基於mapreduce實現圖的三角形計數
源代碼放在我的github上,想細致了解的可以訪問:TriangleCount on github
一、實驗要求
1.1 實驗背景
????????圖的三角形計數問題是一個基本的圖計算問題,是很多復雜網絡分析(比如社交網絡分析)的基礎。目前圖的三角形計數問題已經成為了 Spark 系統中 GraphX 圖計算庫所提供的一個算法級 API。本次實驗任務就是要在 Hadoop 系統上實現圖的三角形計數任務。
1.2 實驗任務
????????一個社交網絡可以看做是一張圖(離散數學中的圖)。社交網絡中的人對應於圖的頂點;社交網絡中的人際關系對應於圖中的邊。在本次實驗任務中,我們只考慮一種關系——用戶之間的關註關系。假設“王五”在 Twitter/微博中關註了“李四”,則在社交網絡圖中,有一條對應的從“王五”指向“李四”的有向邊。圖 1 中展示了一個簡單的社交網絡圖,人之間的關註關系通過圖中的有向邊標識了出來。本次的實驗任務就是在給定的社交網絡圖中,統計圖中所有三角形的數量。在統計前,需要先進行有向邊到無向邊的轉換,依據如下邏輯轉換:
????????“A→B”表示從頂點 A 到頂點 B 有一條有向邊。A-B 表示頂點 A 和頂點 B 之間有一條無向邊。一個示例見圖 1,圖 1 右側的圖就是左側的圖去除邊方向後對應的無向圖。
????????請在無向圖上統計三角形的個數。在圖 1 的例子中,一共有 3 個三角形。
????????本次實驗將提供一個 Twitter 局部關系圖作為輸入數據(給出的圖是有向圖),請統計該圖對應的無向圖中的三角形個數。
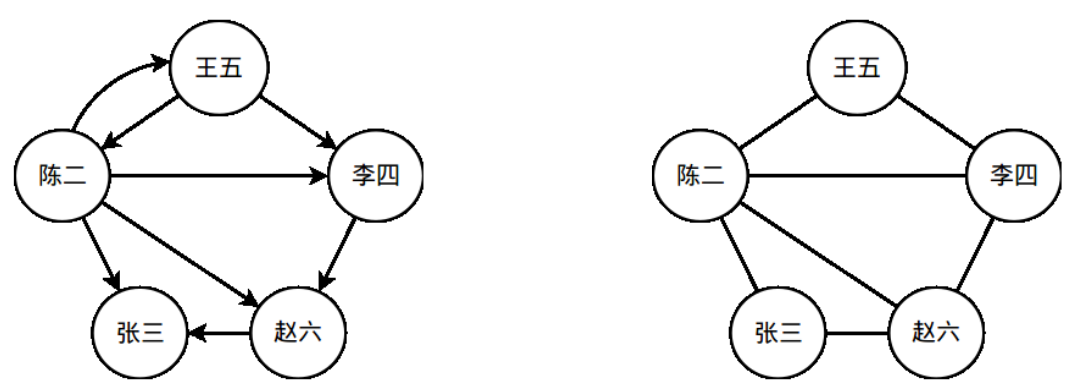
圖 1 一個簡單的社交網絡示例。左側的是一個社交網絡圖,右側的圖是將左側圖中的有向邊轉換為無向邊後的無向圖。
1.3 輸入說明
????????輸入數據僅一個文件。該文件由若幹行組成,每一行由兩個以空格分隔的整數組成:
A,B 分別是兩個頂點的 ID。這一行記錄表示圖中具有一條由 A 到 B 的有向邊。整個圖的結構由該文件唯一確定。
下面的框中是文件部分內容的示例:
87982906 17975898
17809581 35664799
524620711 270231980
247583674 230498574
348281617 255810948
159294262 230766095
14927205 53806721.4 擴展
擴展一:挑戰更大的數據集!使用 Google+的社交關系網數據集作為輸入數據集。
擴展二:考慮將邏輯轉換由or改為and的三角形個數是多少,改變後的邏輯轉換如下:
二、實驗設計與實現
2.1 算法設計
- step1:統計圖中每一個點的度,不關心是入度還是出度,然後對統計到的所有點的度進行排序
- step2:將圖中每一條單向邊轉換成雙向邊,對於圖中a->b and b->a的兩條邊,分別轉換後需要去重,在轉換後的圖中篩選出小度指向大度的邊來建立鄰接表,然後對每個點的鄰接點按從小到大進行排序
- step3:對原圖中的邊進行轉換,確保每條邊是由數值小的點指向數值大的點並去重,然後遍歷每一條邊:求邊的兩個端點對應的鄰接點集的交集大小即為包含這條邊的三角形個數。對每條邊對應的三角形個數進行累加即可得到全圖包含的三角形個數。
2.2 程序設計
- 根據算法步驟將程序設計成4個job來實現:
- job:OutDegreeStat用於對每個點的度進行統計,在類OutDegreeStat中實現
- job:SortedOutDegree用於對所有點的度進行排序,在類OutDegreeStat中實現,在job1之後運行
- job:EdgeConvert用於建立存儲小度指向大度的邊的鄰接表,在類EdgeConvert中實現
- job:GraphTriangleCount用於遍歷每條邊求端點對應鄰接點集的交集來對三角形進行計數,在類GraphTriangleCount中實現
2.3 程序實現
job:OutDegreeStat的實現:
Map階段:(vertex1: Text, vertex2: Text) -> (vertex1: Text, 1: IntWritable) and (vertex2: Text, 1: IntWritable),實現代碼如下:
public static class OutDegreeStatMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable> { private final IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); @Override public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString(); StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line); Text vertex1 = new Text(itr.nextToken()); Text vertex2 = new Text(itr.nextToken()); if (!vertex1.equals(vertex2)) { context.write(vertex1, one); context.write(vertex2, one); } } }Reduce階段:(vertex: Text, degree: Iterable<IntWritable>) -> (vertex: Text, degreeSum: IntWritable),實現代碼如下:
public static class OutDegreeStatReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { @Override public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int sum = 0; for (IntWritable val: values) { sum += val.get(); } context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum)); } }Combiner階段:Combiner邏輯與Reduce邏輯一致,只是為了減少數據量從而減少通信開銷
- job:SortedOutDegree的實現:
- Map階段:由於mapreduce的reduce階段會按key進行排序,為了按度進行排序,只需用hadoop自帶的InverseMapper類對鍵值對做逆映射(vertex: Text, degree: IntWritable) -> (degree: IntWritable, vertex: Text)即可。
- Reduce階段:無需設置Reducer類,hadoop的Reduce階段自動會對degree進行排序
job:EdgeConvert的實現:
Map階段:(vertex1: Text, vertex2: Text) -> (vertex1: Text, vertex2: Text) and (vertex2: Text, vertex1: Text),實現代碼如下:
public static class EdgeConvertMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> { @Override public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); Text vertex1 = new Text(itr.nextToken()); Text vertex2 = new Text(itr.nextToken()); if (!vertex1.equals(vertex2)) { context.write(vertex1, vertex2); context.write(vertex2, vertex1); } } }Reduce階段:在setup函數中讀取存儲節點度的文件,在reduce函數中(vertex1: Text, vertex2List: iterable<Text>) -> (vertex1 with minimal degree: Text, vertex2 with maximal degree: Text),==在對鄰接表節點進行排序時,要重寫一個String Comparator,讓String按它所表示的數值大小進行比較,==實現代碼如下:
public static class EdgeConvertReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> { private Map<String, Integer> degree; private Map<String, Boolean> edgeExisted; private URI[] cacheFiles; @Override public void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { degree = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); //讀取存儲節點度的文件 Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration(); cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles(); for (int i = 0; i < cacheFiles.length; i++) { SequenceFile.Reader reader = new SequenceFile.Reader(conf, SequenceFile.Reader.file(new Path(cacheFiles[i]))); IntWritable key = new IntWritable(); Text value = new Text(); int cnt = 0; while (reader.next(key, value)) { degree.put(value.toString(), cnt); cnt++; } reader.close(); } } @Override public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{ Text vertex = new Text(); List<String> outvertex = new ArrayList<String>(); edgeExisted = new HashMap<String, Boolean>(); //記錄已處理邊以避免重復統計 for (Text val: values) { if (!edgeExisted.containsKey(val.toString())) { edgeExisted.put(val.toString(), true); //比較邊兩個端點的度大小 if (degree.get(val.toString()) > degree.get(key.toString())) { outvertex.add(val.toString()); } } } //對鄰接節點從小到大進行排序,方便後續求交集 Collections.sort(outvertex, new ComparatorString()); for (String vt: outvertex) { vertex.set(vt); context.write(key, vertex); } } } //繼承String比較器按它所表示的數值大小進行比較 public static class ComparatorString implements Comparator<String> { public int compare(String a, String b) { if (a.length() > b.length()) { return 1; } else if (a.length() < b.length()){ return -1; } else { return a.compareTo(b); } } }
job:GraphTriangleCount的實現:
Map階段:以job:EdgeConvert的輸出文件作為讀入,該文件不包含重復邊因此無需判斷轉換,直接按原樣映射(vertex1: Text, vertex2: Text) -> (vertex1: Text, vertex2: Text)即可,實現代碼如下:
public static class GraphTriangleCountMapper extends Mapper<Text, Text, Text, Text> { @Override public void map(Text key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{ context.write(key, value); } }Reduce階段:在setup函數中讀取存儲小度指向大度的鄰接表文件,在reduce函數中(vertex1: Text, vertex2List: Iterable<Text>) -> ("TriangleNum": Text, triangleNum: LongWritable),在cleanup函數中寫當前這個reducer的三角形計數結果,實現代碼如下:
public static class GraphTriangleCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, LongWritable> { private final static String edgePath = TriangleCountDriver.HDFS_PATH + TriangleCountDriver.EdgeConvertPath; //鄰接表文件路徑 private Map<String, Integer> vexIndex; //存儲節點的鄰接表索引 private ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> vec = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>(); //存儲全局鄰接表 private long triangleNum = 0; @Override public void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int cnt = 0; String lastVertex = ""; String sv, tv; ArrayList<String> outVertices = new ArrayList<String>(); vexIndex = new TreeMap<String, Integer>(); //獲取文件系統的接口 Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration(); FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); //讀取小度指向大度的邊鄰接表 for (FileStatus fst: fs.listStatus(new Path(edgePath))) { if (!fst.getPath().getName().startsWith("_")) { SequenceFile.Reader reader = new SequenceFile.Reader(conf, SequenceFile.Reader.file(fst.getPath())); Text key = new Text(); Text value = new Text(); while (reader.next(key, value)) { sv = key.toString(); tv = value.toString(); if (!sv.equals(lastVertex)) { if (cnt != 0) vec.add(outVertices); vexIndex.put(sv, cnt); cnt++; outVertices = new ArrayList<String>(); outVertices.add(tv); } else { outVertices.add(tv); } lastVertex = sv; } reader.close(); } } vec.add(outVertices); } @Override public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{ for (Text val: values) if (vexIndex.containsKey(val.toString())) //調用求交集函數獲取包含邊(key,val)的三角形個數 triangleNum += intersect(vec.get(vexIndex.get(key.toString())), vec.get(vexIndex.get(val.toString()))); } @Override public void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{ //將計數結果寫入文件 context.write(new Text("TriangleNum"), new LongWritable(triangleNum)); } //求有序集合的交集 private long intersect(ArrayList<String> avex, ArrayList<String> bvex) { long num = 0; int i = 0, j = 0; int cv; while (i != avex.size() && j != bvex.size()) { if (avex.get(i).length() > bvex.get(j).length()) { cv = 1; } else if (avex.get(i).length() < bvex.get(j).length()) { cv = -1; } else { cv = avex.get(i).compareTo(bvex.get(j)); } if (cv == 0) { i++; j++; num++; } else if (cv > 0) { j++; } else { i++; } } return num; } }
2.4 擴展2的設計與實現
對於a->b and b->a then a-b的條件,只需改變job:EdgeConvert的實現即可,新建一個job:UndirectionalEdgeConvert:
Map階段:以原數據文件作為輸入進行映射轉換:(vertex1: Text, vertex2: Text) -> ((vertex1, vertex2): Text, flag: Text) and ((vertex2, vertex1): Text, flag:Text),按vertex1進行分區,其中flag作為節點序標記,用於幫助在Reducer中對雙向邊進行判斷,如果輸入的vertex1 > vertex2則flag置1,如果vertex1 < vertex2則flag置0,實現代碼如下:
public static class UndirectionalEdgeConvertMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> { @Override public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); String vertex1 = itr.nextToken(); String vertex2 = itr.nextToken(); String flag = "0"; //節點序標記,幫助Reducer判斷雙向邊 if (!vertex1.equals(vertex2)) { if (vertex1.compareTo(vertex2) > 0) flag = "1"; context.write(new Text(vertex1 + '\t' + vertex2), new Text(flag)); context.write(new Text(vertex2 + '\t' + vertex1), new Text(flag)); } } }Reduce階段:((vertex1, vertex2): Text, flagList: Iterable<Text>) -> (vertex1 with minimal degree: Text, vertex2 with maximal degree: Text),如果flagList既包含0又包含1,則(vertex1, verex2)屬於雙向邊,然後判斷如果vertex2的度大於vertex1,則將vertex2加入到vertex1的鄰接表中,reduce函數部分的實現代碼如下:
@Override public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{ String[] term = key.toString().split("\t"); //如果鄰接表出點變了則寫出lastkey為出點的鄰接表 if (!lastKey.equals(term[0])) { if (outvertex.size() != 0) { Text vertex = new Text(); Text lastKeyText = new Text(lastKey); Collections.sort(outvertex, new EdgeConvert.ComparatorString()); for (String vt: outvertex) { vertex.set(vt); context.write(lastKeyText, vertex); } outvertex = new ArrayList<String>(); } } //判斷(term[0], term[1])是否是雙向邊 boolean flag0 = false, flag1 = false; for (Text val: values) { if (val.toString().equals("0")) flag0 = true; else flag1 = true; } if (flag0 && flag1) { if (degree.get(term[1]) > degree.get(term[0])) { outvertex.add(term[1]); } } lastKey = term[0]; }
三、性能分析與優化
3.1 性能分析
- 該算法的性能瓶頸在遍歷每一條邊然後邊兩個端節點對應鄰接表的交集,然後對每個頂點出發的鄰接表進行排序也比較耗時,算法整體的時間復雜度是O(E^1.5^),E為邊的數目
- 目前這個1.0版本的實現魯棒性比較好,節點編號用Text存儲,所以無論節點編號多大都可以存儲以及比較,輸入的圖可以允許重復邊的出現,不會影響結果的正確性。但由於mapreduce涉及大量的排序過程,用Text存儲節點也就意味著使用字符串排序,字符串之間的比較當然比整型比較開銷大,從而會影響程序的整體性能。除此之外,hadoop需要對數據進行序列化之後才能在網絡上傳輸,數據以文本文件輸入導致大量的數據序列化轉換也會降低程序性能。
3.2 性能優化
2.0版本,在1.0的版本上進行了數據儲存和表示方面的優化,相同實驗環境(6個Reducer,每個Reducer2G物理內存,Reducer中的java heapsize -Xmx2048m)跑Goolge+數據能快50s左右,具體優化細節如下:
- 將離散化稀疏的節點轉換成順序化的,這樣就可以用IntWritabel表示節點(前提是節點數未超過INT_MAX)而不用Text來表示節點編號,這樣就可以避免字符串排序,減少map和reduce階段的排序開銷
- 將原始Text輸入文件轉換成Sequence,因為hadoop傳輸在網絡上的數據是序列化的,這樣可以避免數據的序列化轉換開銷。但是由於數據是串行轉換的,影響整體性能,但是可以在第一次運行過後存起來,以後運行直接加載sequence的數據文件即可。這一步是和第一步順序化節點一起完成的,轉換後的sequence文件存儲的是順序化的節點表示的邊。
- 在a->b and b->a then a-b的條件下,在獲取小度指向大度的邊集任務中,mapper需要將一條邊的點對合並為key以在reducer中判斷是否是雙向邊,看似只能用Text來存儲了,實則這裏有一個trick,在對節點順序化之後的節點數通常不會超過INT_MAX,因此可以使用考慮將兩個int型表示的節點轉換成long,key存儲在高32位,value存儲在低32位,通過簡單的位操作即可實現,這樣mapper輸出的key就是long而非Text,從而避免了字符串的比較排序,由於mapreduce涉及大量排序過程,因此在涉及程序的時候盡量用一些trick避免用Text表示key.
三、程序運行結果及時耗
實驗環境:CPU型號Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2630 v2 @ 2.60GHz,雙物理CPU,單CPU6核12線程,所以一共24個虛擬核,程序設置6個reducer,每個reducer配置2GB物理內存,reducer中的java heapsize配置-Xmx2048m
=="or"表示if a->b or b->a then a-b的情況,"and"表示if a->b and b->a then a-b的情況==
- 1.0版本的測試結果:
| 數據集 | 三角形個數 | Driver程序在集群上的運行時間(秒) |
|---|---|---|
| Twitter(or) | 13082506 | 127s |
| Google+(or) | 1073677742 | 278s |
| Twitter(and) | 1818304 | 125s |
| Goolge+(and) | 27018510 | 156s |
- 2.0版本的測試結果(不包含輸入文件轉換的時間):
| 數據集 | 三角形個數 | Driver程序在集群上的運行時間(秒) |
|---|---|---|
| Twitter(or) | 13082506 | 115s |
| Google+(or) | 1073677742 | 230s |
| Twitter(and) | 1818304 | 118s |
| Goolge+(and) | 27018510 | 181s |
評估:2.0版本相對1.0版本在節點數據類型上作了優化,當數據量很大的時候,or情況的性能有顯著的提升,Google+數據比1.0版本快了差不多50s左右,但是and情況下2.0版本跑Google+數據性能卻下降了,個人猜測可能是job:UnidirectionalEdgeConvert中的Mapper,Reducer,Partitioner,比較函數中涉及大量的位操作或者int與long之間的類型轉換,這個開銷比1.0版本的對字符串排序開銷更大。目前沒有很好的想法來避免頻繁的位操作與類型轉換,有idea的朋友可以給我留言~
基於mapreduce實現圖的三角形計數
