tarjan求點雙+樹上倍增/圓方樹+並查集--business
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-25
對我沒打錯名字,就是
題目:

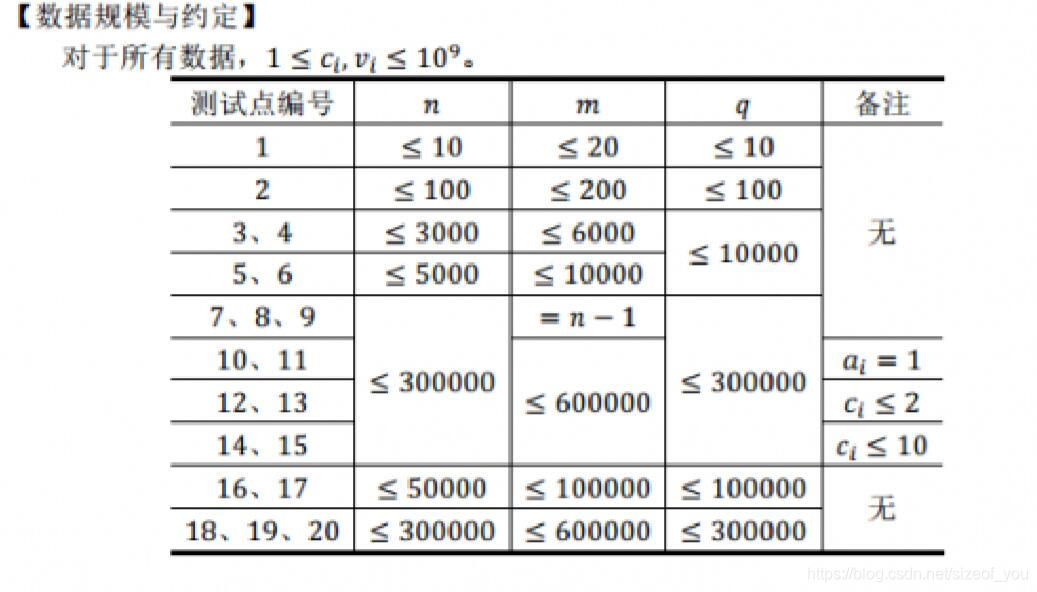
solution:
這道題有很多種寫法,先說我的:
先
求點雙,一個點雙裡的點都可以到達那個最小的點,然後每個割點向他在的點雙連邊建出一棵樹,然後用
表一類的樹上倍增方法求解,細節很多,注意有些陣列空間要開大一倍,注意特判
在同一個點的情況
還有一種高階寫法:圓方樹
當然我是沒有寫的了,也是找到點雙然後建圓方樹,可以在圓方樹上倍增,也可以使用並查集把這個樹建成樹高
級別的,然後直接跳就行,具體怎麼建就是,將點權看成邊權,從大到小排序,按秩合併,這樣就能保證正確性了
放上我的程式碼
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#define N 300005
#define M 600005
#define LL long long
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
inline int rd(){
int x=0,f=1;char c=' ';
while(c<'0' || c>'9') f=c=='-'?-1:1,c=getchar();
while(c<='9' && c>='0') x=x*10+c-'0',c=getchar();
return x*f;
}
inline int min(int x,int y){return x<y?x:y;}
int n,m,q,cnt,head[N],dfn[N],low[N],stk[N],num,top,tot,root;
int ecnt,ehead[N<<1],val[N<<1],a[N],totn;
int id[N],dep[N<<1],f[N<<1][20],g[N<<1][20];
bool cut[N];
vector<int> dcc[N],bel[N];
struct EDGE{
int to,nxt;
}edge[M<<1],e[M<<1];
inline void add(int x,int y){
edge[++cnt].to=y; edge[cnt].nxt=head[x]; head[x]=cnt;
}
inline void add2(int x,int y){
e[++ecnt].to=y; e[ecnt].nxt=ehead[x]; ehead[x]=ecnt;
}
inline void tarjan(int u){
dfn[u]=low[u]=++num; stk[++top]=u;
if(u==root && head[u]==0){
dcc[++tot].push_back(u);
return;
}
int flg=0;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=edge[i].nxt){
int v=edge[i].to;
if(!dfn[v]){
tarjan(v);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
if(low[v]>=dfn[u]){
flg++;
if(u!=root || flg>1) cut[u]=true;
++tot; int z; bel[u].push_back(tot);
do{
z=stk[top--]; id[z]=tot;
val[tot]=min(val[tot],a[z]);
dcc[tot].push_back(z);
bel[z].push_back(tot);
}while(z!=v);
dcc[tot].push_back(u); id[u]=tot;//id[u]
val[tot]=min(val[tot],a[u]);
}
}
else low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
}
inline void rebuild(){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(cut[i]) {
val[id[i]=((++totn)+tot)]=a[i];
for(int j=0;j<bel[i].size();j++)
add2(bel[i][j],id[i]),add2(id[i],bel[i][j]);
}
}
inline void dfs(int u,int fa){
for(int i=ehead[u];i;i=e[i].nxt){
int v=e[i].to;
if(v==fa)continue;
dep[v]=dep[u]+1; f[v][0]=u; g[v][0]=val[v];
for(int j=1;j<=19;j++)
f[v][j]=f[f[v][j-1]][j-1],
g[v][j]=min(g[v][j-1],g[f[v][j-1]][j-1]);
dfs(v,u);
} return;
}
inline int get_ans(int x,int y){
if(x==y) return val[x];
if(dep[x]<dep[y]) swap(x,y);
int ans=inf;
for(int i=19;i>=0;i--)
if(dep[f[x][i]]>=dep[y])
ans=min(ans,g[x][i]),x=f[x][i];
if(x==y) return min(ans,val[x]);
for(int i=19;i>=0;i--)
if(f[x][i]!=f[y][i])
ans=min(ans,min(g[x][i],g[y][i])),
x=f[x][i],y=f[y][i];
ans=min(min(ans,val[f[x][0]]),min(val[x],val[y]));
return ans;
}
int main(){
freopen("business.in","r",stdin);
freopen("business.out","w",stdout);
n=rd(); m=rd(); q=rd();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) a[i]=rd();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int x=rd(),y=rd();
add(x,y); add(y,x);
}
memset(val,0x3f,sizeof val); memset(g,0x3f,sizeof g);
root=1; tarjan(root);
rebuild(); totn+=tot; dep[1]=1;
for(int i=0;i<=19;i++) g[1][i]=val[1];
dfs(1,0);
while(q--){
int s=rd(),t=rd(),x=rd();//注意特判
if(s==t) {printf("%lld\n",1LL*a[s]*x);continue;}
int res=get_ans(id[s],id[t]);
printf("%lld\n",1LL*res*x);
}
return 0;
}
/*
7 9 3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 2
2 5
1 5
2 3
3 4
2 4
5 6
6 7
5 7
2 3 1
4 6 2
6 7 3
*/
/*
10 20 5
3 4 7 6 8 10 7 4 8 1
10 2
3 7
6 2
7 1
10 7
8 4
3 2
3 9
5 2
2 1
1 6
6 5
8 4
7 4
3 4
5 8
1 8
8 10
8 2
1 1
1 7 9
1 4 2
9 2 4
3 8 1
7 9 1
*/
