Pytorch實戰(3)----分類
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-18
一、分類任務:
將以下兩類分開。

建立資料程式碼:
# make fake data n_data = torch.ones(100, 2) x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data, 1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2) y0 = torch.zeros(100) # class0 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1) x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data, 1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2) y1 = torch.ones(100) #class1 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1) x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating y = torch.cat((y0, y1), ).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer # torch can only train on Variable, so convert them to Variable x, y = Variable(x), Variable(y) plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:,1], c=y.data.numpy(), s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn') plt.show()
二、步驟
-
匯入包
-
建立模型
-
設定優化器和損失函式
-
訓練模型
三、程式碼:
匯入包:
import torch from torch.autograd import Variable import torch.nn.functional as F import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline torch.manual_seed(1) #reproducible
建立模型:
class Net(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output): super(Net, self).__init__() self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # hidden layer self.out = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # output layer def forward(self, x): x = F.relu(self.hidden(x)) # activation function for hidden layer x = self.out(x) return x
設定優化器和損失函式
#輸入的x為2維張量,輸出有兩類 net = Net(n_feature=2, n_hidden=10, n_output=2) # define the network print(net) # net architecture # Loss and Optimizer # Softmax is internally computed. # Set parameters to be updated. optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.02) loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is NOT an one-hotted
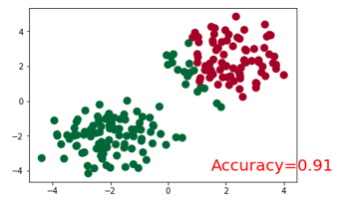
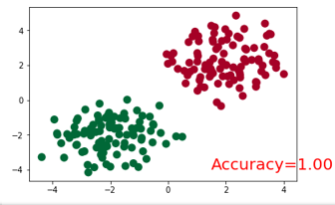
訓練模型並畫圖展示
plt.ion() # something about plotting plt.show() for t in range(100): out = net(x) # input x and predict based on x loss = loss_func(out, y) # must be (1. nn output, 2. target), the target label is NOT one-hotted optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients optimizer.step() # apply gradients if t % 10 == 0 or t in [3, 6]: # plot and show learning process plt.cla() _, prediction = torch.max(F.softmax(out), 1) #這裡是得到softmax之後最大概率的y預測值。 pred_y = prediction.data.numpy().squeeze() print(pred_y) target_y = y.data.numpy() plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=pred_y, s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn') accuracy = sum(pred_y == target_y)/200. plt.text(1.5, -4, 'Accuracy=%.2f' % accuracy, fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'}) plt.show() # plt.pause(0.1) plt.ioff()
結果展示: