【9】netty4原始碼分析- read
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-29
轉自 http://xw-z1985.iteye.com/blog/1972779
當selector檢測到OP_READ事件時,觸發read操作:
//NioEventLoop if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) { unsafe.read(); if (!ch.isOpen()) { // Connection already closed - no need to handle write. return; } }
Read方法由NioByteUnsafe實現:
public void read() { assert eventLoop().inEventLoop(); final SelectionKey key = selectionKey(); final ChannelConfig config = config(); if (!config.isAutoRead()) { int interestOps = key.interestOps(); if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) != 0) { // only remove readInterestOp if needed key.interestOps(interestOps & ~readInterestOp); } } final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline(); RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = this.allocHandle; if (allocHandle == null) { this.allocHandle = allocHandle = config.getRecvByteBufAllocator().newHandle(); } final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator(); final int maxMessagesPerRead = config.getMaxMessagesPerRead(); boolean closed = false; Throwable exception = null; ByteBuf byteBuf = null; int messages = 0; try { for (;;) { byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator); int localReadAmount = doReadBytes(byteBuf); if (localReadAmount == 0) { byteBuf.release(); byteBuf = null; break; } if (localReadAmount < 0) { closed = true; byteBuf.release(); byteBuf = null; break; } pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf); allocHandle.record(localReadAmount); byteBuf = null; if (++ messages == maxMessagesPerRead) { break; } } } catch (Throwable t) { exception = t; } finally { if (byteBuf != null) { if (byteBuf.isReadable()) { pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf); } else { byteBuf.release(); } } pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete(); if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof IOException) { closed = true; } pipeline().fireExceptionCaught(exception); } if (closed) { setInputShutdown(); if (isOpen()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.ALLOW_HALF_CLOSURE))) { key.interestOps(key.interestOps() & ~readInterestOp); pipeline.fireUserEventTriggered(ChannelInputShutdownEvent.INSTANCE); } else { close(voidPromise()); } } } } } }
一、首先分析this.allocHandle = allocHandle = config.getRecvByteBufAllocator().newHandle()
config.getRecvByteBufAllocator()返回RecvByteBufAllocator,可以取名為接受快取分配器。該分配器用於為channel分配receive buffers以儲存隨後讀取的位元組。預設返回的分配器型別是自適應快取分配器AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator,它能根據前一次實際讀取的位元組數量,自適應調整當前快取分配的大小,以防止快取分配過多或過少。其結構如下:
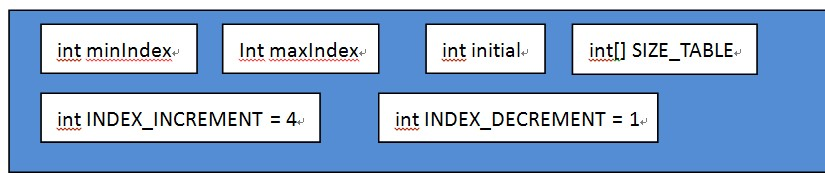
其中:
- SIZE_TABLE:為固定的靜態陣列,按照從小到大的順序預先儲存可以分配的快取大小。最小的為16,然後每次累加16,直到496。然後從512開始,每次向走位移1(即放大兩倍),直到int發生溢位。本機的最大值為1073741824,所以陣列的size為52。
- MinIndex和maxIndex為最小快取(64)和最大快取(65536)在SIZE_TABLE中對應的下標。分別為3和38
- 第一次分配快取時,由於沒有上一次的實際接收到的位元組數做參考,因此需要給出初始值,由Initial指定,預設值為1024
- INDEX_INCREMENT:上次預估快取偏小時,下次Index的遞增值。預設為4
- INDEX_DECREMENT:上次預估快取偏大時,下次Index的遞減值。預設為1
快取的分配以及大小的自適應調整實際上都是由自適應快取分配器裡面的一個內部類HandleImpl代勞的,由快取分配器的newHandle()方法返回。以下是HandleImpl的實現:
//AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator
private static final class HandleImpl implements Handle {
private final int minIndex;
private final int maxIndex;
private int index;
private int nextReceiveBufferSize;
private boolean decreaseNow;
HandleImpl(int minIndex, int maxIndex, int initial) {
this.minIndex = minIndex;
this.maxIndex = maxIndex;
index = getSizeTableIndex(initial);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
}
@Override
public ByteBuf allocate(ByteBufAllocator alloc) {
return alloc.ioBuffer(nextReceiveBufferSize);
}
@Override
public int guess() {
return nextReceiveBufferSize;
}
@Override
public void record(int actualReadBytes) {
if (actualReadBytes <= SIZE_TABLE[Math.max(0, index - INDEX_DECREMENT - 1)]) {
if (decreaseNow) {
index = Math.max(index - INDEX_DECREMENT, minIndex);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
decreaseNow = false;
} else {
decreaseNow = true;
}
} else if (actualReadBytes >= nextReceiveBufferSize) {
index = Math.min(index + INDEX_INCREMENT, maxIndex);
nextReceiveBufferSize = SIZE_TABLE[index];
decreaseNow = false;
}
}
}
private static int getSizeTableIndex(final int size) {
for (int low = 0, high = SIZE_TABLE.length - 1;;) {
if (high < low) {
return low;
}
if (high == low) {
return high;
}
int mid = low + high >>> 1;
int a = SIZE_TABLE[mid];
int b = SIZE_TABLE[mid + 1];
if (size > b) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (size < a) {
high = mid - 1;
} else if (size == a) {
return mid;
} else {
return mid + 1;
}
}
}
- nextReceiveBufferSize記錄下次分配快取時應該分配的大小,即index下標在陣列SIZE_TABLE中的值。
- ByteBuf allocate(ByteBufAllocator alloc)方法則根據上次預估的位元組大小nextReceiveBufferSize分配快取。
- Index記錄nextReceiveBufferSize在陣列SIZE_TABLE中的索引值:
a)如果是第一次分配,則該值由getSizeTableIndex方法根據initial的值(預設為1024)計算而來。 getSizeTableIndex採用二分查詢演算法計算SIZE_TABLE陣列中值最接近initial的下標。
b)如果非第一次分配,則由record 方法根據上一次實際讀取到的位元組數actualReadBytes自適應的調整nextReceiveBufferSize的大小:
b.1 如果actualReadBytes連續兩次都小於SIZE_TABLE[Math.max(0, index - INDEX_DECREMENT - 1)](為啥在INDEX_DECREMENT的基礎上再減1?),即連續兩次預估的快取大小都偏大導致浪費了,則更新index為Math.max(index - INDEX_DECREMENT, minIndex)
b.2 如果actualReadBytes大於nextReceiveBufferSize,即上次預估的快取大小偏小,則更新index為Math.min(index + INDEX_INCREMENT, maxIndex)
b.3 否則,保持index不變。
二、接下來分析for迴圈中的邏輯首 - 先呼叫自適應接受快取分配器中的handleImpl的allocate方法,分配大小為nextReceiveBufferSize的快取
- 然後通過read系統呼叫,將資料從channel中讀取到上一步分配的接受快取中。
a)如果返回0,則表示沒有讀取到資料,則退出迴圈
b)如果返回-1,表示對端已經關閉連線,則退出迴圈
c)否則,表示讀到了資料,則觸發ChannelRead事件(inbound處理器可以通過實現channelRead方法對本次讀取到的訊息進行處理)。接著呼叫handleImpl的record方法,根據本次讀取的位元組數,自適應調整下次待分配的快取大小。然後退出迴圈 - 最後觸發ChannelReadComplete事件(inbound處理器可以通過實現channelReadComplete方法對該事件進行響應)。
- 關於close、shutdown以及半關閉等,留待以後搞清楚後再進行分析。
總結可以借鑑的點:快取分配大小的自適應調整策略
