day20 Python實現迷宮演算法 v1版本
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-20
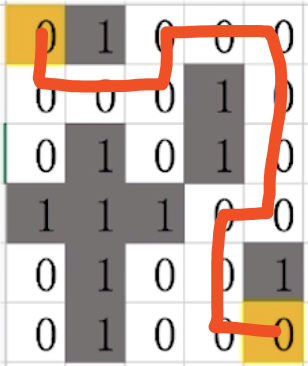
# 深度遍歷實現的迷宮演算法
lookup_path = []
history_path = []
# maze = [[0, 0, 1, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0]]
maze = [[0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0, 0, 0]]
# 列印二維陣列
for k in maze:
for v in k:
print(v, end=" ")
print("")
print("\n")
def up(location):
# 到達了陣列頂端
if location[0] == 0:
return False
else:
new_location = [location[0] - 1, location[1]]
# 走過的路不再走
if new_location in history_path:
return False
# 遇到牆不走
elif maze[new_location[0]][new_location[1]] == 1:
return False
else:
lookup_path.append(new_location)
history_path.append(new_location)
return True
def down(location):
# 遇到迷宮最下方的時候,不能繼續往下走
if location[0] == len(maze) - 1: # 6行5列的二維陣列行數,從0開始計算所以是6-1=5 行
return False
else:
new_location = [location[0] + 1, location[1]]
# 走過的路不再走
if new_location in history_path:
return False
# 遇到牆不走
elif maze[new_location[0]][new_location[1]] == 1:
return False
else:
history_path.append(new_location)
lookup_path.append(new_location)
return True
def left(location):
# 遇到迷宮最左邊,不能繼續往左走
if location[1] == 0:
return False
else:
new_location = [location[0], location[1] - 1]
# 走過的路不再走
if new_location in history_path:
return False
# 遇到牆不走
elif maze[new_location[0]][new_location[1]] == 1:
return False
else:
history_path.append(new_location)
lookup_path.append(new_location)
return True
def right(location):
# 遇到迷宮最右邊,不能繼續向右移動
if location[1] == len(maze[0]) - 1: # 6行5列的二維陣列列數,從0開始計算所以是5-1=4行
return False
else:
new_location = [location[0], location[1] + 1]
# 走過的路不再走
if new_location in history_path:
return False
# 遇到牆不走
elif maze[new_location[0]][new_location[1]] == 1:
return False
else:
history_path.append(new_location)
lookup_path.append(new_location)
return True
start = [0, 0]
end = [5, 4]
print("start: %s --> end: %s\n" % (start, end))
lookup_path.append(start)
history_path.append(start)
while lookup_path[-1] != end:
now = lookup_path[-1]
# print("retry:%s, Lookup path:%s" % (now, route_stack))
if up(now) or down(now) or left(now) or right(now):
continue
lookup_path.pop()
print("final path: ", lookup_path)
