ListView(1)控制元件架構與ArrayAdapter詳解
ListView是Android開發中比較常用的一個元件,它以列表的形式展示資訊,並能根據資訊的長度自適應顯示。比如說我們手機裡的通訊錄就用到了ListView顯示聯絡人資訊。在大量的場合下,我們都需要使用這個控制元件。雖然在Android 5.0時代,RecyclerView在很多地方都在逐漸取代ListView,但ListView的使用範圍依然非常的廣泛。我們也不能跳過ListView直接去學習RecyclerView,對ListView的透徹理解是十分有必要的。
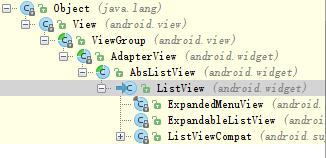
首先來看ListView在View樹中所處的位置:
ListView的官方解釋:
A view that shows items in a vertically scrolling list.
The items come from the {@link ListAdapter} associated with this view.
即:一種在垂直滾動列表中顯示專案的檢視。
顯示的專案(資料)通過ListAdapter介面卡來與檢視關聯。
資料介面卡是連線資料來源和檢視介面的橋樑,它用來把複雜的資料(陣列、連結串列、資料庫、集合等)填充在指定檢視介面上。資料介面卡的實現過程為:1.新建介面卡–>2.新增資料來源到介面卡–>3.檢視載入介面卡。
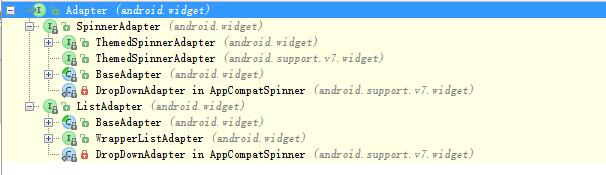
那麼ListAdapter是什麼介面卡呢?Adapter是所有介面卡的祖先介面,下圖為ListAdapter在所有介面卡繼承樹中的位置:
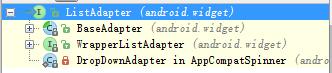
自定義資料介面卡的時候用到了BaseAdapter類,那麼ListAdapter和BaseAdapter是什麼關係呢?只看名字好像BaseAdapter是ListAdapter的長輩,但實際上ListAdapter是所有可以用於ListView的介面卡的祖先,且僅僅為一個介面。下面為ListAdapter的繼承樹:
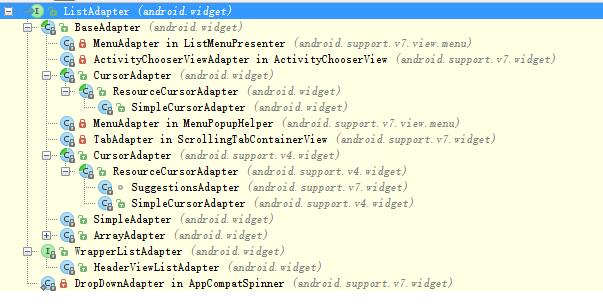
這樣,顯示的專案(資料)通過ListAdapter介面卡來與檢視關聯這句話的含義便很易理解了,不管是ArrayAdapter、SimpleAdapter、SimpleCursorAdapter或者自定義BaseAdapter,只要這些介面卡實現了ListAdapter介面,就可以統稱為ListAdapter介面卡,繼而用於ListView的資料適配,下面為展開的繼承樹:
這下我們就不用去詢問別人ListView有哪幾種介面卡了,我們已經自己推匯出上圖除紅鎖標記的私有類外的其他介面卡都可以給ListView用。下面來看比較常用的四種介面卡:ArrayAdapter、SimpleAdapter、SimpleCursorAdapter以及自定義BaseAdapter。
ArrayAdapter(陣列介面卡)
用於繫結格式單一的資料,資料來源可以是集合或陣列。
佈局檔案:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</RelativeLayout>
MainActivity.java 如下:
package com.example.listview;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Adapter;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ListView mListView;
private ArrayAdapter<String> arrayAdapter;
private String[] data = new String[]{"熊大", "熊二", "跳跳","熊大", "熊二", "跳跳",
"熊大", "熊二", "跳跳","熊大", "熊二", "跳跳"};//資料來源
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView);
//1.新建資料介面卡 2.新增資料來源到介面卡
arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, data);
//3.檢視載入介面卡
mListView.setAdapter(arrayAdapter);
}
}
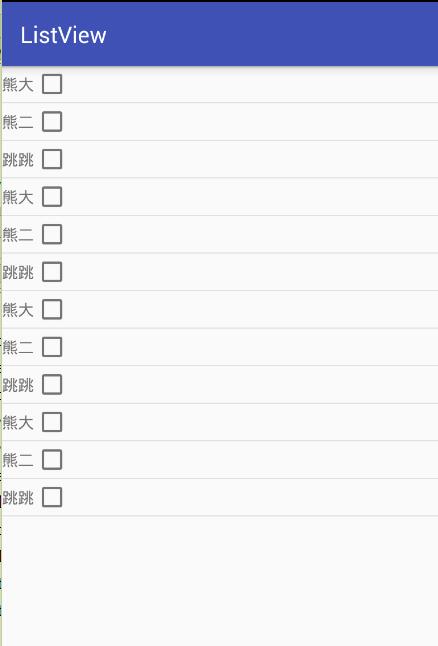
執行效果如下:
到這裡對ArrayAdapter的一個簡單示例就完成了,那對ArrayAdapter的學習到這就可以結束了嗎?可以跳到SimpleAdapter的學習了嗎?本來是這麼打算的,畢竟最常用的是自定義BaseAdapter資料介面卡,ArrayAdapter瞭解一下就可以了啦。可是…可是我看到了這個:
記得面試官問我缺點的時候我說我的缺點是不求甚解的反面,導致學習進度很慢…BaseAdapter萬能介面卡什麼鬼的你們在後邊等著我吧…我們接著來看ArrayAdapter……
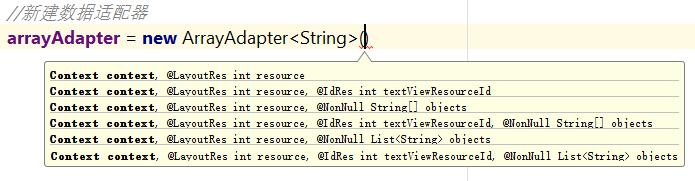
上面示例新建資料介面卡的方式是上圖中的第三種建立方式,要掌握其他建立方式,先要了解引數含義:
context : 當前上下文
resource : item的佈局檔案
textViewResourceId : item佈局檔案中的TextView的ID (可不指定)
objects : 資料來源 (可不指定)
如果引數resource設定為只含有一個TextView控制元件(可為TextView衍生出的控制元件如CheckedTextView)的佈局檔案,則可不指定textViewResourceId引數,比如上面示例中的android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1就是一個TextView,Item內容直接顯示在resource佈局中,也就是TextView中。
如果引數resource沒有設定成僅含有一個TextView的佈局檔案,則必須在這個佈局檔案中包含一個TextView,且必須設定引數textViewResourceId指定其中的TextView的ID。此時Item就不再只是單調的TextView佈局,而可以在resource指定的佈局檔案中自定義。但資料只能顯示在其中的TextView中,示例如下:
Item佈局檔案:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/within_textview"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>新建介面卡程式碼修改為下:
arrayAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, R.layout.item,R.id.textView,data);
執行效果:
看來一開始對ArrayAdapter的定義還是挺準確的:用於繫結格式單一的資料,資料來源可以是集合或陣列。格式單一的是資料,佈局可以自己定義,但是資料只能在一個TextView上顯示。這種也可以記作樣式豐富但內容簡單的,而第一個示例可以記作樣式和內容都簡單的。如果我們需要展示的內容是僅一個textview承載不了的,還需要其它元件,怎麼辦?那麼有沒有一個方法可以實現樣式和內容都是豐富的呢?有,但是原生的ArrayAdapter無法實現這個功能,需要自定義一個ArrayAdapter類並重寫getView()方法才能實現。
豐富的內容通過User類來實現:
package com.example.listview;
/**
* Created by yinghao on 2016/6/10.
*/
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
豐富的佈局通過自定義item佈局檔案來實現:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/within_textview"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
將豐富的內容顯示在豐富的控制元件上通過自定義ArrayAdapter類來實現:
package com.example.listview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
/**
* Created by yinghao on 2016/6/10.
*/
public class MyArrayAdapter extends ArrayAdapter<User> {
private int resourceId;
public MyArrayAdapter(Context context, int resource, User[] objects) {
super(context, resource, objects);
this.resourceId = resource;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
User user = getItem(position);
LinearLayout userListItem = new LinearLayout(getContext());
String inflater = Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE;
LayoutInflater vi = (LayoutInflater)getContext().getSystemService(inflater);
vi.inflate(resourceId, userListItem, true);
TextView name = (TextView) userListItem.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
TextView age = (TextView) userListItem.findViewById(R.id.tv_age);
name.setText(user.getName());
age.setText(String.valueOf(user.getAge()));
return userListItem;
}
}
MainActivity.java 檔案程式碼如下:
package com.example.listview;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ListView mListView;
private User[] users = new User[10];//資料來源
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//準備資料來源
for (int i = 0;i<10;i++) {
User user = new User("name"+i,15+i);
users[i] = user;
}
mListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView);
//1.新建資料介面卡 // 2.新增資料來源到介面卡
MyArrayAdapter arrayAdapter = new MyArrayAdapter(this, R.layout.item, users);
//3.檢視載入介面卡
mListView.setAdapter(arrayAdapter);
}
}
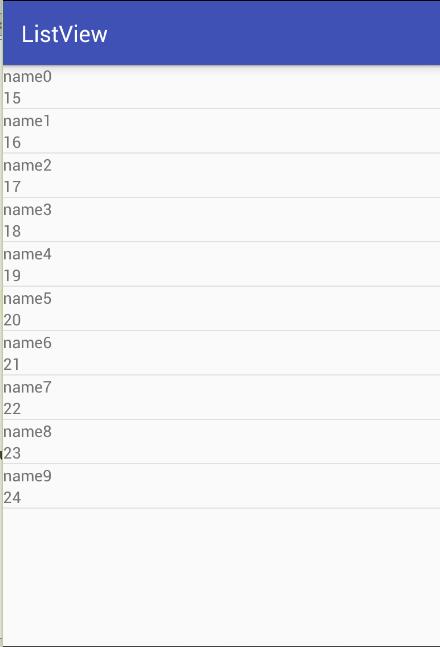
顯示結果如下:
總結:以上學習了ListView與listAdapter介面卡的概念及其關係,然後演繹了ArrayAdapter的三種實現方式,分別是樣式和內容都是簡單的、樣式豐富但內容簡單的、樣式和內容都豐富的三種。其中前兩種用原生的ArrayAdapter就可以實現,通過對原生ArrayAdapter幾種構造方法的研究得出了資料只能顯示在TextView上的結論;第三種方式需要自己重寫getView()方法,在一定程度上也可以算作自定義Adapter。另外對於繫結的資料可以為格式單一的泛型的陣列或集合,上面涉及到的為String陣列和User陣列,也可以為List集合。
關於ArrayAdapter先學到這,接下來學習SimpleAdapter、SimpleCursorAdapter以及自定義BaseAdapter…