《演算法導論》第十八章——B樹
雖然寫這個部落格主要目的是為了給我自己做一個思路記憶錄,但是如果你恰好點了進來,那麼先對你說一聲歡迎。我並不是什麼大觸,只是一個菜菜的學生,如果您發現了什麼錯誤或者您對於某些地方有更好的意見,非常歡迎您的斧正!
B樹是為磁碟或其他直接存取的輔助儲存裝置而設計的一種平衡搜尋樹。
B數與紅黑樹的不同之處在於B樹的結點可以有很多個孩子。
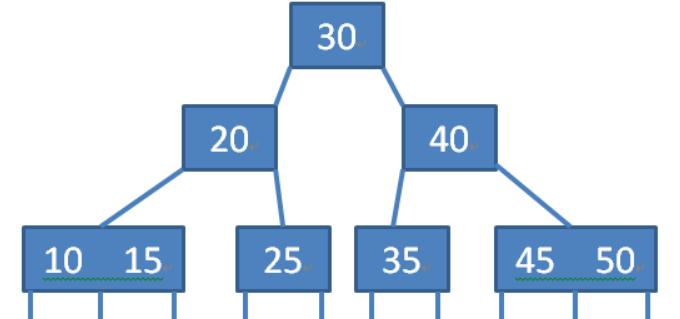
18.1B樹的定義
一棵B樹T具有以下性質(根為T.root)
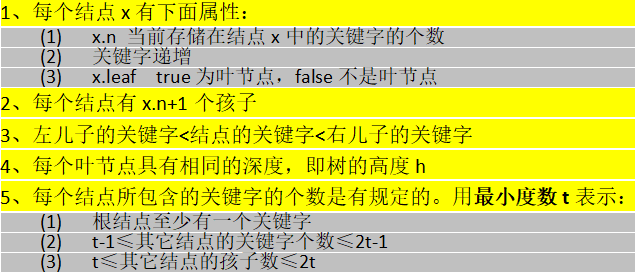
B樹的高度

18.2B樹上的基本操作
搜尋B樹
搜尋B樹與二叉樹搜尋相似,只是每個結點做的不是二叉而是根據結點的孩子做分支選擇。更嚴格地說,是做(x.n+1)路的分支選擇。

建立一棵空的B樹
為了建立一棵B樹,先用B_Tree_Create來建立一個空的根結點,然後呼叫B_Tree_Insert來新增新的結點。

向B樹中插入一個關鍵字
經典二叉樹插入:找到位置,新建結點,插入進去。
對於B樹,我們可以看一下這個過程:
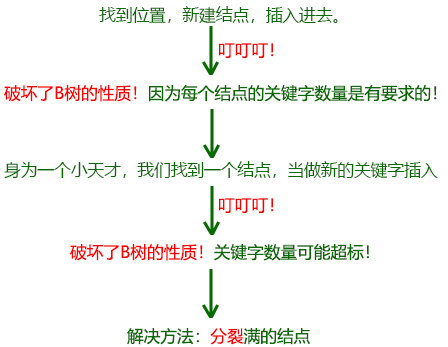
分裂B樹中的結點
圖解過程我找到一篇非常好的部落格,在這裡分享給大家,它的圖畫的很清晰。
慵懶de瘋子的部落格:淺析B-樹分裂
https://blog.csdn.net/apt1203jn/article/details/79587593
我對分裂的理解:如果一個結點滿了,就按其中間關鍵字分裂,這樣就保證了每個關鍵字都不是滿的。插入的時候,就可以直接插入到結點中,如果這個插入操作使得這個結點滿了,就對這個結點再進行分裂。
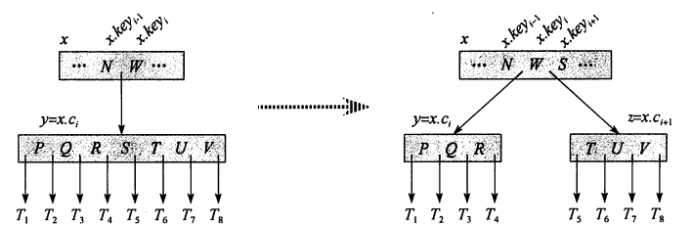

在沿樹單程下行方式向B樹插入關鍵字


18.3從B樹中刪除關鍵字
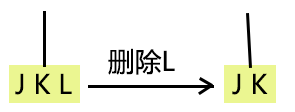
1、如果是葉節點中的關鍵字,直接刪除
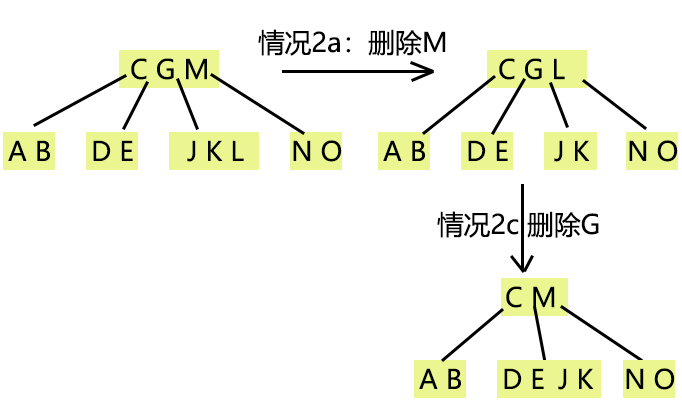
2、a:如果左兒子中關鍵字個數≥t,在左兒子中尋找前驅,代替刪除結點
b:如果右兒子中關鍵字個數≤t,在左兒子中尋找後繼,代替刪除結點
c:如果左右兒子關鍵字都只有t-1個,合併左右結點
3、還有兩種情況,不知道怎麼描述,看圖吧!
第一種:
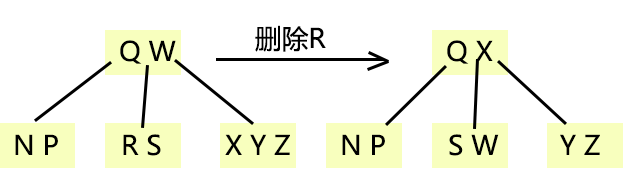
第二種:
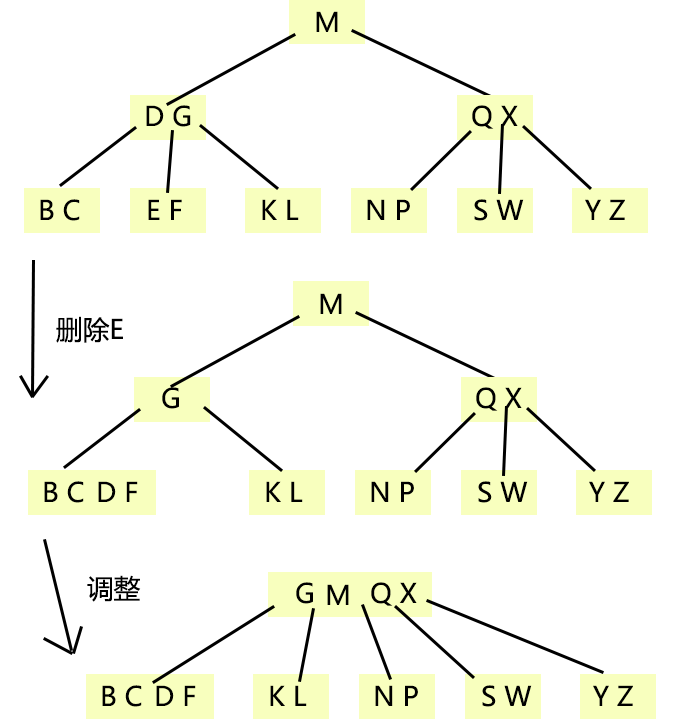
這個第三種情況看看是能看懂的,不過程式碼十分複雜的,我借鑑了windmissing的部落格:演算法導論 第18章 B樹
https://blog.csdn.net/mishifangxiangdefeng/article/details/7798672
有興趣的話可以去看看她的程式碼。
最後是程式碼部分(建議貼上到自己的編輯器中執行一下:)
B樹.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#define Disk_Write(x)
#define Disk_Read(x)
#define t 2 /*最小度數*/
#define MAX 2*t /*內部結點最多的孩子個數*/
using namespace std;
/*B樹的結點*/
typedef struct BTreeNode
{
int n; /*儲存在這個結點中的關鍵字個數*/
char key[MAX]; /*MAX個關鍵字,升序*/
bool leaf; /*判斷是否是葉結點*/
BTreeNode *child[MAX + 1]; /*指向孩子結點*/
}BTnode;
/*B樹*/
typedef struct BTree
{
BTnode* root;
}BTree;
/*搜尋B樹*/
BTnode* B_Tree_Search(BTnode* x, char k, int &i);
/*建立一棵空的B樹*/
void B_Tree_Create(BTree* T, string ch);
/*分裂B樹中的結點*/
void B_Tree_Split_Child(BTnode* x, int i);
/*將關鍵字插入到結點x*/
void B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(BTnode* x, char k);
/*向B樹中插入一個關鍵字*/
void B_Tree_Insert(BTree* T, char k);
/*從B樹中刪除關鍵字*/
void B_Tree_Delete(BTree* &T, BTnode* x, char k);
/*列印B樹*/
void B_Tree_Print(BTnode* x);
void B_Tree_PrintDetail(BTnode *x);
/*測試函式*/
void TestBTree();
B樹.cpp
#include "B樹.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
/*搜尋B樹*/
BTnode* B_Tree_Search(BTnode* x, char k, int &i)
{
i = 1;
while (i <= x->n && k > x->key[i])/*計算最小下標i,使得k≤x.key[i]*/
i++;
if (i <= x->n && k == x->key[i])
return x;
else if (x->leaf)/*沒有找到這個關鍵字*/
{
i = 0;
return NULL;
}
else
{
Disk_Read(x->child[i]);
return B_Tree_Search(x->child[i], k, i);/*對子樹再次尋找*/
}
}
/*建立一棵空的B樹*/
void B_Tree_Create(BTree* T, string ch)
{
BTnode* x = new BTnode();/*新建一個結點*/
x->leaf = true;
x->n = 0;
Disk_Write(x);
T->root = x;
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length(); i++)
{
B_Tree_Insert(T, ch[i]);
}
}
/*分裂B樹中的結點*/
void B_Tree_Split_Child(BTnode* x, int i)/*一個非滿的內部結點x,使x.child[i]為滿子結點的下標i*/
{
BTnode* z = new BTnode();
BTnode* y = x->child[i];
z->leaf = y->leaf;
z->n = t - 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= t - 1; j++)/*把y的t-1個關鍵字分給z*/
{
z->key[j] = y->key[j + t];
}
if (y->leaf==false)/*如果y有孩子,就把這個孩子給z*/
{
for (int j = 1; j <= t; j++)
{
z->child[j] = y->child[j + t];
}
}
y->n = t - 1;
for (int j = x->n + 1; j >= i + 1; j--)/*把z插入為x的一個孩子*/
{
x->child[j + 1] = x->child[j];
}
x->child[i + 1] = z;
for (int j = x->n; j >= i; j--)/*提升y的中間關鍵字到x*/
{
x->key[j + 1] = x->key[j];
}
x->key[i] = y->key[t];
x->n++;
Disk_Write(y);
Disk_Write(z);
Disk_Write(x);
}
/*將關鍵字插入到結點x*/
void B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(BTnode* x, char k)
{
int i = x->n;
if (x->leaf)/*x是葉結點*/
{
while (i >= 1 && k < x->key[i])/*尋找要插入的位置*/
{
x->key[i + 1] = x->key[i];/*把資料後移*/
i--;
}
x->key[i + 1] = k;
x->n++;
Disk_Write(x);
}
else/*x不是葉節點*/
{
while (i >= 1 && k < x->key[i])
{
i--;
}
i++;
Disk_Read(x->child[i]);
if (x->child[i]->n == 2 * t - 1)/*如果x的子結點是滿的*/
{
B_Tree_Split_Child(x, i);/*分裂這個孩子*/
if (k > x->key[i])
i++;
}
B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(x->child[i], k);/*插入到孩子中*/
}
}
/*向B樹中插入一個關鍵字*/
void B_Tree_Insert(BTree* T, char k)
{
BTnode* r = T->root;
if (r->n == 2 * t - 1)
{
BTnode* s = new BTnode();
T->root = s;
s->leaf = false;
s->n = 0;
s->child[1] = r;
B_Tree_Split_Child(s, 1);/*分裂原來的根結點*/
B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(s, k);
}
else
{
B_Tree_Insert_Nonfull(r, k);
}
}
/*從B樹中刪除關鍵字*/
void B_Tree_Delete(BTree* &T,BTnode* x, char k)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 1; i <= x->n; i++)
{
if (x->key[i] >= k)
break;
}
BTnode* y = x->child[i];/*y是k前面的結點*/
BTnode* z = x->child[i + 1];/*z是k後面的結點*/
BTnode *d;
if (x->key[i] == k && i <= x->n)/*關鍵字在x中第i個位置*/
{
if (x->leaf == true)/*x是葉結點*/
{
for (j = i; j < x->n; j++)
{
x->key[j] = x->key[j + 1];/*關鍵字前移*/
}
x->n--;
return;
}
if (y->n >= t)/*情況2a*/
{
d = y;
while (d->leaf == false)
{
d = d->child[d->n + 1];/*尋找前驅*/
}
x->key[i] = d->key[d->n];
B_Tree_Delete(T, y, d->key[d->n]);
}
else if (z->n >= t)/*情況2b*/
{
d = z;
while (d->leaf == false)
{
d = d->child[1];/*尋找後繼*/
}
x->key[i] = d->key[1];
B_Tree_Delete(T, y, d->key[d->n]);
}
else/*情況2c*/
{
y->key[y->n + 1] = k;
for (j = 1; j <= z->n; j++)
y->key[y->n + j + 1] = z->key[j];
if (y->leaf == false)
{
for (j = 1; j <= z->n + 1; j++)
y->child[y->n + j + 1] = z->child[j];
}
y->n = y->n + 1 + z->n;
for (j = i; j < x->n; j++)
x->key[j] = x->key[j + 1];
for (j = i + 1; j <= x->n; j++)
x->child[j] = x->child[j + 1];
x->n--;
if (x->n == 0 && T->root == x)
T->root = y;
delete z;
B_Tree_Delete(T, y, k);
}
}
else
{
if (x->leaf == true)
{
cout << "不存在!" << endl;
return;
}
if (y->n == t - 1)/*情況3第一種*/
{
if (i <= x->n && i <= x->n && z->n >= t)
{
y->n++;
y->key[y->n] = x->key[i];
x->key[i] = z->key[1];
for (j = 1; j < z->n; j++)
z->key[j] = z->key[j + 1];
if (y->leaf == false)
{
y->child[y->n + 1] = z->child[1];
for (j = 1; j <= z->n; j++)
z->child[j] = z->child[j + 1];
}
z->n--;
}
//它的相鄰兄弟x->child[i-1]包含至少t個關鍵字
else if (i > 1 && x->child[i - 1]->n >= t)
{
//將x中的關鍵字下降至y
for (j = y->n; j >= 1; j--)
y->key[j + 1] = y->key[j];
y->key[1] = x->key[i - 1];
y->n++;
//將y的相鄰兄弟x->child[i-1]的某一關鍵字上升至x
x->key[i - 1] = x->child[i - 1]->key[x->child[i - 1]->n];
//將該兄弟適合的子女指標移到y
if (y->leaf == false)
{
for (j = y->n; j >= 1; j--)
y->child[j + 1] = y->child[j];
y->child[1] = x->child[i - 1]->child[x->child[i - 1]->n + 1];
}
//x->child[i-1]的關鍵字數-1
x->child[i - 1]->n--;
}
//y和其所有相鄰兄弟都只有t-1個關鍵字,則與其中一個兄弟合併
else
{
//與後面一個結點(用z表示)合併
if (i <= x->n)
{
//將x->key[i]併入y中
y->key[y->n + 1] = x->key[i];
//將z中所有關鍵字併入y中
for (j = 1; j <= z->n; j++)
y->key[j + y->n + 1] = z->key[j];
//如果有孩子,所有孩子也要併入
if (y->leaf == false)
{
for (j = 1; j <= z->n + 1; j++)
y->child[j + y->n + 1] = z->child[j];
}
//修改y的關鍵字數
y->n = y->n + 1 + z->n;
//將x->key[i]從x中移出
for (j = i; j < x->n; j++)
x->key[j] = x->key[j + 1];
//把指向z的指標從x->child中移出
for (j = i + 1; j <= x->n; j++)
x->child[j] = x->child[j + 1];
//x的關鍵字數-1
x->n--;
//若根結點被刪除,更新根結點
if (x->n == 0 && T->root == x)
T->root = y;
}
//與前面一個結點合併
else
{
//令z=x->child[i-1],y=x->child[i],把z併入y中
z = y; i--;
y = x->child[i];
//將x->key[i]併入y中
y->key[y->n + 1] = x->key[i];
//將z中所有關鍵字併入y中
for (j = 1; j <= z->n; j++)
y->key[j + y->n + 1] = z->key[j];
//如果有孩子,所有孩子也要併入
if (y->leaf == false)
{
for (j = 1; j <= z->n + 1; j++)
y->child[j + y->n + 1] = z->child[j];
}
//修改y的關鍵字數
y->n = y->n + 1 + z->n;
//將x->key[i]從x中移出
for (j = i; j < x->n; j++)
x->key[j] = x->key[j + 1];
for (j = i + 1; j <= x->n; j++)
x->child[j] = x->child[j + 1];
x->n--;
if (x->n == 0 && T->root == x)
T->root = y;
}
}
}
B_Tree_Delete(T,y, k);
}
}
/*列印B樹*/
void B_Tree_Print(BTnode* x)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= x->n; i++)
{
if (x->leaf == false)
B_Tree_Print(x->child[i]);
cout << x->key[i] << " ";
}
if (x->leaf == false)
B_Tree_Print(x->child[x->n+1]);
}
void B_Tree_PrintDetail(BTnode *x)
{
cout << "根結點:";
for (int i = 1; i <= x->n; i++)
cout << x->key[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "根結點的孩子:" << endl;
for (int j = 1; j <= x->n + 1; j++)
{
BTnode *child = x->child[j];
for (int i = 1; i <= child->n; i++)
cout << child->key[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= x->n + 1; i++)
{
cout << "第 " << i << "個孩子" << endl;
BTnode *ccc = x->child[i];
int m = ccc->n + 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
BTnode *c1 = ccc->child[j];
for (int jj = 1; jj <= c1->n; jj++)
cout << c1->key[jj] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
}
/*測試函式*/
void TestBTree()
{
string ch= "KSQFCLHTVWMRNPABXYDZE";
BTree *T = new BTree();
B_Tree_Create(T, ch);
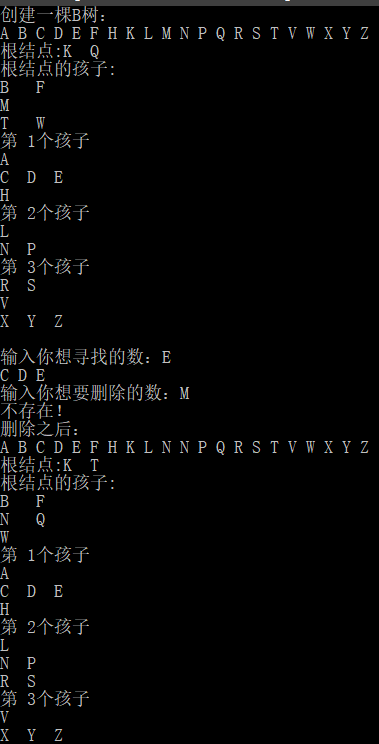
cout << "建立一棵B樹:" << endl;
B_Tree_Print(T->root);
cout << endl;
B_Tree_PrintDetail(T->root);
cout << endl;
cout << "輸入你想尋找的數:";
char key;
int i = 0;
cin >> key;
BTnode* value = B_Tree_Search(T->root, key, i);
if (value == NULL)
cout << "不存在!" << endl;
else
{
for (int j = 1; j <= value->n; j++)
cout << value->key[j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "輸入你想要刪除的數:";
cin >> key;
B_Tree_Delete(T, T->root, key);
cout << "刪除之後:" << endl;
B_Tree_Print(T->root);
cout << endl;
B_Tree_PrintDetail(T->root);
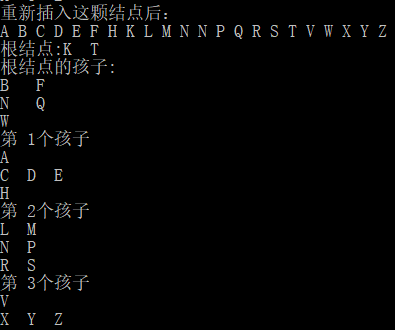
cout << "重新插入這顆結點後:" << endl;
B_Tree_Insert(T, key);
B_Tree_Print(T->root);
cout << endl;
B_Tree_PrintDetail(T->root);
}
主函式
#include "B樹.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
TestBTree();
getchar();
getchar();
return 0;
}
執行結果
參考文章與部落格:
慵懶de瘋子的部落格:淺析B-樹分裂
https://blog.csdn.net/apt1203jn/article/details/79587593
iffTimes的部落格:演算法導論 第十八章;B樹
https://blog.csdn.net/u010183397/article/details/46941045
windmissing的部落格:演算法導論 第18章 B樹
https://blog.csdn.net/mishifangxiangdefeng/article/details/7798672
