,s; int path[maxn];//path[i]表示路徑上第i個結點的編號 void dfs(int index,int numnode,int sum)//訪問結點為index,當前結點個數numnode,和sum { if(sum>s) return ; if(sum==s) { if(node[index].child.size()!=0)//非葉子結點 return ; for(int i=0;i<numnode;i++) { printf("%d",node[path[i]].weight); if(i<numnode-1) printf(" "); else printf("\n"); } return ; } for(int i=0;i<node[index].child.size();i++) { int child=node[index].child[i]; path[numnode]=child; dfs(child,numnode+1,sum+node[child].weight); } } int main() { scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&s); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&node[i].weight); int id,k,child; for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&id,&k); for(int j=0;j<k;j++) { scanf("%d",&child); node[id].child.push_back(child);//向vector中存入孩子 } sort(node[id].child.begin(),node[id].child.end(),cmp);//對每一個結點的子孩子們的weight排序 } path[0]=0; dfs(0,1,node[0].weight); return 0; }
多看多做,才能更加熟悉樹方面的知識!Very important!!