1086. Tree Traversals Again (樹的遍歷,前序中序轉後序)
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.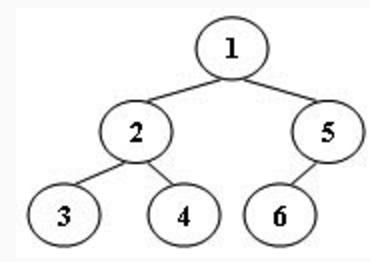
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<=30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: “Push X” where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or “Pop” meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
題目大意:用棧的形式給出一棵二叉樹的建立的順序,求這棵二叉樹的後序遍歷
需要一個堆結構s,一個child變數(表示該節點是其父親節點的左孩子還是右孩子),父親節點fa
對於push v操作:
1).第一個push肯定是根節點root。
2).根據child變數,建立fa與v的父子關係。
3).由於是中序遍歷,所以接下來的節點必定是v的left(如果有的話),child=left,fa=v;
4).然後進行push操作
對於pop操作:
1).根據中序遍歷性質,可知接下來的節點必定是pop節點的右孩子(如果有的話),child=right,fa=s.top()
2).進行pop操作。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string.h>
#include<stack>
#define LEFT 0
#define RIGHT 1
#define maxn 100
using namespace std;
stack<int> s;
//著重注意這題考查的是"建樹"的技巧
struct NODE
{
int left=-1;
int right=-1;
}node[maxn];
bool first=true;
void postOrder(int u){//雖然建樹時是按中序建的樹
if(u==-1) //但是按後序掃的
return;
postOrder(node[u].left);
postOrder(node[u].right);
if(first){
first=false;
printf("%d",u);
}
else{
printf(" %d",u);
}
}
int main()
{
int n,v;
int root=-1,fa;
//fa是為了記錄當前結點
//以便把各個node結點相連
int child=LEFT;
//child變數記錄的是,
//當前父節點往左走,還是往右走
char str[10];
scanf("%d",&n);
while(scanf("%s",str)!=EOF)
{
if(strcmp(str,"Push")==0)
{
scanf("%d",&v);
if(root==-1)//為這棵樹找根節點,入口
root=v;
else
{
if(child==LEFT)
node[fa].left=v;
else node[fa].right=v;
}
fa=v;//更新父節點
child=LEFT;
s.push(v);
}//對於入棧的操作,
//由於是中序,新節點優先進左子樹
else//出棧後在改變方向,
//再次push時向右子樹push
{
child=RIGHT;
fa=s.top();
s.pop();
}
}
postOrder(root);
return 0;
}
