pytorch 中的grid_sample和affine_grid
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-13
pytorch 中提供了對Tensor進行Crop的方法,可以使用GPU實現。具體函式是torch.nn.functional.affine_grid和torch.nn.functional.grid_sample。前者用於生成二維網格,後者對輸入Tensor按照網格進行雙線性取樣。
grid_sample函式中將影象座標歸一化到$[-1, 1]$,其中0對應-1,width-1對應1。
affine_grid的輸入是仿射矩陣(Nx2x3)和輸出Tensor的尺寸(Tensor.Size(NxHxWx2)),輸出的是歸一化的二維網格。
在Faster R CNN中,用到了Crop Pooling, 需要在feature map 中裁剪出與proposal region 對應的部分,可以使用這兩個函式實現。具體參考 http://www.telesens.co/2018/03/11/object-detection-and-classification-using-r-cnns/#ITEM-1455-4
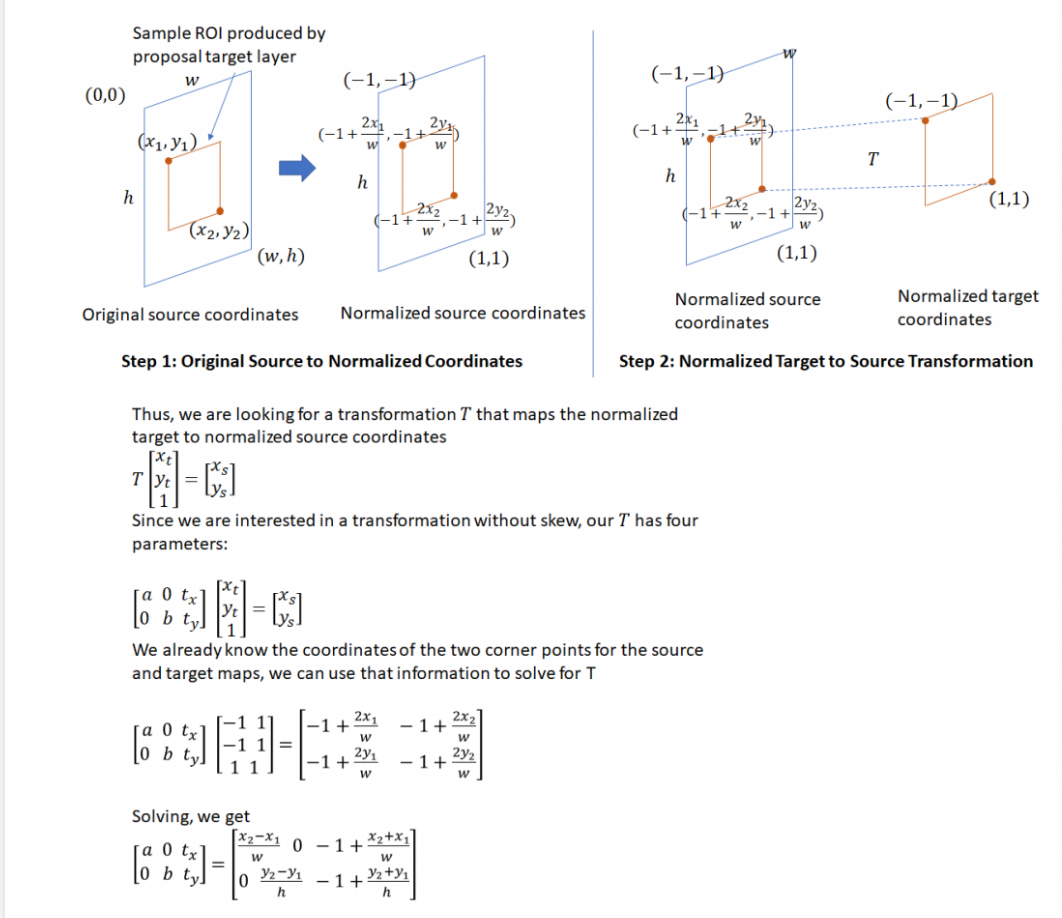
下面進行簡單的實驗:
- 首先生成一個1x1x5x5的Tensor變數
- 裁剪視窗為x1 = 2.5, x2 = 4.5, y1 = 0.5, y2 = 3.5,size為1x1x3x2,根據座標設定theta矩陣
- 進行裁剪,並與numpy計算結果相比較。
a = torch.rand((1, 1, 5, 5)) print(a) # x1 = 2.5, x2 = 4.5, y1 = 0.5, y2 = 3.5 # out_w = 2, out_h = 3 size = torch.Size((1, 1, 3, 2)) print(size) # theta theta_np = np.array([[0.5, 0, 0.75], [0, 0.75, 0]]).reshape(1, 2, 3) theta = torch.from_numpy(theta_np) print('theta:') print(theta) print() flowfield = torch.nn.functional.affine_grid(theta, size) sampled_a = torch.nn.functional.grid_sample(a, flowfield.to(torch.float32)) sampled_a = sampled_a.numpy().squeeze() print('sampled_a:') print(sampled_a) # compute bilinear at (0.5, 2.5), using (0, 3), (0, 4), (1, 3), (1, 4) # quickly compute(https://blog.csdn.net/lxlclzy1130/article/details/50922867) print() coeff = np.array([[0.5, 0.5]]) A = a[0, 0, 0:2, 2:2+2] print('torch sampled at (0.5, 3.5): %.4f' % sampled_a[0,0]) print('numpy compute: %.4f' % np.dot(np.dot(coeff, A), coeff.T).squeeze())
執行結果為:

可以看到結果是相同的
