[樹] 6.74 以廣義表的形式輸出樹(孩子兄弟連結串列CSTree)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-13
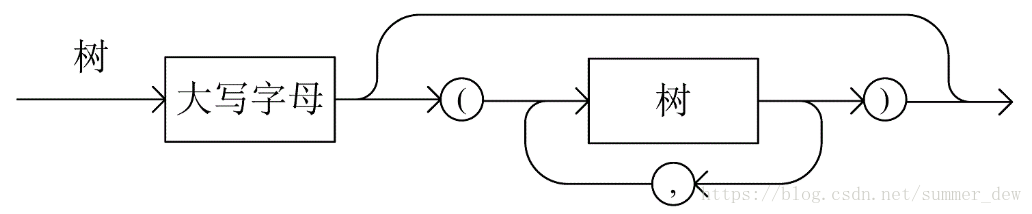
題目來源:嚴蔚敏《資料結構》C語言版本習題冊 6.74
【題目】6.74 試寫一遞迴演算法,以6.73題給定的樹的廣義表表示法的字元序列形式輸出以孩子-兄弟連結串列表示的樹
【答案】
/*-----------------------------------------
|6.74 以廣義表的形式輸出 |
-----------------------------------------*/
void PrintAsGList(CSTree T) {
CSNode *child;
visit(T->data);
if (T->firstchild) 【完整答案】
/*-------------------
|樹-孩子兄弟表達法 |
-------------------*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>