ELF格式探析之三:sections
前文連結:
今天我們講對目標檔案(可重定位檔案)和可執行檔案都很重要的section。
我們在講ELF Header的時候,講到了section header table。它是一個section header的集合,每個section header是一個描述section的結構體。在同一個ELF檔案中,每個section header大小是相同的。(其實看了原始碼就知道,32位ELF檔案中的section header都是一樣的大小,64位ELF檔案中的section header也是一樣的大小)
每個section都有一個section header描述它,但是一個section header可能在檔案中沒有對應的section,因為有的section是不佔用檔案空間的。每個section在檔案中是連續的位元組序列。section之間不會有重疊。
一個目標檔案中可能有未覆蓋到的空間,比如各種header和section都沒有覆蓋到。這部分位元組的內容是未指定的,也是沒有意義的。
section header定義
section header結構體的定義可以在 /usr/include/elf.h 中找到。
/* Section header. */ typedef struct { Elf32_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */ Elf32_Word sh_type; /* Section type */ Elf32_Word sh_flags; /* Section flags */ Elf32_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */ Elf32_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */ Elf32_Word sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */ Elf32_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */ Elf32_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */ Elf32_Word sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */ Elf32_Word sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */ } Elf32_Shdr; typedef struct { Elf64_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */ Elf64_Word sh_type; /* Section type */ Elf64_Xword sh_flags; /* Section flags */ Elf64_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */ Elf64_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */ Elf64_Xword sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */ Elf64_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */ Elf64_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */ Elf64_Xword sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */ Elf64_Xword sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */ } Elf64_Shdr;
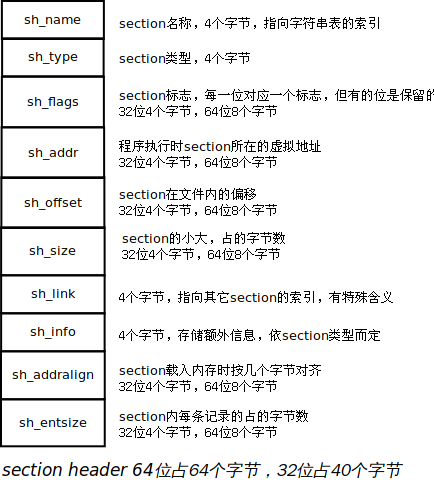
下面我們依次講解結構體各個欄位:
sh_name,4位元組,是一個索引值,在shstrtable(section header string table,包含section name的字串表,也是一個section)中的索引。第二講介紹ELF檔案頭時,裡面專門有一個欄位e_shstrndx,其含義就是shstrtable對應的section header在section header table中的索引。sh_type,4位元組,描述了section的型別,常見的取值如下:SHT_NULL0,表明section header無效,沒有關聯的section。SHT_PROGBITS1,section包含了程式需要的資料,格式和含義由程式解釋。SHT_SYMTAB2, 包含了一個符號表。當前,一個ELF檔案中只有一個符號表。SHT_SYMTAB提供了用於(link editor)連結編輯的符號,當然這些符號也可能用於動態連結。這是一個完全的符號表,它包含許多符號。SHT_STRTAB3,包含一個字串表。一個物件檔案包含多個字串表,比如.strtab(包含符號的名字)和.shstrtab(包含section的名稱)。SHT_RELA4,重定位節,包含relocation入口,參見Elf32_Rela。一個檔案可能有多個Relocation Section。比如.rela.text,.rela.dyn。SHT_HASH5,這樣的section包含一個符號hash表,參與動態連線的目的碼檔案必須有一個hash表。目前一個ELF檔案中只包含一個hash表。講連結的時候再細講。SHT_DYNAMIC6,包含動態連結的資訊。目前一個ELF檔案只有一個DYNAMIC section。SHT_NOTE7,note section, 以某種方式標記檔案的資訊,以後細講。SHT_NOBITS8,這種section不含位元組,也不佔用檔案空間,section header中的sh_offset欄位只是概念上的偏移。SHT_REL9, 重定位節,包含重定位條目。和SHT_RELA基本相同,兩者的區別在後面講重定位的時候再細講。SHT_SHLIB10,保留,語義未指定,包含這種型別的section的elf檔案不符合ABI。SHT_DYNSYM11, 用於動態連線的符號表,推測是symbol table的子集。SHT_LOPROC0x70000000 到SHT_HIPROC0x7fffffff,為特定於處理器的語義保留。SHT_LOUSER0x80000000 andSHT_HIUSER0xffffffff,指定了為應用程式保留的索引的下界和上界,這個範圍內的索引可以被應用程式使用。
sh_flags, 32位佔4位元組, 64位佔8位元組。包含位標誌,用readelf -S <elf>可以看到很多標誌。常用的有:SHF_WRITE0x1,程序執行的時候,section內的資料可寫。SHF_ALLOC0x2,程序執行的時候,section需要佔據記憶體。SHF_EXECINSTR0x4,節內包含可以執行的機器指令。SHF_STRINGS0x20,包含0結尾的字串。SHF_MASKOS0x0ff00000,這個mask為OS特定的語義保留8位。SHF_MASKPROC0xf0000000,這個mask包含的所有位保留(也就是最高位元組的高4位),為處理器相關的語義使用。
sh_addr, 對32位來說是4位元組,64位是8位元組。如果section會出現在程序的記憶體映像中,給出了section第一位元組的虛擬地址。sh_offset,對於32位來說是4位元組,64位是8位元組。section相對於檔案頭的位元組偏移。對於不佔檔案空間的section(比如SHT_NOBITS),它的sh_offset只是給出了section邏輯上的位置。sh_size,section佔多少位元組,對於SHT_NOBITS型別的section,sh_size沒用,其值可能不為0,但它也不佔檔案空間。sh_link,含有一個section header的index,該值的解釋依賴於section type。- 如果是
SHT_DYNAMIC,sh_link是string table的section header index,也就是說指向字串表。 - 如果是
SHT_HASH,sh_link指向symbol table的section header index,hash table應用於symbol table。 - 如果是重定位節
SHT_REL或SHT_RELA,sh_link指向相應符號表的section header index。 - 如果是
SHT_SYMTAB或SHT_DYNSYM,sh_link指向相關聯的符號表,暫時不解。 - 對於其它的section type,
sh_link的值是SHN_UNDEF
- 如果是
sh_info,存放額外的資訊,值的解釋依賴於section type。- 如果是
SHT_REL和SHT_RELA型別的重定位節,sh_info是應用relocation的節的節頭索引。 - 如果是
SHT_SYMTAB和SHT_DYNSYM,sh_info是第一個non-local符號在符號表中的索引。推測local symbol在前面,non-local symbols緊跟在後面,所以文件中也說,sh_info是最後一個本地符號的在符號表中的索引加1。 - 對於其它型別的section,sh_info是0。
- 如果是
sh_addralign,地址對齊,如果一個section有一個doubleword欄位,系統在載入section時的記憶體地址必須是doubleword對齊。也就是說sh_addr必須是sh_addralign的整數倍。只有2的正整數冪是有效的。0和1說明沒有對齊約束。sh_entsize,有些section包含固定大小的記錄,比如符號表。這個值給出了每個記錄大小。對於不包含固定大小記錄的section,這個值是0。
系統預定義的section name
系統預定義了一些節名(以.開頭),這些節有其特定的型別和含義。
- .bss:包含程式執行時未初始化的資料(全域性變數和靜態變數)。當程式執行時,這些資料初始化為0。 其型別為
SHT_NOBITS,表示不佔檔案空間。SHF_ALLOC+SHF_WRITE,執行時要佔用記憶體的。 - .comment 包含版本控制資訊(是否包含程式的註釋資訊?不包含,註釋在預處理時已經被刪除了)。型別為
SHT_PROGBITS。 - .data和.data1,包含初始化的全域性變數和靜態變數。 型別為
SHT_PROGBITS,標誌為SHF_ALLOC+SHF_WRITE(佔用記憶體,可寫)。 - .debug,包含了符號除錯用的資訊,我們要想用
gdb等工具除錯程式,需要該型別資訊,型別為SHT_PROGBITS。 - .dynamic,型別
SHT_DYNAMIC,包含了動態連結的資訊。標誌SHF_ALLOC,是否包含SHF_WRITE和處理器有關。 - .dynstr,
SHT_STRTAB,包含了動態連結用的字串,通常是和符號表中的符號關聯的字串。標誌SHF_ALLOC - .dynsym,型別
SHT_DYNSYM,包含動態連結符號表, 標誌SHF_ALLOC。 - .fini,型別
SHT_PROGBITS,程式正常結束時,要執行該section中的指令。標誌SHF_ALLOC + SHF_EXECINSTR(佔用記憶體可執行)。現在ELF還包含.fini_arraysection。 - .got,型別
SHT_PROGBITS,全域性偏移表(global offset table),以後會重點講。 - .hash,型別
SHT_HASH,包含符號hash表,以後細講。標誌SHF_ALLOC。 - .init,
SHT_PROGBITS,程式執行時,先執行該節中的程式碼。SHF_ALLOC + SHF_EXECINSTR,和.fini對應。現在ELF還包含.init_arraysection。 - .interp,
SHT_PROGBITS,該節內容是一個字串,指定了程式直譯器的路徑名。如果檔案中有一個可載入的segment包含該節,屬性就包含SHF_ALLOC,否則不包含。 - .line,
SHT_PROGBITS,包含符號除錯的行號資訊,描述了源程式和機器程式碼的對應關係。gdb等偵錯程式需要此資訊。 - .note
Note Section, 型別SHT_NOTE,以後單獨講。 - .plt 過程連結表(Procedure Linkage Table),型別
SHT_PROGBITS,以後重點講。 - .relNAME,型別
SHT_REL, 包含重定位資訊。如果檔案有一個可載入的segment包含該section,section屬性將包含SHF_ALLOC,否則不包含。NAME,是應用重定位的節的名字,比如.text的重定位資訊儲存在.rel.text中。 - .relaname 型別
SHT_RELA,和.rel相同。SHT_RELA和SHT_REL的區別,會在講重定位的時候說明。 - .rodata和.rodata1。型別
SHT_PROGBITS, 包含只讀資料,組成不可寫的段。標誌SHF_ALLOC。 - .shstrtab,型別
SHT_STRTAB,包含section的名字。有讀者可能會問:section header中不是已經包含名字了嗎,為什麼把名字集中存放在這裡?sh_name包含的是.shstrtab 中的索引,真正的字串儲存在.shstrtab中。那麼section names為什麼要集中儲存?我想是這樣:如果有相同的字串,就可以共用一塊儲存空間。如果字串存在包含關係,也可以共用一塊儲存空間。 - .strtab
SHT_STRTAB,包含字串,通常是符號表中符號對應的變數名字。如果檔案有一個可載入的segment包含該section,屬性將包含SHF_ALLOC。字串以\0結束, section以\0開始,也以\0結束。一個.strtab可以是空的,它的sh_size將是0。針對空字串表的非0索引是允許的。 - symtab,型別
SHT_SYMTAB,Symbol Table,符號表。包含了定位、重定位符號定義和引用時需要的資訊。符號表是一個數組,Index 0 第一個入口,它的含義是undefined symbol index,STN_UNDEF。如果檔案有一個可載入的segment包含該section,屬性將包含SHF_ALLOC。
練習:讀取section names
從這一講開始,都會有練習,方便我們把前面的理論知識綜合運用。
下面這個練習的目標是:從一個ELF檔案中讀取儲存section name的字串表。前面講過,該字串表也是一個section,section header table中有其對應的section header,並且ELF檔案頭中給出了節名字串表對應的section header的索引,e_shstrndx。
我們的思路是這樣:
- 從ELF header中讀取section header table的起始位置,每個section header的大小,以及節名字串表對應section header的索引。
- 計算
section_header_table_offset+section_header_size*e_shstrndx就是節名字串表對應section header的偏移。 - 讀取section header,可以從中得到節名字串表在檔案中的偏移和大小。
- 把節名字串表讀取到記憶體中,列印其內容。
程式碼如下:
/* 64位ELF檔案讀取section name string table */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* 開啟本地的ELF可執行檔案hello */
FILE *fp = fopen("./hello", "rb");
if(!fp) {
perror("open ELF file");
exit(1);
}
/* 1. 通過讀取ELF header得到section header table的偏移 */
/* for 64 bit ELF,
e_ident(16) + e_type(2) + e_machine(2) +
e_version(4) + e_entry(8) + e_phoff(8) = 40 */
fseek(fp, 40, SEEK_SET);
uint64_t sh_off;
int r = fread(&sh_off, 1, 8, fp);
if (r != 8) {
perror("read section header offset");
exit(2);
}
/* 得到的這個偏移值,可以用`reaelf -h hello`來驗證是否正確 */
printf("section header offset in file: %ld (0x%lx)\n", sh_off, sh_off);
/* 2. 讀取每個section header的大小e_shentsize,
section header的數量e_shnum,
以及對應section name字串表的section header的索引e_shstrndx
得到這些值後,都可以用`readelf -h hello`來驗證是否正確 */
/* e_flags(4) + e_ehsize(2) + e_phentsize(2) + e_phnum(2) = 10 */
fseek(fp, 10, SEEK_CUR);
uint16_t sh_ent_size; /* 每個section header的大小 */
r = fread(&sh_ent_size, 1, 2, fp);
if (r != 2) {
perror("read section header entry size");
exit(2);
}
printf("section header entry size: %d\n", sh_ent_size);
uint16_t sh_num; /* section header的數量 */
r = fread(&sh_num, 1, 2, fp);
if (r != 2) {
perror("read section header number");
exit(2);
}
printf("section header number: %d\n", sh_num);
uint16_t sh_strtab_index; /* 節名字串表對應的節頭的索引 */
r = fread(&sh_strtab_index, 1, 2, fp);
if (r != 2) {
perror("read section header string table index");
exit(2);
}
printf("section header string table index: %d\n", sh_strtab_index);
/* 3. read section name string table offset, size */
/* 先找到節頭字串表對應的section header的偏移位置 */
fseek(fp, sh_off + sh_strtab_index * sh_ent_size, SEEK_SET);
/* 再從section header中找到節頭字串表的偏移 */
/* sh_name(4) + sh_type(4) + sh_flags(8) + sh_addr(8) = 24 */
fseek(fp, 24, SEEK_CUR);
uint64_t str_table_off;
r = fread(&str_table_off, 1, 8, fp);
if (r != 8) {
perror("read section name string table offset");
exit(2);
}
printf("section name string table offset: %ld\n", str_table_off);
/* 從section header中找到節頭字串表的大小 */
uint64_t str_table_size;
r = fread(&str_table_size, 1, 8, fp);
if (r != 8) {
perror("read section name string table size");
exit(2);
}
printf("section name string table size: %ld\n", str_table_size);
/* 動態分配記憶體,把節頭字串表讀到記憶體中 */
char *buf = (char *)malloc(str_table_size);
if(!buf) {
perror("allocate memory for section name string table");
exit(3);
}
fseek(fp, str_table_off, SEEK_SET);
r = fread(buf, 1, str_table_size, fp);
if(r != str_table_size) {
perror("read section name string table");
free(buf);
exit(2);
}
uint16_t i;
for(i = 0; i < str_table_size; ++i) {
/* 如果節頭字串表中的位元組是0,就列印`\0` */
if (buf[i] == 0)
printf("\\0");
else
printf("%c", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n");
free(buf);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}把以上程式碼存為chap3_read_section_names.c,執行gcc -Wall -o secnames chap3_read_section_names.c進行編譯,輸出的執行檔名叫secnames。執行secnames,輸出如下:
./secnames
section header offset in file: 14768 (0x39b0)
section header entry size: 64
section header number: 29
section header string table index: 28
section name string table offset: 14502
section name string table size: 259
\0.symtab\0.strtab\0.shstrtab\0.interp\0.note.ABI-tag\0.note.gnu.build-id\0.gnu.hash\0.dynsym\0.dynstr\0.gnu.version\0.gnu.version_r\0.rela.dyn\0.rela.plt\0.init\0.text\0.fini\0.rodata\0.eh_frame_hdr\0.eh_frame\0.init_array\0.fini_array\0.dynamic\0.got\0.got.plt\0.data\0.bss\0.comment\0可以發現,節頭字串表以\0開始,以\0結束。如果一個section的name欄位指向0,則他指向的位元組值是0,則它沒有名稱,或名稱是空。
總結
本章主要講解了section header的定義,各欄位含義和可能的取值。然後介紹了系統預定義的一些section名稱。最後我們綜合運用第二章和第三章的知識,做了一個讀取section names的練習。
下一章我們將講述符號表和重定位的原理。此係列文章也會在微信公眾號“歡欣之翼”上同步更新,歡迎關注。
