回溯法總結+四個小例題(裝載問題,01揹包,n後,最大團,m著色)
目錄
回溯法的基本策略
- 回溯法的基本策略
- 回溯法的解空間
- 回溯法基本思想
- 回溯法解題步驟
- 遞歸回溯和迭代回溯
- 子集樹和排列樹
- 裝載問題
- 01揹包問題回溯法求解
- n後問題
- 圖的最大團問題
- 圖的m著色問題
回溯法的基本策略
策略:回溯法在問題的解空間樹中,按深度優先搜尋,從根節點出發搜尋解空間。
演算法搜尋至某一結點時,先判斷該結點是否包含問題的解,如果肯定不包含,則跳過,對以該節點為根的子樹的搜尋,逐層向其祖先回溯。否則,進入該子樹,繼續按照深度優先搜尋。
回溯法求解問題的所有解時,要回溯到根,且根節點的所有子樹都已經搜尋時遍歷才結束。
回溯法求解問題的一個解時,只要搜尋到問題的一個解就可以結束。這種以深度優先方式系統搜尋問題解的演算法稱為回溯法,適合解組合數較大的問題
回溯法的解空間
用回溯法解決問題時,應明確問題的解空間。問題的解空間至少應包含問題的一個最優解。例如對於有3種可選物品的01揹包問題,解空間包含所有的01取值可能如下:
(0,0,0),(0,0,1),(0,1,0),(0,1,1),(1,0,0),(1,0,1),(1,1,0),(1,1,1),總共8種可以選擇的解。相應的解空間樹如下
回溯法基本思想
確定瞭解空間的組織結構之後,回溯從根節點以深度優先搜尋開始,根節點首先成為一個活結點,同時也成為當前的擴充套件節點。在當前擴充套件節點處,搜尋向縱深方向移至一個新節點。這個新節點就成為一個新的活結點,併成為當前擴充套件節點。如果當前擴充套件節點不能再向縱深方向移動,則當前的擴充套件節點就成為死結點。此時,往回回溯至最近的一個活節點處,並使這個活結點成為當前的擴充套件節點。
回溯法以這種方式遞迴地在解空間中搜索,直至找到所有要求的解或解空間已無活結點為止。
剪枝:在搜尋至樹中任一結點時,先判斷該結點對應的部分解是否滿足約束條件(約束函式),或者是否超出目標函式的界(限界函式);也即判斷該結點是否包含問題的解,如果肯定不包含,則跳過對以該結點為根的子樹的搜尋,即剪枝;否則,進入以該結點為根的子樹,繼續按照深度優先的策略搜尋。
回溯法解題步驟
回溯法步驟:針對所給問題,定義問題的解空間;
確定易於搜尋的解空間結構;
以深度優先方式搜尋解空間,並在搜尋過程中利用剪枝函式(約束函式和限界函式)剪去無效的搜尋。
遞歸回溯和迭代回溯
回溯法具體使用的又可以使用遞歸回溯和迭代回溯:
遞歸回溯:
void BackTrack(int t){ if(t > n)Output(x); else { for(int i = f(n,t); i <= g(n,t); i++){ x[i] = h(i); if(Constraint(t) && Bound(t)) BackTrack(t+1); } } }
注意幾點 :
上面的程式碼中,形式引數t表示遞迴深度,即當前擴充套件結點在解空間樹中的深度。n控制遞迴深度,當t > n時,演算法以及搜尋到葉子結點,此時,由Output(x)記錄或輸出得到的可行解x。for迴圈中的f(n,t)和g(n,t)表示的是當前結點處未搜尋過的子樹的起始編號和終止編號。h(i)表示在當前結點處x[t] (t是層數)的第i個可選值。Constrain和Bound函式是約束函式和限界函式。
執行完演算法的for迴圈之後,已經搜尋遍當前擴充套件結點的所有未搜尋過的子樹。BackTrack(t)已經執行完畢,返回t-1層繼續執行,對還沒有測試過的x[t-1]的值繼續搜尋。
當t = 1時,若已經測試完x[1]的所有值,外層的呼叫就全部結束。
一開始呼叫BackTrack(1)即可完成這次深度優先遍歷。
迭代回溯:
void BackTrack(int t){
if(t > n)Output(x);
else {
for(int i = f(n,t); i <= g(n,t); i++){
x[i] = h(i);
if(Constraint(t) && Bound(t)) BackTrack(t+1);
}
}
}
注意一般回溯演算法只儲存從根節點到當前擴充套件結點的路徑,如果解空間樹中從根節點到葉子結點的最長路徑的長度未h(n),那麼計算空間就是O(h(n)),如果需要顯示的儲存整個解,那麼需要O(2^h(n))或者O(h(n!))記憶體空間。
子集樹和排列樹
兩種解空間樹:
子集樹:當所給的問題是從n個元素的集合S中找出滿足某種性質的子集時,相應的解空間是子集樹。例如01揹包問題的解空間樹就是子集樹。這類樹通常有2^n個葉子結點,結點總數是2^(n+1) - 1個。時間複雜度O(2^n)。
排列樹:當所給的問題是確定n個元素滿足某種性質的排列的時候,相應的解空間樹是排列樹。排列樹有n!個葉子結點,時間複雜度O(n!)。比較經典的有旅行售貨員問題:售貨員要去n個城市,已知各個城市之間的旅費,他要選定一條從駐地出發,經過每一個城市,最後回到駐地的路線使得總的消費最小。把這個問題組織成一顆排列樹如下(1,2,3,4個城市):
子集樹和排列樹的程式碼如下:
//子集樹的一般演算法
void BackTrack(int t){
if(t > n)Output(x);
else{
for(int i = 0; i <= 1; i++){ //只有左右子樹兩種可能
x[t] = i;
if(Constraint(t) && Bound(t)) BackTrack(t+1);
}
}
}
//排列樹的一般演算法
void BackTrack(int t){
if(t > n)Output(x);
else {
for(int i = t; i <= n; i++){
Swap(x[t],x[i]);
if(Constraint(t) && Bound(t)) BackTrack(t+1);
Swap(x[t],x[i]);
}
}
}
裝載問題
問題描述:就是將n個集裝箱裝入2艘載重量為C1,C2的輪船,其中集裝箱i的重量為w[i],問題要求如果可以裝上去,求一個最優裝載方案。
可以證明,先將第一個集裝箱裝滿,剩餘的裝入第二個可以得到一個最優裝載方案。然後使用回溯法設計裝載問題。
普通的回溯法中如果不剪枝右子樹的話,右子樹可以直接進入,這樣到達葉子結點的時候,要更新一下最優解,使用一個上界函式,用r表示剩餘集裝箱的重量,定義上界函式cw(當前的載重量)+r,如果cw+r <= bestw的話,就不用進入右子樹。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 回溯法解決裝載問題
* @author 鄭鑫
*/
public class MaxLoading {
private int n,C;
private int cw,bestw,r;//當前載重量
private int[] w,x,bestx;
public MaxLoading(int n, int c, int cw, int bestw, int r, int[] w, int[] x, int[] bestx) {
super();
this.n = n;
C = c;
this.cw = cw;
this.bestw = bestw;
this.r = r;
this.w = w;
this.x = x;
this.bestx = bestx;
}
public void BackTrack(int i){
if(i >= n){
if(cw > bestw){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)bestx[j] = x[j];
bestw = cw;
}
return;
}
r -= w[i]; //剩下的重量 r 一開始賦值為所有w[i]的和
if(cw + w[i] <= C){
x[i] = 1; //裝入
cw += w[i];
BackTrack(i+1);
cw -= w[i];
x[i] = 0;
}
if(cw + r > bestw) { //只有大於才進入右子樹
x[i] = 0;
BackTrack(i+1);
}
r += w[i]; //回溯
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = cin.nextInt(),r = 0;
int C1 = cin.nextInt(); //第一艘輪船
int C2 = cin.nextInt(); //第二艘輪船
int[] w = new int [n+1];
int[] x = new int [n+1];
int[] bestx = new int [n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
w[i] = cin.nextInt();
r += w[i];
}
MaxLoading ml = new MaxLoading(n, C1, 0, 0, r, w, x, bestx);
ml.BackTrack(1);
int w1 = ml.bestw;
int w2 = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)w2 += w[i]*(1-bestx[i]);
if(w2 > C2){
System.out.println("---無法將全部物品裝入兩個集裝箱!---");
}else {
System.out.println("第一艘船裝入的重量是 : " + w1);
System.out.println("第二艘船裝入的重量是 : " + w2);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(bestx[i] == 1)System.out.println("物體" + i + "裝入第一艘輪船!");
else System.out.println("物體" + i + "裝入第二艘輪船!");
}
}
}
}
兩個測試樣例
01揹包問題回溯法求解
前面已經說過,01揹包的解空間可以使用子集樹表示。搜尋解空間樹時,只要其左兒子結點是一個可行的結點(揹包已經裝的重量+w[i] <= C),搜尋就進入左子樹。
當右子樹中有可能包含最優解時才進入右子樹進行搜尋,否則將右子樹減去。試想,如果當前所剩的價值(Vleft)加上當前已經獲得價值(nowV)小於等於記錄好的最大價值(bestV),右子樹就沒有必要搜尋。
剪枝函式更好的設計方法是:將剩餘物品按照其單位重量價值降序排列。然後依此裝入物品,直到裝不下,再裝一部分(實際上不可能(因為是01揹包)),由此得到的價值是右子樹中解的上界。
舉個栗子:n = 4,C = 7,v = [9,10,7,4],w = [3,5,2,1];
這四個物品的單位重量價值為[3,2,3.5,4]。按照遞減的順序裝入物品,按照4,3,1物品序號裝入後,揹包容量僅剩1,這是我們再裝0.2的物品2,此時,相應價值為22,解為[1,0.2,1,1],儘管這不是可行解,但是可以知道其價值是最優值的上界。也就是說右子樹按照這樣裝都小於當前的bestV的話就肯定剪枝。看程式碼吧:
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
// *排序的另一種方法
class UnitWSort implements Comparator<UnitW>{ //對單位重量的類按照單位重量d來排序
@Override
public int compare(UnitW o1,UnitW o2) {
return -(o1.getD() > o2.getD() ? 1 :(o1.getD() == o2.getD() ? 0: -1));
}
}
*/
class UnitW implements Comparable<UnitW>{
private double d;
private int id;
public UnitW(int id,double d) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.d = d;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public double getD() {
return d;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(UnitW o) {
return -(this.d > o.d ? 1: (this.d == o.d ? 0: -1));
}
}
class Knapsack {
private int C; //揹包容量
private int n; //物品數目
private int[] w; //物品重量
private int[] v; //物品價值
private int nowW; //當前重量
private int nowV; //當前價值
private int bestV; //當前最優價值
public int getBestV(){ //獲得最優值
return bestV;
}
public Knapsack(int c, int n, int[] w, int[] v, int nowW, int nowV, int bestV) {
super();
C = c;
this.n = n;
this.w = w;
this.v = v;
this.nowW = nowW;
this.nowV = nowV;
this.bestV = bestV;
}
public void Backtrack(int i){
if(i >= n){ //達到葉子結點
bestV = nowV;
return ;
}
if(nowW + w[i] <= C){ //能裝就裝,進入左邊葉子
nowW += w[i];
nowV += v[i];
Backtrack(i+1);
nowW -= w[i];
nowV -= v[i];
}
if(Bound(i+1) > bestV){ //如果往右邊走,揹包裝滿了都沒有現在的最優值,就剪枝這顆子樹
Backtrack(i+1);
}
}
//計算上界的函式
public double Bound(int i){
int Cleft = C - nowW; //剩餘容量
int nowBest = nowV;
while( i < n && w[i] < Cleft ){ //計算整數的
Cleft -= w[i];
nowBest += v[i];
i++;
}
//把揹包裝滿
if(i < n)nowBest += v[i]*Cleft/w[i];
return nowBest;
}
}
public class BackTrack01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int W = 0,V = 0,n,C;
n = cin.nextInt(); C = cin.nextInt();
int[] w = new int[n+1];
int[] v = new int[n+1];
ArrayList<UnitW>unit = new ArrayList<UnitW>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)w[i] = cin.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)v[i] = cin.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
unit.add(new UnitW(i,v[i]*1.0/w[i]));
W += w[i];
V += v[i];
}
if(W <= C){
System.out.println(V);
System.exit(0);
}
Collections.sort(unit); //按照單位重量進行降序排序
//Collections.sort(unit,new UnitWSort()); //按照單位重量進行降序排序
//for(int i = 0; i < unit.size(); i++)System.out.println(unit.get(i).getD());
int[] neww = new int[n+1];
int[] newv = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
neww[i] = w[unit.get(i).getId()];
newv[i] = v[unit.get(i).getId()];
}
Knapsack K = new Knapsack(C,n,neww,newv,0,0,0);
K.Backtrack(0); //從第0層開始呼叫
System.out.println(K.getBestV());
}
}
效果
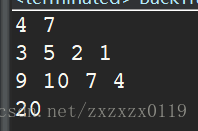
n後問題
問題描述:n*n格的棋盤上放置彼此不受攻擊的n個皇后,要求任何2個皇后不放在同一行或同一列或同一斜線上。
用n元組C[1:n]表示問題的解:C[i]表示的是i行皇后所在的列。
由於不允許兩個皇后在同一列上,所以解向量中的C[i]互不相同。
還有一個要注意的就是2個皇后不能在同意斜線上,所以很容易得到兩點之間的連線的斜率不能為1或-1,即:C[i] ! =C[col] && abs(col-i) != abs(C[col] - C[i]);如圖
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NQueen {
private int n;
private int[] C; //i行C[i]列 -->代表的是解
private int sum; // 解的個數
private int[][] map; //輸出解
//一開始都是0
public NQueen(int n,int sum,int[] C,int[][] map) {
super();
this.n = n;
this.sum = sum;
this.C = C;
this.map = map;
}
public int getSum(){
return sum;
}
public void BackTrack(int cur){
if(cur >= n){
sum++;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)map[i][C[i]] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)map[i][j] = 0;
}
else for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ //嘗試在cur行的各列放置皇后
C[cur] = i; //cur行和i列
if(Constraint(cur))BackTrack(cur+1); //檢查一下 -->可以的話就放置下一行
}
}
public boolean Constraint(int col){
for(int i = 0; i < col; i++){
if(C[i] == C[col] || (Math.abs(col - i) == Math.abs(C[col] - C[i])))return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n; n = cin.nextInt();
int[] C = new int[n+1];
int[][] map = new int[n+1][n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)map[i][j] = 0; //賦初值0
int sum = 0;
NQueen nq = new NQueen(n,sum,C,map);
nq.BackTrack(0);
System.out.println(nq.getSum());
}
}
展示一下8皇后的執行效果(只顯示了兩種解)
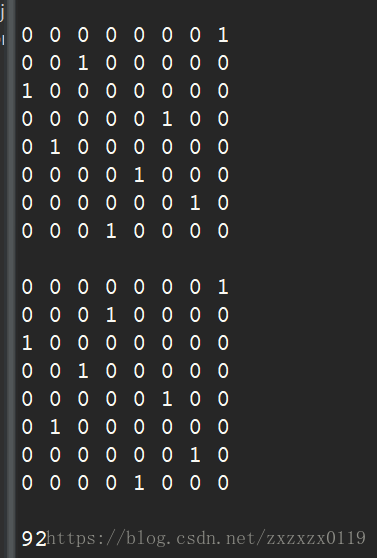
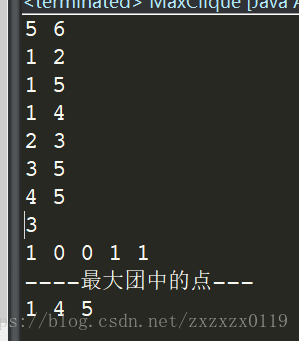
圖的最大團問題
最大團問題:
順便看一下獨立集,和最大團對應:
注意回溯的過程中:
設當前擴充套件結點Z位於解空間樹的第i層:在進入左子樹之前,必須確認從頂點i到以選入的頂點集中的每一個頂點有邊相連。
在進入右子樹之前,必須確認還有足夠多的可選擇頂點使得演算法有可能在右子樹中找到更大的團,也就是說剩下的點加上目前的點要比儲存的最多的點要大才搜尋。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 最大團問題
* @author 鄭鑫
*/
public class MaxClique {
private int[][] map; //圖的鄰接矩陣
private int n; //圖的頂點數
private int[] ans; //記錄當前的解
private int[] bestAns; //記錄當前的最優解
private int nowN; //記錄當前的頂點數
private int bestN; //記錄最大的頂點數
public int getBestN(){
return bestN;
}
public void getBestAns(){ //輸出最優解
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)System.out.print(bestAns[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----最大團中的點---");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)if(bestAns[i] == 1)System.out.print(i+1 + " ");
System.out.println();
}
public MaxClique(int[][] map, int n, int[] ans, int[] bestAns, int nowN, int bestN) {
super();
this.map = map;
this.n = n;
this.ans = ans;
this.bestAns = bestAns;
this.nowN = nowN;
this.bestN = bestN;
}
public void BackTrack(int i){
if(i >= n){
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)bestAns[j] = ans[j];
bestN = nowN;
return;
}
boolean flag = true;
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
if(map[i][j] == 0 && map[j][i] == 0&& ans[j] == 1){ //前面已經選的和這個不相連-->肯定不行(團的概念(完全圖))
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){ //進入左子樹
ans[i] = 1;
nowN++;
BackTrack(i+1);
nowN--; //記得回溯的時候減掉
ans[i] = 0; //回溯
}
if(nowN + n - i > bestN){
ans[i] = 0; //第i個不選
BackTrack(i+1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n,m; //頂點數,邊數
n = cin.nextInt(); //頂點的序號是0~n-1
m = cin.nextInt();
int[] ans = new int[n+1] ;// 記錄每一個頂點
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) ans[i] = 0; //一開始都不在團裡面
int[] bestAns = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) bestAns[i] = 0; //一開始都不在團裡面
int[][] map = new int[n+1][n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)map[i][j] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a = cin.nextInt();
int b = cin.nextInt();
map[a-1][b-1] = map[b-1][a-1] = 1;
}
int bestN = 0;
MaxClique mC = new MaxClique(map, n, ans, bestAns, 0, bestN);
mC.BackTrack(0);
System.out.println(mC.getBestN());
mC.getBestAns();
}
}
看這個例子和執行效果

圖的m著色問題
問題描述:
給定無向圖G和m中不同的顏色,用這些顏色為圖G的各個頂點著色,每個頂點著一種顏色。若一個圖最少需要m中顏色才能使得圖中每條邊相連的2個頂點著不同的顏色。則稱m為圖的色數。
現在的問題是: 給你一個圖G = (V,E)和m種顏色,如果這個圖不是m可著色,給出否定答案,如果這個圖是m可著色,找出所有的著色法。
例如下圖四個頂點四條邊,如果用三種(注意這題也可以用2種顏色,總的著色數是18,但是有三種顏色的著色法是12)顏色著色的12種情況
這個題目也是用一個ans陣列儲存解,ans[i] 表示的是 頂點i 用的顏色是ans[i],Ok函式的約束保證了相連的不是同一個顏色。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 圖的m著色問題
* @author 鄭鑫
*/
public class Color {
private int n; //圖的頂點數
private int m;
private int sum;
private int[][] map;
private int[] ans; //記錄解
public int getSum(){
return sum;
}
public Color(int n, int m, int sum, int[][] map, int[] ans) {
super();
this.n = n;
this.m = m;
this.sum = sum;
this.map = map;
this.ans = ans;
}
public void BackTrack(int t){
if( t >= n){
sum++; //達到葉子結點,解的個數加1
for(int i = 0; i < t; i++)System.out.print(ans[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
return;
}else for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
ans[t] = i;
if(Ok(t))BackTrack(t+1);
}
}
//可行性約束
public boolean Ok(int i){
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
if(map[i][j] == 1 && ans[j] == ans[i])return false; //如果相連而且顏色相同則不行
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = cin.nextInt(),edgeSum = cin.nextInt(),m = cin.nextInt(); //m是顏色數
int[] ans = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)ans[i] = -1;
int[][] map = new int[n+1][n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)map[i][j] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < edgeSum; i++){
int a = cin.nextInt();
int b = cin.nextInt();
map[a-1][b-1] = map[b-1][a-1] = 1;
}
Color c = new Color(n, m, 0, map, ans);
c.BackTrack(0);
System.out.println(c.getSum());
}
}
上面的例子輸入:
4 4 3
1 2
1 4
2 3
3 4
1
2
3
4
5
上面的例子輸出
0 1 0 1
0 1 0 2
0 1 2 1
0 2 0 1
0 2 0 2
0 2 1 2
1 0 1 0
1 0 1 2
1 0 2 0
1 2 0 2
1 2 1 0
1 2 1 2
2 0 1 0
2 0 2 0
2 0 2 1
2 1 0 1
2 1 2 0
2 1 2 1
18







