FFmpeg原始碼簡單分析 avcodec encode video
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-21
=====================================================
FFmpeg的庫函式原始碼分析文章列表:
【架構圖】
【通用】
【解碼】
【編碼】
【其它】
【指令碼】
【H.264】
=====================================================
本文簡單分析FFmpeg的avcodec_encode_video2()函式。該函式用於編碼一幀視訊資料。avcodec_encode_video2()函式的宣告位於libavcodec\avcodec.h,如下所示。
/** * Encode a frame of video. * * Takes input raw video data from frame and writes the next output packet, if * available, to avpkt. The output packet does not necessarily contain data for * the most recent frame, as encoders can delay and reorder input frames * internally as needed. * * @param avctx codec context * @param avpkt output AVPacket. * The user can supply an output buffer by setting * avpkt->data and avpkt->size prior to calling the * function, but if the size of the user-provided data is not * large enough, encoding will fail. All other AVPacket fields * will be reset by the encoder using av_init_packet(). If * avpkt->data is NULL, the encoder will allocate it. * The encoder will set avpkt->size to the size of the * output packet. The returned data (if any) belongs to the * caller, he is responsible for freeing it. * * If this function fails or produces no output, avpkt will be * freed using av_free_packet() (i.e. avpkt->destruct will be * called to free the user supplied buffer). * @param[in] frame AVFrame containing the raw video data to be encoded. * May be NULL when flushing an encoder that has the * CODEC_CAP_DELAY capability set. * @param[out] got_packet_ptr This field is set to 1 by libavcodec if the * output packet is non-empty, and to 0 if it is * empty. If the function returns an error, the * packet can be assumed to be invalid, and the * value of got_packet_ptr is undefined and should * not be used. * @return 0 on success, negative error code on failure */ 該函式每個引數的含義在註釋裡面已經寫的很清楚了,在這裡用中文簡述一下:
avctx:編碼器的AVCodecContext。
avpkt:編碼輸出的AVPacket。
frame:編碼輸入的AVFrame。
got_packet_ptr:成功編碼一個AVPacket的時候設定為1。
函式返回0代表編碼成功。
函式呼叫關係圖
函式的呼叫關係如下圖所示。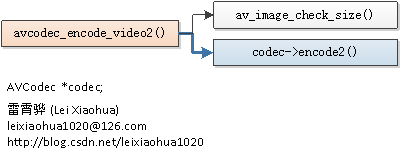
avcodec_encode_video2()
avcodec_encode_video2()的定義位於libavcodec\utils.c,如下所示。int attribute_align_arg avcodec_encode_video2(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVPacket *avpkt, const AVFrame *frame, int 從函式的定義可以看出,avcodec_encode_video2()首先呼叫了av_image_check_size()檢查設定的寬高參數是否合理,然後呼叫了AVCodec的encode2()呼叫具體的解碼器。
av_image_check_size()
av_image_check_size()是一個很簡單的函式,用於檢查影象寬高是否正常,它的定義如下所示。int av_image_check_size(unsigned int w, unsigned int h, int log_offset, void *log_ctx){ ImgUtils imgutils = { &imgutils_class, log_offset, log_ctx }; if ((int)w>0 && (int)h>0 && (w+128)*(uint64_t)(h+128) < INT_MAX/8) return 0; av_log(&imgutils, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Picture size %ux%u is invalid\n", w, h); return AVERROR(EINVAL);}從程式碼中可以看出,av_image_check_size()主要是要求影象寬高必須為正數,而且取值不能太大。
AVCodec->encode2()
AVCodec的encode2()是一個函式指標,指向特定編碼器的編碼函式。在這裡我們以libx264為例,看一下它對應的AVCodec的結構體的定義,如下所示。AVCodec ff_libx264_encoder = { .name = "libx264", .long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("libx264 H.264 / AVC / MPEG-4 AVC / MPEG-4 part 10"), .type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, .id = AV_CODEC_ID_H264, .priv_data_size = sizeof(X264Context), .init = X264_init, .encode2 = X264_frame, .close = X264_close, .capabilities = CODEC_CAP_DELAY | CODEC_CAP_AUTO_THREADS, .priv_class = &x264_class, .defaults = x264_defaults, .init_static_data = X264_init_static,};從ff_libx264_encoder的定義可以看出,encode2()函式指向的是X264_frame()函式。
X264_frame()
X264_frame()函式的定義位於libavcodec\libx264.c,如下所示。static int X264_frame(AVCodecContext *ctx, AVPacket *pkt, const AVFrame *frame, int *got_packet){ X264Context *x4 = ctx->priv_data; x264_nal_t *nal; int nnal, i, ret; x264_picture_t pic_out = {0}; AVFrameSideData *side_data; x264_picture_init( &x4->pic ); x4->pic.img.i_csp = x4->params.i_csp; if (x264_bit_depth > 8) x4->pic.img.i_csp |= X264_CSP_HIGH_DEPTH; x4->pic.img.i_plane = avfmt2_num_planes(ctx->pix_fmt); if (frame) { for (i = 0; i < x4->pic.img.i_plane; i++) { x4->pic.img.plane[i] = frame->data[i]; x4->pic.img.i_stride[i] = frame->linesize[i]; } x4->pic.i_pts = frame->pts; x4->pic.i_type = frame->pict_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I ? X264_TYPE_KEYFRAME : frame->pict_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_P ? X264_TYPE_P : frame->pict_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B ? X264_TYPE_B : X264_TYPE_AUTO; if (x4->avcintra_class < 0) { if (x4->params.b_interlaced && x4->params.b_tff != frame->top_field_first) { x4->params.b_tff = frame->top_field_first; x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params); } if (x4->params.vui.i_sar_height != ctx->sample_aspect_ratio.den || x4->params.vui.i_sar_width != ctx->sample_aspect_ratio.num) { x4->params.vui.i_sar_height = ctx->sample_aspect_ratio.den; x4->params.vui.i_sar_width = ctx->sample_aspect_ratio.num; x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params); } if (x4->params.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size != ctx->rc_buffer_size / 1000 || x4->params.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate != ctx->rc_max_rate / 1000) { x4->params.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size = ctx->rc_buffer_size / 1000; x4->params.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate = ctx->rc_max_rate / 1000; x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params); } if (x4->params.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_ABR && x4->params.rc.i_bitrate != ctx->bit_rate / 1000) { x4->params.rc.i_bitrate = ctx->bit_rate / 1000; x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params); } if (x4->crf >= 0 && x4->params.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF && x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant != x4->crf) { x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant = x4->crf; x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params); } if (x4->params.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CQP && x4->cqp >= 0 && x4->params.rc.i_qp_constant != x4->cqp) { x4->params.rc.i_qp_constant = x4->cqp; x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params); } if (x4->crf_max >= 0 && x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant_max != x4->crf_max) { x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant_max = x4->crf_max; x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params); } } side_data = av_frame_get_side_data(frame, AV_FRAME_DATA_STEREO3D); if (side_data) { AVStereo3D *stereo = (AVStereo3D *)side_data->data; int fpa_type; switch (stereo->type) { case AV_STEREO3D_CHECKERBOARD: fpa_type = 0; break; case AV_STEREO3D_COLUMNS: fpa_type = 1; break; case AV_STEREO3D_LINES: fpa_type = 2; break; case AV_STEREO3D_SIDEBYSIDE: fpa_type = 3; break; case AV_STEREO3D_TOPBOTTOM: fpa_type = 4; break; case AV_STEREO3D_FRAMESEQUENCE: fpa_type = 5; break; default: fpa_type = -1; break; } if (fpa_type != x4->params.i_frame_packing) { x4->params.i_frame_packing = fpa_type; x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params); } } } do { if (x264_encoder_encode(x4->enc, &nal, &nnal, frame? &x4->pic: NULL, &pic_out) < 0) return -1; ret = encode_nals(ctx, pkt, nal, nnal); if (ret < 0) return -1; } while (!ret && !frame && x264_encoder_delayed_frames(x4->enc)); pkt->pts = pic_out.i_pts; pkt->dts = pic_out.i_dts; switch (pic_out.i_type) { case X264_TYPE_IDR: case X264_TYPE_I: ctx->coded_frame->pict_type = AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I; break; case X264_TYPE_P: ctx->coded_frame->pict_type = AV_PICTURE_TYPE_P; break; case X264_TYPE_B: case X264_TYPE_BREF: ctx->coded_frame->pict_type = AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B; break; } pkt->flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY*pic_out.b_keyframe; if (ret) ctx->coded_frame->quality = (pic_out.i_qpplus1 - 1) * FF_QP2LAMBDA; *got_packet = ret; return 0;}有關X264編碼的程式碼在以後分析X264的時候再進行詳細分析。在這裡我們可以我們可以簡單看出該函式中有一個do while迴圈,其中呼叫了x264_encoder_encode()完成了編碼的工作。
雷霄驊
[email protected]
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
