DeepLearning tutorial(1)Softmax迴歸原理簡介+程式碼詳解
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-14
分享一下我老師大神的人工智慧教程!零基礎,通俗易懂!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow
也歡迎大家轉載本篇文章。分享知識,造福人民,實現我們中華民族偉大復興!
DeepLearning tutorial(1)Softmax迴歸原理簡介+程式碼詳解
@author:wepon
@blog:http://blog.csdn.net/u012162613/article/details/43157801
本文介紹Softmax迴歸演算法,特別是詳細解讀其程式碼實現,基於python theano,程式碼來自:Classifying MNIST digits using Logistic Regression,參考UFLDL。
一、Softmax迴歸簡介
關於演算法的詳細教程本文沒必要多說,可以參考UFLDL。下面只簡單地總結一下,以便更好地理解程式碼。 Softmax迴歸其實就相當於多類別情況下的邏輯迴歸,對比如下: 邏輯迴歸的假設函式(hypothesis):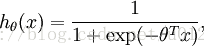
整個邏輯迴歸模型的引數就是theta,h(*)是sigmoid函式,輸出在0~1之間,一般作為二分類演算法。對於具體的問題,找出最合適的theta便是最重要的步驟,這是最優化問題,一般通過定義代價函式,然後最小化代價函式來求解,邏輯迴歸的代價函式為
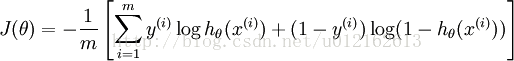
最小化J(theta),一般採用梯度下降演算法,迭代計算梯度並更新theta。
Softmax的假設函式:

邏輯迴歸裡將-theta*x作為sigmoid函式的輸入,得到的是0或者1,兩個類別。而softmax有有k個類別,並且將-theta*x作為指數的係數,所以就有e^(-theta_1*x)至e^( -theta_k*x)共k項,然後除以它們的累加和,這樣做就實現了歸一化,使得輸出的k個數的和為1,而每一個數就代表那個類別出現的概率。因此:softmax的假設函式輸出的是一個k維列向量,每一個維度的數就代表那個類別出現的概率。
Softmax的代價函式:
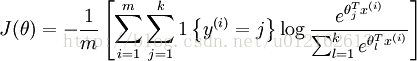
本質上跟邏輯迴歸是一樣的,採用NLL,如果加上權重衰減項(正則化項),則為:
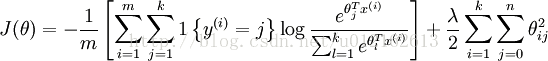
最小化代價函式,同樣可以採用簡單而有效的梯度下降,需要提到的是,在程式實現中,我們一般採用批量隨機梯度下降,即MSGD,minibatch Stochastic Gradient Descent,簡單來說,就是每遍歷完一個batch的樣本才計算梯度和更新引數,一個batch一般有幾十到幾百的單個樣本。PS:隨機梯度下降則是一個樣本更新一次。
二、Softmax程式碼詳細解讀
首先說明一點,下面的程式採用的是MSGD演算法,代價函式是不帶權重衰減項的,整個程式實現用Softmax迴歸來classfy MINST資料集(識別手寫數字0~9)。程式碼解讀是個人理解,僅供參考,不一定正確,如有錯誤請不吝指出。
原始程式碼和經過我註釋的程式碼:github地址
引數說明:上面第一部分我們的引數用theta表示,在下面的程式中,用的是W,權重,這兩者是一樣的。還有一點需要注意,上面的假設函式中是-theta*x,而在程式中,用的是W*X+b,本質也是一樣的,因為可以將b看成W0,增加一個x0=1,則W*X+b=WX=-theta*x。
(1)匯入一些必要的模組
import cPickleimport gzipimport osimport sysimport timeimport numpyimport theanoimport theano.tensor as T(2)定義Softmax迴歸模型
在deeplearning tutorial中,直接將LogisticRegression視為Softmax,而我們所認識的二類別的邏輯迴歸就是當n_out=2時的LogisticRegression,因此下面程式碼定義的LogisticRegression就是Softmax。程式碼解讀見註釋:
#引數說明:#input,輸入的一個batch,假設一個batch有n個樣本(n_example),則input大小就是(n_example,n_in)#n_in,每一個樣本的大小,MNIST每個樣本是一張28*28的圖片,故n_in=784#n_out,輸出的類別數,MNIST有0~9共10個類別,n_out=10 class LogisticRegression(object): def __init__(self, input, n_in, n_out):#W大小是n_in行n_out列,b為n_out維向量。即:每個輸出對應W的一列以及b的一個元素。WX+b #W和b都定義為theano.shared型別,這個是為了程式能在GPU上跑。 self.W = theano.shared( value=numpy.zeros( (n_in, n_out), dtype=theano.config.floatX ), name='W', borrow=True ) self.b = theano.shared( value=numpy.zeros( (n_out,), dtype=theano.config.floatX ), name='b', borrow=True )#input是(n_example,n_in),W是(n_in,n_out),點乘得到(n_example,n_out),加上偏置b,#再作為T.nnet.softmax的輸入,得到p_y_given_x#故p_y_given_x每一行代表每一個樣本被估計為各類別的概率 #PS:b是n_out維向量,與(n_example,n_out)矩陣相加,內部其實是先複製n_example個b,#然後(n_example,n_out)矩陣的每一行都加b self.p_y_given_x = T.nnet.softmax(T.dot(input, self.W) + self.b)#argmax返回最大值下標,因為本例資料集是MNIST,下標剛好就是類別。axis=1表示按行操作。 self.y_pred = T.argmax(self.p_y_given_x, axis=1)#params,模型的引數 self.params = [self.W, self.b]#代價函式NLL#因為我們是MSGD,每次訓練一個batch,一個batch有n_example個樣本,則y大小是(n_example,),#y.shape[0]得出行數即樣本數,將T.log(self.p_y_given_x)簡記為LP,#則LP[T.arange(y.shape[0]),y]得到[LP[0,y[0]], LP[1,y[1]], LP[2,y[2]], ...,LP[n-1,y[n-1]]]#最後求均值mean,也就是說,minibatch的SGD,是計算出batch裡所有樣本的NLL的平均值,作為它的cost def negative_log_likelihood(self, y): return -T.mean(T.log(self.p_y_given_x)[T.arange(y.shape[0]), y])#batch的誤差率 def errors(self, y): # 首先檢查y與y_pred的維度是否一樣,即是否含有相等的樣本數 if y.ndim != self.y_pred.ndim: raise TypeError( 'y should have the same shape as self.y_pred', ('y', y.type, 'y_pred', self.y_pred.type) ) # 再檢查是不是int型別,是的話計算T.neq(self.y_pred, y)的均值,作為誤差率 #舉個例子,假如self.y_pred=[3,2,3,2,3,2],而實際上y=[3,4,3,4,3,4] #則T.neq(self.y_pred, y)=[0,1,0,1,0,1],1表示不等,0表示相等 #故T.mean(T.neq(self.y_pred, y))=T.mean([0,1,0,1,0,1])=0.5,即錯誤率50% if y.dtype.startswith('int'): return T.mean(T.neq(self.y_pred, y)) else: raise NotImplementedError()上面已經定義好了softmax模型,包括輸入的batch :input,每個樣本的大小n_in,輸出的類別n_out,模型的引數W、b,模型預測的輸出y_pred,代價函式NLL,以及誤差率errors。
(3)載入MNIST資料集
def load_data(dataset): # dataset是資料集的路徑,程式首先檢測該路徑下有沒有MNIST資料集,沒有的話就下載MNIST資料集 #這一部分就不解釋了,與softmax迴歸演算法無關。 data_dir, data_file = os.path.split(dataset) if data_dir == "" and not os.path.isfile(dataset): # Check if dataset is in the data directory. new_path = os.path.join( os.path.split(__file__)[0], "..", "data", dataset ) if os.path.isfile(new_path) or data_file == 'mnist.pkl.gz': dataset = new_path if (not os.path.isfile(dataset)) and data_file == 'mnist.pkl.gz': import urllib origin = ( 'http://www.iro.umontreal.ca/~lisa/deep/data/mnist/mnist.pkl.gz' ) print 'Downloading data from %s' % origin urllib.urlretrieve(origin, dataset) print '... loading data'#以上是檢測並下載資料集mnist.pkl.gz,不是本文重點。下面才是load_data的開始 #從"mnist.pkl.gz"里加載train_set, valid_set, test_set,它們都是包括label的#主要用到python裡的gzip.open()函式,以及 cPickle.load()。#‘rb’表示以二進位制可讀的方式開啟檔案 f = gzip.open(dataset, 'rb') train_set, valid_set, test_set = cPickle.load(f) f.close() #將資料設定成shared variables,主要時為了GPU加速,只有shared variables才能存到GPU memory中#GPU裡資料型別只能是float。而data_y是類別,所以最後又轉換為int返回 def shared_dataset(data_xy, borrow=True): data_x, data_y = data_xy shared_x = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(data_x, dtype=theano.config.floatX), borrow=borrow) shared_y = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(data_y, dtype=theano.config.floatX), borrow=borrow) return shared_x, T.cast(shared_y, 'int32') test_set_x, test_set_y = shared_dataset(test_set) valid_set_x, valid_set_y = shared_dataset(valid_set) train_set_x, train_set_y = shared_dataset(train_set) rval = [(train_set_x, train_set_y), (valid_set_x, valid_set_y), (test_set_x, test_set_y)] return rval(4)將模型應用於MNIST資料集
def sgd_optimization_mnist(learning_rate=0.13, n_epochs=1000, dataset='mnist.pkl.gz', batch_size=600):#載入資料 datasets = load_data(dataset) train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0] valid_set_x, valid_set_y = datasets[1] test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2]#計算有多少個minibatch,因為我們的優化演算法是MSGD,是一個batch一個batch來計算cost的 n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size n_valid_batches = valid_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size n_test_batches = test_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size ###################### # 開始建模 # ###################### print '... building the model'#設定變數,index表示minibatch的下標,x表示訓練樣本,y是對應的label index = T.lscalar() x = T.matrix('x') y = T.ivector('y') #定義分類器,用x作為input初始化。 classifier = LogisticRegression(input=x, n_in=28 * 28, n_out=10)#定義代價函式,用y來初始化,而其實還有一個隱含的引數x在classifier中。#這樣理解才是合理的,因為cost必須由x和y得來,單單y是得不到cost的。 cost = classifier.negative_log_likelihood(y)#這裡必須說明一下theano的function函式,givens是字典,其中的x、y是key,冒號後面是它們的value。#在function被呼叫時,x、y將被具體地替換為它們的value,而value裡的引數index就是inputs=[index]這裡給出。#下面舉個例子:#比如test_model(1),首先根據index=1具體化x為test_set_x[1 * batch_size: (1 + 1) * batch_size],#具體化y為test_set_y[1 * batch_size: (1 + 1) * batch_size]。然後函式計算outputs=classifier.errors(y),#這裡面有引數y和隱含的x,所以就將givens裡面具體化的x、y傳遞進去。 test_model = theano.function( inputs=[index], outputs=classifier.errors(y), givens={ x: test_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size], y: test_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size] } ) validate_model = theano.function( inputs=[index], outputs=classifier.errors(y), givens={ x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size], y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size] }# 計算各個引數的梯度 g_W = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=classifier.W) g_b = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=classifier.b)#更新的規則,根據梯度下降法的更新公式 updates = [(classifier.W, classifier.W - learning_rate * g_W), (classifier.b, classifier.b - learning_rate * g_b)]#train_model跟上面分析的test_model類似,只是這裡面多了updatas,更新規則用上面定義的updates 列表。 train_model = theano.function( inputs=[index], outputs=cost, updates=updates, givens={ x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size], y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size] } ) ############### # 開始訓練 # ############### print '... training the model' patience = 5000 patience_increase = 2 #提高的閾值,在驗證誤差減小到之前的0.995倍時,會更新best_validation_loss improvement_threshold = 0.995 #這樣設定validation_frequency可以保證每一次epoch都會在驗證集上測試。 validation_frequency = min(n_train_batches, patience / 2) best_validation_loss = numpy.inf #最好的驗證集上的loss,最好即最小。初始化為無窮大 test_score = 0. start_time = time.clock() done_looping = False epoch = 0 #下面就是訓練過程了,while迴圈控制的時步數epoch,一個epoch會遍歷所有的batch,即所有的圖片。#for迴圈是遍歷一個個batch,一次一個batch地訓練。for迴圈體裡會用train_model(minibatch_index)去訓練模型,#train_model裡面的updatas會更新各個引數。#for迴圈裡面會累加訓練過的batch數iter,當iter是validation_frequency倍數時則會在驗證集上測試,#如果驗證集的損失this_validation_loss小於之前最佳的損失best_validation_loss,#則更新best_validation_loss和best_iter,同時在testset上測試。#如果驗證集的損失this_validation_loss小於best_validation_loss*improvement_threshold時則更新patience。#當達到最大步數n_epoch時,或者patience<iter時,結束訓練 while (epoch < n_epochs) and (not done_looping): epoch = epoch + 1 for minibatch_index in xrange(n_train_batches): minibatch_avg_cost = train_model(minibatch_index) # iteration number iter = (epoch - 1) * n_train_batches + minibatch_index if (iter + 1) % validation_frequency == 0: # compute zero-one loss on validation set validation_losses = [validate_model(i) for i in xrange(n_valid_batches)] this_validation_loss = numpy.mean(validation_losses) print( 'epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, validation error %f %%' % ( epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, this_validation_loss * 100. ) ) # if we got the best validation score until now if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss: #improve patience if loss improvement is good enough if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss * \ improvement_threshold: patience = max(patience, iter * patience_increase) best_validation_loss = this_validation_loss # test it on the test set test_losses = [test_model(i) for i in xrange(n_test_batches)] test_score = numpy.mean(test_losses) print( ( ' epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, test error of' ' best model %f %%' ) % ( epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, test_score * 100. ) ) if patience <= iter: done_looping = True break#while迴圈結束 end_time = time.clock() print( ( 'Optimization complete with best validation score of %f %%,' 'with test performance %f %%' ) % (best_validation_loss * 100., test_score * 100.) ) print 'The code run for %d epochs, with %f epochs/sec' % ( epoch, 1. * epoch / (end_time - start_time)) print >> sys.stderr, ('The code for file ' + os.path.split(__file__)[1] + ' ran for %.1fs' % ((end_time - start_time)))完
給我老師的人工智慧教程打call!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow

