Java註解-超詳細教程(附原始碼)
1:Java中常見註解
- @Override 用在方法上,表示這個方法重寫了父類的方法,如toString()。
- @Deprecated 表示這個方法已經過期,不建議開發者使用。(暗示在將來某個不確定的版本,就有可能會取消掉)
- @SuppressWarnings 這個註解的用處是忽略警告資訊
- @SafeVarargs 引數安全型別註解。它的目的是提醒開發者不要用引數做一些不安全的操作,它的存在會阻止編譯器產生 unchecked 這樣的警告
- @FunctionalInterface 用於約定函式式介面。 如果介面中只有一個抽象方法(可以包含多個預設方法或多個static方法),該介面稱為函式式介面。函式式介面其存在的意義,主要是配合Lambda 表示式 來使用。
2: 註解分類
按執行機制分:
- 原始碼註解 註解只在原始碼中存在,編譯成.class檔案就不存在了
- 編譯時註解 註解在原始碼和.class檔案中都會存在。比如說@Override
- 執行時註解 在執行階段還會起作用,甚至會影響執行邏輯的註解。比如說@Autowired
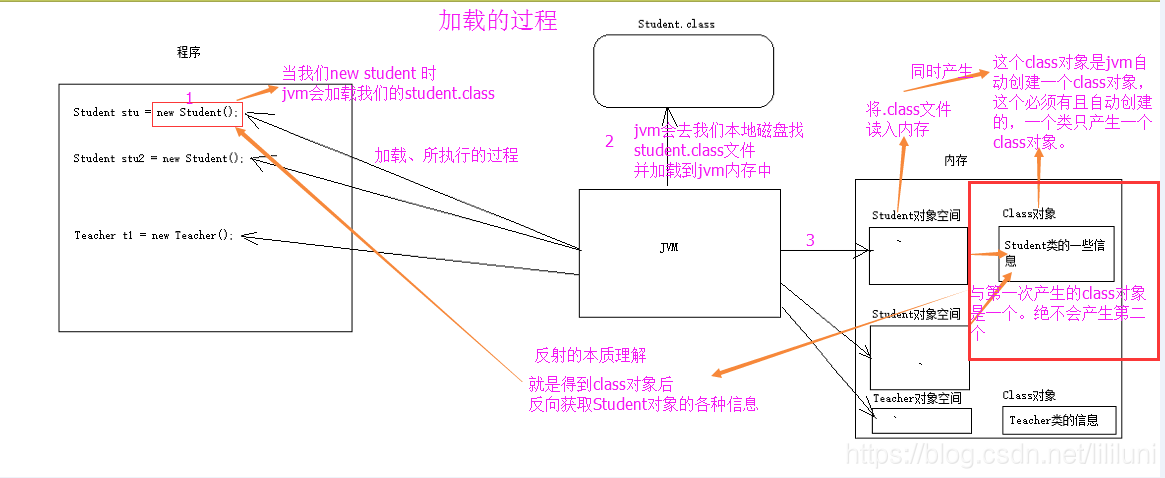
下圖是類載入的過程,更好的理解三種註解(圖片來源)
按來源分:
- JDK內建註解
- java第三方註解
- 自定義註解
- 元註解
3:自定義註解
1:自定義註解的語法要求
在這裡不詳細記錄,僅展示一個 @Description 註解示例,關於元註解詳見元註解詳細內容
package grammar;
import java. 2:使用自定義註解
@<註解名>(<成員名1>=<成員值1>,<成員名2>=<成員值2>,..)
package grammar;
@Description(desc="I am" ,author="liu",age=22)
public class UseAnnotation {
public String Test() {
return "red";
}
}
3:解析註解
概念: 通過反射獲取類、函式或成員上的執行時註解資訊,從而實現動態控制程式執行的邏輯。注意,解析註解時, @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 是必須的。
- 先獲取類物件
- 類物件呼叫
isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass)判斷是否應用了某個註解- 通過 getAnnotation() 方法來獲取 Annotation 物件,或者getAnnotations() 方法獲取所有應用在該類上的註解
示例: 註解類:
package grammar;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD , ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention( RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface DesSimple {
String value();
}
應用註解類:
package grammar;
@DesSimple("this is a type ano")
public class Child {
@DesSimple("this is a method ano")
public String name() {
return "name";
}
}
解析註解類:
package grammar;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ParseAnnotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//1.使用類載入器載入類物件
Class clazz = Class.forName("grammar.Child");
//2. 判斷是否應用了這個註解
boolean hasAnno = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(DesSimple.class);
//3. 獲取Annotation物件
if(hasAnno) {
DesSimple ds = (DesSimple)clazz.getAnnotation(DesSimple.class);
System.out.println(ds.value());
}
//4. 找到方法上的註解
Method[] ms = clazz.getMethods();
/******** 第一種解析方式 ************/
for(Method m:ms) {
boolean isMExist = m.isAnnotationPresent(DesSimple.class);
if(isMExist ) {
DesSimple dsm = (DesSimple)m.getAnnotation(DesSimple.class);
System.out.println(dsm.value());
}
}
/************ 另一種解析方式 ******************/
for(Method m: ms) {
Annotation[] ans = m.getAnnotations();//獲取所有註解在該方法上的註解
for(Annotation an:ans) {
if(an instanceof DesSimple) {
DesSimple desSimple = (DesSimple)an;
System.out.println(desSimple.value());
}
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4:自定義註解的應用-仿Hibernate註解
- hibernate兩種配置方式
hibernate有兩種配置方式,分別是*.hbm.xml 配置方式 和註解方式。 雖然方式不一樣,但是都是用於解決如下問題:
- 當前類是否實體類
- 對應的表名稱
- 主鍵對應哪個屬性, 自增長策略是什麼,對應欄位名稱是什麼
- 非主鍵屬性對應欄位名稱是什麼
接下來,我會做一套仿hibernate的註解,並且在一個實體類Hero上運用這些註解,並通過反射解析這些註解資訊,來解決上述的問題
- 自定義hibernate註解 1
參考hibernate的 註解配置方式 ,自定義5個註解,分別對應hibernate中用到的註解: hibernate_annotation.MyEntity 對應 javax.persistence.Entity hibernate_annotation.MyTable 對應 javax.persistence.Table hibernate_annotation.MyId 對應 javax.persistence.Id hibernate_annotation.MyGeneratedValue 對應 javax.persistence.GeneratedValue hibernate_annotation.MyColumn 對應 javax.persistence.Column
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyEntity {
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyTable {
//對應表名
String name();
}
@Target({METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyId {
}
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyGeneratedValue {
//增長策略
String strategy();
}
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyColumn {
//對應列名
String value();
}
- 運用在Hero物件上
package hibernate;
@MyEntity
@MyTable(name="hero_")
public class Hero {
private int id;
private String name;
private int damage;
private int armor;
@MyId
@MyGeneratedValue(strategy = "identity")
@MyColumn("id_")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@MyColumn("name_")
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@MyColumn("damage_")
public int getDamage() {
return damage;
}
public void setDamage(int damage) {
this.damage = damage;
}
@MyColumn("armor_")
public int getArmor() {
return armor;
}
public void setArmor(int armor) {
this.armor = armor;
}
}
- 建立一個解析類ParseHibernateAnnotation ,獲取Hero類上配置的註解資訊 思路如下:
- 首先獲取Hero.class類物件
- 判斷本類是否進行了MyEntity 註解
- 獲取註解 MyTable
- 遍歷所有的方法,如果某個方法有MyId註解,那麼就記錄為主鍵方法primaryKeyMethod
- 把主鍵方法的自增長策略註解MyGeneratedValue和對應的欄位註解MyColumn 取出來,並列印
- 遍歷所有非主鍵方法,並且有MyColumn註解的方法,列印屬性名稱和欄位名稱的對應關係。
示例:
package hibernate;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ParseHibernateAnnotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//1. 獲取class類物件
Class hclass = Class.forName("hibernate.Hero");
//判斷本類是否進行了MyEntity 註解
boolean isEntity = hclass.isAnnotationPresent(MyEntity.class);
if(!isEntity) {
System.out.println("Hero 不是實體類");
}
else {
System.out.println("Hero 是實體類");//獲取註解MyTable
boolean isTable = hclass.isAnnotationPresent(MyTable.class);
if(isTable) {
MyTable table = (MyTable)hclass.getAnnotation(MyTable.class);
System.out.println("其對應的表名為:"+table.name());
}
// 遍歷所有的方法,如果某個方法有MyId註解,那麼就記錄為主鍵方法primaryKeyMethod
Method[] ms = hclass.getMethods();
Method primaryKeyMethod = null;
for(Method m:ms) {
MyId myId = m.getAnnotation(MyId.class);
if(null!=myId){
primaryKeyMethod = m;
break;
}
}
//存在主鍵方法
if(null!=primaryKeyMethod){
System.out.println("找到主鍵:" + method2attribute( primaryKeyMethod.getName() ));
MyGeneratedValue myGeneratedValue =
primaryKeyMethod.getAnnotation(MyGeneratedValue.class);
System.out.println("其自增長策略是:" +myGeneratedValue.strategy());
MyColumn myColumn = primaryKeyMethod.getAnnotation(MyColumn.class);
System.out.println("對應資料庫中的欄位是:" +myColumn.value());
}
System.out.println("其他非主鍵屬性分別對應的資料庫欄位如下:");
for (Method m: ms) {
//判斷是否非主鍵方法
if(m==primaryKeyMethod){
continue;
}
MyColumn myColumn = m.getAnnotation(MyColumn.class);
//那些setter方法上是沒有MyColumn註解的
if(null==myColumn)
continue;
System.out.format("屬性: %s\t對應的資料庫欄位是:%s%n",method2attribute(m.getName()),myColumn.value());
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static String method2attribute(String methodName) {
String result = methodName; ;
result = result.replaceFirst("get", "");
result = result.replaceFirst("is", "");
if(result.length()<=1){
return result.toLowerCase();
}
else{
return result.substring(0,1).toLowerCase() + result.substring(1,result.length());
}
}
}
註解的內容就暫時寫到這,從最後一個例子很明顯看出了註解和反射對於加深框架的理解很有幫助,接下來計劃去學習瞭解Spring框架原始碼
