FFmpeg與libx264介面原始碼簡單分析
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-08
=====================================================
H.264原始碼分析文章列表:
【編碼 - x264】
【解碼 - libavcodec H.264 解碼器】
=====================================================
本文簡單記錄一下FFmpeg的libavcodec中與libx264介面部分的原始碼。該部分原始碼位於“libavcodec/libx264.c”中。正是有了這部分程式碼,使得FFmpeg可以呼叫libx264編碼H.264視訊。
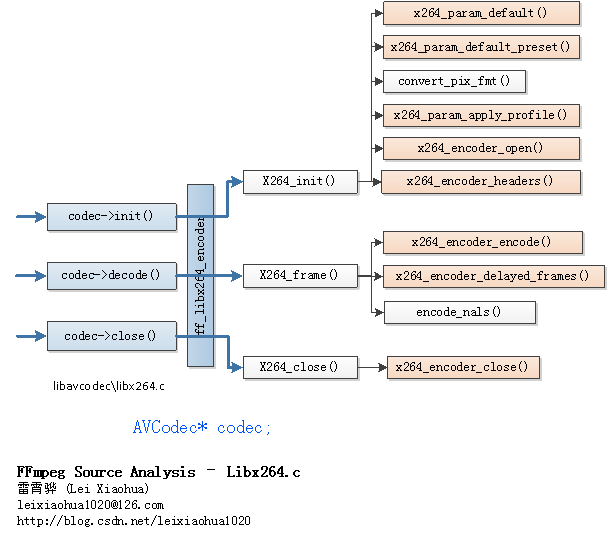
函式呼叫關係圖
FFmpeg的libavcodec中的libx264.c的函式呼叫關係如下圖所示。
從圖中可以看出,libx264對應的AVCodec結構體ff_libx264_encoder中設定編碼器初始化函式是X264_init(),編碼一幀資料的函式是X264_frame(),編碼器關閉函式是X264_close()。
X264_init()呼叫瞭如下函式:[libx264 API] x264_param_default():設定預設引數。
[libx264 API] x264_param_default_preset():設定預設preset。
convert_pix_fmt():將FFmpeg畫素格式轉換為libx264畫素格式。
[libx264 API] x264_param_apply_profile():設定Profile。
[libx264 API] x264_encoder_open():開啟編碼器。
[libx264 API] x264_encoder_headers():需要全域性頭的時候,輸出頭資訊。
[libx264 API] x264_encoder_encode():編碼一幀資料。X264_close()呼叫瞭如下函式:
[libx264 API] x264_encoder_delayed_frames():輸出編碼器中快取的資料。
encode_nals():將編碼後得到的x264_nal_t轉換為AVPacket。
[libx264 API] x264_encoder_close():關閉編碼器。
下文將會分別分析X264_init(),X264_frame()和X264_close()這三個函式。
ff_libx264_encoder
ff_libx264_encoder是libx264對應的AVCodec結構體,定義如下所示。//libx264對應的AVCodec結構體 AVCodec ff_libx264_encoder = { .name = "libx264", .long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("libx264 H.264 / AVC / MPEG-4 AVC / MPEG-4 part 10"), .type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, .id = AV_CODEC_ID_H264, .priv_data_size = sizeof(X264Context), .init = X264_init, .encode2 = X264_frame, .close = X264_close, .capabilities = CODEC_CAP_DELAY | CODEC_CAP_AUTO_THREADS, .priv_class = &x264_class, .defaults = x264_defaults, .init_static_data = X264_init_static, };
從ff_libx264_encoder定義中可以看出:init()指向X264_init(),encode2()指向 X264_frame(), close()指向 X264_close()。此外priv_class指向一個x264_class靜態結構體,該結構體是libx264對應的AVClass,定義如下。
static const AVClass x264_class = {
.class_name = "libx264",
.item_name = av_default_item_name,
.option = options,//選項
.version = LIBAVUTIL_VERSION_INT,
};x264_class中的option指向一個options[]靜態陣列,其中包含了libx264支援的AVOption選項,如下所示。
//FFmpeg針對libx264提供的可以通過AVOption設定的選項
#define OFFSET(x) offsetof(X264Context, x)
#define VE AV_OPT_FLAG_VIDEO_PARAM | AV_OPT_FLAG_ENCODING_PARAM
static const AVOption options[] = {
{ "preset", "Set the encoding preset (cf. x264 --fullhelp)", OFFSET(preset), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, { .str = "medium" }, 0, 0, VE},
{ "tune", "Tune the encoding params (cf. x264 --fullhelp)", OFFSET(tune), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, { 0 }, 0, 0, VE},
{ "profile", "Set profile restrictions (cf. x264 --fullhelp) ", OFFSET(profile), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, { 0 }, 0, 0, VE},
{ "fastfirstpass", "Use fast settings when encoding first pass", OFFSET(fastfirstpass), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = 1 }, 0, 1, VE},
{"level", "Specify level (as defined by Annex A)", OFFSET(level), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, {.str=NULL}, 0, 0, VE},
{"passlogfile", "Filename for 2 pass stats", OFFSET(stats), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, {.str=NULL}, 0, 0, VE},
{"wpredp", "Weighted prediction for P-frames", OFFSET(wpredp), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, {.str=NULL}, 0, 0, VE},
{"x264opts", "x264 options", OFFSET(x264opts), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, {.str=NULL}, 0, 0, VE},
{ "crf", "Select the quality for constant quality mode", OFFSET(crf), AV_OPT_TYPE_FLOAT, {.dbl = -1 }, -1, FLT_MAX, VE },
{ "crf_max", "In CRF mode, prevents VBV from lowering quality beyond this point.",OFFSET(crf_max), AV_OPT_TYPE_FLOAT, {.dbl = -1 }, -1, FLT_MAX, VE },
{ "qp", "Constant quantization parameter rate control method",OFFSET(cqp), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, INT_MAX, VE },
{ "aq-mode", "AQ method", OFFSET(aq_mode), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, INT_MAX, VE, "aq_mode"},
{ "none", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_AQ_NONE}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "aq_mode" },
{ "variance", "Variance AQ (complexity mask)", 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_AQ_VARIANCE}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "aq_mode" },
{ "autovariance", "Auto-variance AQ (experimental)", 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_AQ_AUTOVARIANCE}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "aq_mode" },
{ "aq-strength", "AQ strength. Reduces blocking and blurring in flat and textured areas.", OFFSET(aq_strength), AV_OPT_TYPE_FLOAT, {.dbl = -1}, -1, FLT_MAX, VE},
{ "psy", "Use psychovisual optimizations.", OFFSET(psy), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 1, VE },
{ "psy-rd", "Strength of psychovisual optimization, in <psy-rd>:<psy-trellis> format.", OFFSET(psy_rd), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, {0 }, 0, 0, VE},
{ "rc-lookahead", "Number of frames to look ahead for frametype and ratecontrol", OFFSET(rc_lookahead), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, INT_MAX, VE },
{ "weightb", "Weighted prediction for B-frames.", OFFSET(weightb), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 1, VE },
{ "weightp", "Weighted prediction analysis method.", OFFSET(weightp), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, INT_MAX, VE, "weightp" },
{ "none", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_WEIGHTP_NONE}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "weightp" },
{ "simple", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_WEIGHTP_SIMPLE}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "weightp" },
{ "smart", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_WEIGHTP_SMART}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "weightp" },
{ "ssim", "Calculate and print SSIM stats.", OFFSET(ssim), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 1, VE },
{ "intra-refresh", "Use Periodic Intra Refresh instead of IDR frames.",OFFSET(intra_refresh),AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 1, VE },
{ "bluray-compat", "Bluray compatibility workarounds.", OFFSET(bluray_compat) ,AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 1, VE },
{ "b-bias", "Influences how often B-frames are used", OFFSET(b_bias), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = INT_MIN}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE },
{ "b-pyramid", "Keep some B-frames as references.", OFFSET(b_pyramid), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, INT_MAX, VE, "b_pyramid" },
{ "none", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_B_PYRAMID_NONE}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "b_pyramid" },
{ "strict", "Strictly hierarchical pyramid", 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_B_PYRAMID_STRICT}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "b_pyramid" },
{ "normal", "Non-strict (not Blu-ray compatible)", 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_B_PYRAMID_NORMAL}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "b_pyramid" },
{ "mixed-refs", "One reference per partition, as opposed to one reference per macroblock", OFFSET(mixed_refs), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1}, -1, 1, VE },
{ "8x8dct", "High profile 8x8 transform.", OFFSET(dct8x8), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 1, VE},
{ "fast-pskip", NULL, OFFSET(fast_pskip), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 1, VE},
{ "aud", "Use access unit delimiters.", OFFSET(aud), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 1, VE},
{ "mbtree", "Use macroblock tree ratecontrol.", OFFSET(mbtree), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 1, VE},
{ "deblock", "Loop filter parameters, in <alpha:beta> form.", OFFSET(deblock), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, { 0 }, 0, 0, VE},
{ "cplxblur", "Reduce fluctuations in QP (before curve compression)", OFFSET(cplxblur), AV_OPT_TYPE_FLOAT, {.dbl = -1 }, -1, FLT_MAX, VE},
{ "partitions", "A comma-separated list of partitions to consider. "
"Possible values: p8x8, p4x4, b8x8, i8x8, i4x4, none, all", OFFSET(partitions), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, { 0 }, 0, 0, VE},
{ "direct-pred", "Direct MV prediction mode", OFFSET(direct_pred), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, INT_MAX, VE, "direct-pred" },
{ "none", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, { .i64 = X264_DIRECT_PRED_NONE }, 0, 0, VE, "direct-pred" },
{ "spatial", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, { .i64 = X264_DIRECT_PRED_SPATIAL }, 0, 0, VE, "direct-pred" },
{ "temporal", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, { .i64 = X264_DIRECT_PRED_TEMPORAL }, 0, 0, VE, "direct-pred" },
{ "auto", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, { .i64 = X264_DIRECT_PRED_AUTO }, 0, 0, VE, "direct-pred" },
{ "slice-max-size","Limit the size of each slice in bytes", OFFSET(slice_max_size),AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, INT_MAX, VE },
{ "stats", "Filename for 2 pass stats", OFFSET(stats), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, { 0 }, 0, 0, VE },
{ "nal-hrd", "Signal HRD information (requires vbv-bufsize; "
"cbr not allowed in .mp4)", OFFSET(nal_hrd), AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, INT_MAX, VE, "nal-hrd" },
{ "none", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_NAL_HRD_NONE}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "nal-hrd" },
{ "vbr", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_NAL_HRD_VBR}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "nal-hrd" },
{ "cbr", NULL, 0, AV_OPT_TYPE_CONST, {.i64 = X264_NAL_HRD_CBR}, INT_MIN, INT_MAX, VE, "nal-hrd" },
{ "avcintra-class","AVC-Intra class 50/100/200", OFFSET(avcintra_class),AV_OPT_TYPE_INT, { .i64 = -1 }, -1, 200 , VE},
{ "x264-params", "Override the x264 configuration using a :-separated list of key=value parameters", OFFSET(x264_params), AV_OPT_TYPE_STRING, { 0 }, 0, 0, VE },
{ NULL },
};
options[]陣列中包含的選項支援在FFmpeg中通過AVOption進行設定。
X264_init()
X264_init()用於初始化libx264編碼器。該函式的定義如下所示。//libx264編碼器初始化
static av_cold int X264_init(AVCodecContext *avctx)
{
//FFmpeg中針對libx264的私有結構體
X264Context *x4 = avctx->priv_data;
int sw,sh;
if (avctx->global_quality > 0)
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_WARNING, "-qscale is ignored, -crf is recommended.\n");
//[libx264 API] 設定預設引數
x264_param_default(&x4->params);
x4->params.b_deblocking_filter = avctx->flags & CODEC_FLAG_LOOP_FILTER;
if (x4->preset || x4->tune)
if (x264_param_default_preset(&x4->params, x4->preset, x4->tune) < 0) { //[libx264 API] 設定preset
int i;
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error setting preset/tune %s/%s.\n", x4->preset, x4->tune);
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, "Possible presets:");
for (i = 0; x264_preset_names[i]; i++)
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, " %s", x264_preset_names[i]);
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, "\n");
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, "Possible tunes:");
for (i = 0; x264_tune_names[i]; i++)
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, " %s", x264_tune_names[i]);
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, "\n");
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (avctx->level > 0)
x4->params.i_level_idc = avctx->level;
//libx264日誌輸出設定為FFmpeg的日誌輸出
x4->params.pf_log = X264_log;
x4->params.p_log_private = avctx;
x4->params.i_log_level = X264_LOG_DEBUG;
//FFmpeg畫素格式對映到libx264
x4->params.i_csp = convert_pix_fmt(avctx->pix_fmt);
OPT_STR("weightp", x4->wpredp);
//FFmpeg位元速率對映到libx264
if (avctx->bit_rate) {
x4->params.rc.i_bitrate = avctx->bit_rate / 1000;
x4->params.rc.i_rc_method = X264_RC_ABR;
}
x4->params.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size = avctx->rc_buffer_size / 1000;
x4->params.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate = avctx->rc_max_rate / 1000;
x4->params.rc.b_stat_write = avctx->flags & CODEC_FLAG_PASS1;
if (avctx->flags & CODEC_FLAG_PASS2) {
x4->params.rc.b_stat_read = 1;
} else {
if (x4->crf >= 0) {
x4->params.rc.i_rc_method = X264_RC_CRF;
x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant = x4->crf;
} else if (x4->cqp >= 0) {
x4->params.rc.i_rc_method = X264_RC_CQP;
x4->params.rc.i_qp_constant = x4->cqp;
}
if (x4->crf_max >= 0)
x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant_max = x4->crf_max;
}
if (avctx->rc_buffer_size && avctx->rc_initial_buffer_occupancy > 0 &&
(avctx->rc_initial_buffer_occupancy <= avctx->rc_buffer_size)) {
x4->params.rc.f_vbv_buffer_init =
(float)avctx->rc_initial_buffer_occupancy / avctx->rc_buffer_size;
}
OPT_STR("level", x4->level);
if (avctx->i_quant_factor > 0)
x4->params.rc.f_ip_factor = 1 / fabs(avctx->i_quant_factor);
if (avctx->b_quant_factor > 0)
x4->params.rc.f_pb_factor = avctx->b_quant_factor;
if (avctx->chromaoffset)
x4->params.analyse.i_chroma_qp_offset = avctx->chromaoffset;
//FFmpeg運動估計方法對映到libx264
if (avctx->me_method == ME_EPZS)
x4->params.analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_DIA;
else if (avctx->me_method == ME_HEX)
x4->params.analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_HEX;
else if (avctx->me_method == ME_UMH)
x4->params.analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_UMH;
else if (avctx->me_method == ME_FULL)
x4->params.analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_ESA;
else if (avctx->me_method == ME_TESA)
x4->params.analyse.i_me_method = X264_ME_TESA;
//把AVCodecContext的值(主要是編碼時候的一些通用選項)對映到x264_param_t
if (avctx->gop_size >= 0)
x4->params.i_keyint_max = avctx->gop_size;
if (avctx->max_b_frames >= 0)
x4->params.i_bframe = avctx->max_b_frames;
if (avctx->scenechange_threshold >= 0)
x4->params.i_scenecut_threshold = avctx->scenechange_threshold;
if (avctx->qmin >= 0)
x4->params.rc.i_qp_min = avctx->qmin;
if (avctx->qmax >= 0)
x4->params.rc.i_qp_max = avctx->qmax;
if (avctx->max_qdiff >= 0)
x4->params.rc.i_qp_step = avctx->max_qdiff;
if (avctx->qblur >= 0)
x4->params.rc.f_qblur = avctx->qblur; /* temporally blur quants */
if (avctx->qcompress >= 0)
x4->params.rc.f_qcompress = avctx->qcompress; /* 0.0 => cbr, 1.0 => constant qp */
if (avctx->refs >= 0)
x4->params.i_frame_reference = avctx->refs;
else if (x4->level) {
int i;
int mbn = FF_CEIL_RSHIFT(avctx->width, 4) * FF_CEIL_RSHIFT(avctx->height, 4);
int level_id = -1;
char *tail;
int scale = X264_BUILD < 129 ? 384 : 1;
if (!strcmp(x4->level, "1b")) {
level_id = 9;
} else if (strlen(x4->level) <= 3){
level_id = av_strtod(x4->level, &tail) * 10 + 0.5;
if (*tail)
level_id = -1;
}
if (level_id <= 0)
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Failed to parse level\n");
for (i = 0; i<x264_levels[i].level_idc; i++)
if (x264_levels[i].level_idc == level_id)
x4->params.i_frame_reference = av_clip(x264_levels[i].dpb / mbn / scale, 1, x4->params.i_frame_reference);
}
if (avctx->trellis >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.i_trellis = avctx->trellis;
if (avctx->me_range >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.i_me_range = avctx->me_range;
if (avctx->noise_reduction >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.i_noise_reduction = avctx->noise_reduction;
if (avctx->me_subpel_quality >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.i_subpel_refine = avctx->me_subpel_quality;
if (avctx->b_frame_strategy >= 0)
x4->params.i_bframe_adaptive = avctx->b_frame_strategy;
if (avctx->keyint_min >= 0)
x4->params.i_keyint_min = avctx->keyint_min;
if (avctx->coder_type >= 0)
x4->params.b_cabac = avctx->coder_type == FF_CODER_TYPE_AC;
if (avctx->me_cmp >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.b_chroma_me = avctx->me_cmp & FF_CMP_CHROMA;
//把X264Context中的資訊(主要是針對於libx264的一些選項)對映到x264_param_t
if (x4->aq_mode >= 0)
x4->params.rc.i_aq_mode = x4->aq_mode;
if (x4->aq_strength >= 0)
x4->params.rc.f_aq_strength = x4->aq_strength;
PARSE_X264_OPT("psy-rd", psy_rd);
PARSE_X264_OPT("deblock", deblock);
PARSE_X264_OPT("partitions", partitions);
PARSE_X264_OPT("stats", stats);
if (x4->psy >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.b_psy = x4->psy;
if (x4->rc_lookahead >= 0)
x4->params.rc.i_lookahead = x4->rc_lookahead;
if (x4->weightp >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.i_weighted_pred = x4->weightp;
if (x4->weightb >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.b_weighted_bipred = x4->weightb;
if (x4->cplxblur >= 0)
x4->params.rc.f_complexity_blur = x4->cplxblur;
if (x4->ssim >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.b_ssim = x4->ssim;
if (x4->intra_refresh >= 0)
x4->params.b_intra_refresh = x4->intra_refresh;
if (x4->bluray_compat >= 0) {
x4->params.b_bluray_compat = x4->bluray_compat;
x4->params.b_vfr_input = 0;
}
if (x4->avcintra_class >= 0)
#if X264_BUILD >= 142
x4->params.i_avcintra_class = x4->avcintra_class;
#else
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"x264 too old for AVC Intra, at least version 142 needed\n");
#endif
if (x4->b_bias != INT_MIN)
x4->params.i_bframe_bias = x4->b_bias;
if (x4->b_pyramid >= 0)
x4->params.i_bframe_pyramid = x4->b_pyramid;
if (x4->mixed_refs >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.b_mixed_references = x4->mixed_refs;
if (x4->dct8x8 >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.b_transform_8x8 = x4->dct8x8;
if (x4->fast_pskip >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.b_fast_pskip = x4->fast_pskip;
if (x4->aud >= 0)
x4->params.b_aud = x4->aud;
if (x4->mbtree >= 0)
x4->params.rc.b_mb_tree = x4->mbtree;
if (x4->direct_pred >= 0)
x4->params.analyse.i_direct_mv_pred = x4->direct_pred;
if (x4->slice_max_size >= 0)
x4->params.i_slice_max_size = x4->slice_max_size;
else {
/*
* Allow x264 to be instructed through AVCodecContext about the maximum
* size of the RTP payload. For example, this enables the production of
* payload suitable for the H.264 RTP packetization-mode 0 i.e. single
* NAL unit per RTP packet.
*/
if (avctx->rtp_payload_size)
x4->params.i_slice_max_size = avctx->rtp_payload_size;
}
if (x4->fastfirstpass)
x264_param_apply_fastfirstpass(&x4->params);
/* Allow specifying the x264 profile through AVCodecContext. */
//設定Profile
if (!x4->profile)
switch (avctx->profile) {
case FF_PROFILE_H264_BASELINE:
x4->profile = av_strdup("baseline");
break;
case FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH:
x4->profile = av_strdup("high");
break;
case FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_10:
x4->profile = av_strdup("high10");
break;
case FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_422:
x4->profile = av_strdup("high422");
break;
case FF_PROFILE_H264_HIGH_444:
x4->profile = av_strdup("high444");
break;
case FF_PROFILE_H264_MAIN:
x4->profile = av_strdup("main");
break;
default:
break;
}
if (x4->nal_hrd >= 0)
x4->params.i_nal_hrd = x4->nal_hrd;
//
if (x4->profile)
if (x264_param_apply_profile(&x4->params, x4->profile) < 0) {
int i;
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error setting profile %s.\n", x4->profile);
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, "Possible profiles:");
for (i = 0; x264_profile_names[i]; i++)
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, " %s", x264_profile_names[i]);
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, "\n");
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
//寬高,幀率等
x4->params.i_width = avctx->width;
x4->params.i_height = avctx->height;
av_reduce(&sw, &sh, avctx->sample_aspect_ratio.num, avctx->sample_aspect_ratio.den, 4096);
x4->params.vui.i_sar_width = sw;
x4->params.vui.i_sar_height = sh;
x4->params.i_timebase_den = avctx->time_base.den;
x4->params.i_timebase_num = avctx->time_base.num;
x4->params.i_fps_num = avctx->time_base.den;
x4->params.i_fps_den = avctx->time_base.num * avctx->ticks_per_frame;
x4->params.analyse.b_psnr = avctx->flags & CODEC_FLAG_PSNR;
x4->params.i_threads = avctx->thread_count;
if (avctx->thread_type)
x4->params.b_sliced_threads = avctx->thread_type == FF_THREAD_SLICE;
x4->params.b_interlaced = avctx->flags & CODEC_FLAG_INTERLACED_DCT;
x4->params.b_open_gop = !(avctx->flags & CODEC_FLAG_CLOSED_GOP);
x4->params.i_slice_count = avctx->slices;
x4->params.vui.b_fullrange = avctx->pix_fmt == AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P ||
avctx->pix_fmt == AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ422P ||
avctx->pix_fmt == AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ444P ||
avctx->color_range == AVCOL_RANGE_JPEG;
if (avctx->colorspace != AVCOL_SPC_UNSPECIFIED)
x4->params.vui.i_colmatrix = avctx->colorspace;
if (avctx->color_primaries != AVCOL_PRI_UNSPECIFIED)
x4->params.vui.i_colorprim = avctx->color_primaries;
if (avctx->color_trc != AVCOL_TRC_UNSPECIFIED)
x4->params.vui.i_transfer = avctx->color_trc;
if (avctx->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER)
x4->params.b_repeat_headers = 0;
if(x4->x264opts){
const char *p= x4->x264opts;
while(p){
char param[256]={0}, val[256]={0};
if(sscanf(p, "%255[^:=]=%255[^:]", param, val) == 1){
OPT_STR(param, "1");
}else
OPT_STR(param, val);
p= strchr(p, ':');
p+=!!p;
}
}
if (x4->x264_params) {
AVDictionary *dict = NULL;
AVDictionaryEntry *en = NULL;
if (!av_dict_parse_string(&dict, x4->x264_params, "=", ":", 0)) {
while ((en = av_dict_get(dict, "", en, AV_DICT_IGNORE_SUFFIX))) {
if (x264_param_parse(&x4->params, en->key, en->value) < 0)
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_WARNING,
"Error parsing option '%s = %s'.\n",
en->key, en->value);
}
av_dict_free(&dict);
}
}
// update AVCodecContext with x264 parameters
avctx->has_b_frames = x4->params.i_bframe ?
x4->params.i_bframe_pyramid ? 2 : 1 : 0;
if (avctx->max_b_frames < 0)
avctx->max_b_frames = 0;
avctx->bit_rate = x4->params.rc.i_bitrate*1000;
//-------------------------
//設定完引數後,開啟編碼器
x4->enc = x264_encoder_open(&x4->params);
if (!x4->enc)
return -1;
avctx->coded_frame = av_frame_alloc();
if (!avctx->coded_frame)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
//如果需要全域性頭
if (avctx->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER) {
x264_nal_t *nal;
uint8_t *p;
int nnal, s, i;
s = x264_encoder_headers(x4->enc, &nal, &nnal);
avctx->extradata = p = av_malloc(s);
for (i = 0; i < nnal; i++) {
/* Don't put the SEI in extradata. */
if (nal[i].i_type == NAL_SEI) {
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, "%s\n", nal[i].p_payload+25);
x4->sei_size = nal[i].i_payload;
x4->sei = av_malloc(x4->sei_size);
memcpy(x4->sei, nal[i].p_payload, nal[i].i_payload);
continue;
}
memcpy(p, nal[i].p_payload, nal[i].i_payload);
p += nal[i].i_payload;
}
avctx->extradata_size = p - avctx->extradata;
}
return 0;
}
從原始碼可以看出,X264_init()主要將各種選項值傳遞給libx264。這些選項有兩個來源:AVCodecContext和X264Context。AVCodecContext中包含了編碼器的一些通用選項,而X264Context包含了一些libx264特有的選項。在這裡需要注意,FFmpeg中的一些選項的單位和libx264中對應選項的單位是不一樣的,因此需要做一些轉換。例如畫素格式的轉換函式convert_pix_fmt()就是完成了這個功能。該函式的定義如下所示。
//對映FFmpeg和libx264的畫素格式
static int convert_pix_fmt(enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt)
{
switch (pix_fmt) {
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P:
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ420P:
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P9:
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P10: return X264_CSP_I420;
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P:
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ422P:
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV422P10: return X264_CSP_I422;
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P:
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUVJ444P:
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P9:
case AV_PIX_FMT_YUV444P10: return X264_CSP_I444;
#ifdef X264_CSP_BGR
case AV_PIX_FMT_BGR24:
return X264_CSP_BGR;
case AV_PIX_FMT_RGB24:
return X264_CSP_RGB;
#endif
case AV_PIX_FMT_NV12: return X264_CSP_NV12;
case AV_PIX_FMT_NV16:
case AV_PIX_FMT_NV20: return X264_CSP_NV16;
};
return 0;
}
可以看出convert_pix_fmt()將AV_PIX_FMT_XXX轉換成了X264_CSP_XXX。
在一切引數設定完畢後,X264_init()會呼叫x264_encoder_open()開啟編碼器,完成初始化工作。
X264_frame()
X264_frame()用於編碼一幀視訊資料。該函式的定義如下所示。//libx264編碼1幀資料
//
// AVFrame --> x264_picture_t --> x264_nal_t --> AVPacket
//
static int X264_frame(AVCodecContext *ctx, AVPacket *pkt, const AVFrame *frame,
int *got_packet)
{
X264Context *x4 = ctx->priv_data;
x264_nal_t *nal;
int nnal, i, ret;
x264_picture_t pic_out = {0};
AVFrameSideData *side_data;
x264_picture_init( &x4->pic );
x4->pic.img.i_csp = x4->params.i_csp;
if (x264_bit_depth > 8)
x4->pic.img.i_csp |= X264_CSP_HIGH_DEPTH;
x4->pic.img.i_plane = avfmt2_num_planes(ctx->pix_fmt);
if (frame) {
//將AVFrame中的資料賦值給x264_picture_t
//
// AVFrame --> x264_picture_t
//
for (i = 0; i < x4->pic.img.i_plane; i++) {
x4->pic.img.plane[i] = frame->data[i];
x4->pic.img.i_stride[i] = frame->linesize[i];
}
x4->pic.i_pts = frame->pts;
//設定幀型別
x4->pic.i_type =
frame->pict_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I ? X264_TYPE_KEYFRAME :
frame->pict_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_P ? X264_TYPE_P :
frame->pict_type == AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B ? X264_TYPE_B :
X264_TYPE_AUTO;
//檢查引數設定是否正確,不正確就重新設定
if (x4->avcintra_class < 0) {
if (x4->params.b_interlaced && x4->params.b_tff != frame->top_field_first) {
x4->params.b_tff = frame->top_field_first;
x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params);
}
if (x4->params.vui.i_sar_height != ctx->sample_aspect_ratio.den ||
x4->params.vui.i_sar_width != ctx->sample_aspect_ratio.num) {
x4->params.vui.i_sar_height = ctx->sample_aspect_ratio.den;
x4->params.vui.i_sar_width = ctx->sample_aspect_ratio.num;
x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params);
}
if (x4->params.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size != ctx->rc_buffer_size / 1000 ||
x4->params.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate != ctx->rc_max_rate / 1000) {
x4->params.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size = ctx->rc_buffer_size / 1000;
x4->params.rc.i_vbv_max_bitrate = ctx->rc_max_rate / 1000;
x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params);
}
if (x4->params.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_ABR &&
x4->params.rc.i_bitrate != ctx->bit_rate / 1000) {
x4->params.rc.i_bitrate = ctx->bit_rate / 1000;
x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params);
}
if (x4->crf >= 0 &&
x4->params.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CRF &&
x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant != x4->crf) {
x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant = x4->crf;
x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params);
}
if (x4->params.rc.i_rc_method == X264_RC_CQP &&
x4->cqp >= 0 &&
x4->params.rc.i_qp_constant != x4->cqp) {
x4->params.rc.i_qp_constant = x4->cqp;
x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params);
}
if (x4->crf_max >= 0 &&
x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant_max != x4->crf_max) {
x4->params.rc.f_rf_constant_max = x4->crf_max;
x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params);
}
}
side_data = av_frame_get_side_data(frame, AV_FRAME_DATA_STEREO3D);
if (side_data) {
AVStereo3D *stereo = (AVStereo3D *)side_data->data;
int fpa_type;
switch (stereo->type) {
case AV_STEREO3D_CHECKERBOARD:
fpa_type = 0;
break;
case AV_STEREO3D_COLUMNS:
fpa_type = 1;
break;
case AV_STEREO3D_LINES:
fpa_type = 2;
break;
case AV_STEREO3D_SIDEBYSIDE:
fpa_type = 3;
break;
case AV_STEREO3D_TOPBOTTOM:
fpa_type = 4;
break;
case AV_STEREO3D_FRAMESEQUENCE:
fpa_type = 5;
break;
default:
fpa_type = -1;
break;
}
if (fpa_type != x4->params.i_frame_packing) {
x4->params.i_frame_packing = fpa_type;
x264_encoder_reconfig(x4->enc, &x4->params);
}
}
}
do {
//[libx264 API] 編碼
//
// x264_picture_t --> x264_nal_t
//
if (x264_encoder_encode(x4->enc, &nal, &nnal, frame? &x4->pic: NULL, &pic_out) < 0)
return -1;
//把x264_nal_t賦值給AVPacket
//
// x264_nal_t --> AVPacket
//
ret = encode_nals(ctx, pkt, nal, nnal);
if (ret < 0)
return -1;
} while (!ret && !frame && x264_encoder_delayed_frames(x4->enc));
//賦值AVPacket相關的欄位
pkt->pts = pic_out.i_pts;
pkt->dts = pic_out.i_dts;
switch (pic_out.i_type) {
case X264_TYPE_IDR:
case X264_TYPE_I:
ctx->coded_frame->pict_type = AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I;
break;
case X264_TYPE_P:
ctx->coded_frame->pict_type = AV_PICTURE_TYPE_P;
break;
case X264_TYPE_B:
case X264_TYPE_BREF:
ctx->coded_frame->pict_type = AV_PICTURE_TYPE_B;
break;
}
pkt->flags |= AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY*pic_out.b_keyframe;
if (ret)
ctx->coded_frame->quality = (pic_out.i_qpplus1 - 1) * FF_QP2LAMBDA;
*got_packet = ret;
return 0;
}
從原始碼可以看出,X264_frame()呼叫x264_encoder_encode()完成了編碼工作。x264_encoder_encode()的輸入是x264_picture_t,輸出是x264_nal_t;而X264_frame()的輸入是AVFrame,輸出是AVPacket。因此X264_frame()在呼叫編碼函式前將AVFrame轉換成了x264_picture_t,而在呼叫編碼函式之後呼叫encode_nals()將x264_nal_t轉換成了AVPacket。轉換函式encode_nals()的定義如下所示。
//把x264_nal_t賦值給AVPacket
//
// x264_nal_t --> AVPacket
//
static int encode_nals(AVCodecContext *ctx, AVPacket *pkt,
const x264_nal_t *nals, int nnal)
{
X264Context *x4 = ctx->priv_data;
uint8_t *p;
int i, size = x4->sei_size, ret;
if (!nnal)
return 0;
//NALU的大小
//可能有多個NALU
for (i = 0; i < nnal; i++)
size += nals[i].i_payload;
if ((ret = ff_alloc_packet2(ctx, pkt, size)) < 0)
return ret;
//p指向AVPacket的data
p = pkt->data;
/* Write the SEI as part of the first frame. */
if (x4->sei_size > 0 && nnal > 0) {
if (x4->sei_size > size) {
av_log(ctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error: nal buffer is too small\n");
return -1;
}
memcpy(p, x4->sei, x4->sei_size);
p += x4->sei_size;
x4->sei_size = 0;
av_freep(&x4->sei);
}
//拷貝x264_nal_t的資料至AVPacket的資料
//可能有多個NALU
for (i = 0; i < nnal; i++){
memcpy(p, nals[i].p_payload, nals[i].i_payload);
p += nals[i].i_payload;
}
return 1;
}
從原始碼可以看出,encode_nals()的作用就是將多個x264_nal_t合併為一個AVPacket。
X264_close()
X264_close()用於關閉libx264解碼器。該函式的定義如下所示。//libx264關閉解碼器
static av_cold int X264_close(AVCodecContext *avctx)
{
X264Context *x4 = avctx->priv_data;
av_freep(&avctx->extradata);
av_freep(&x4->sei);
//[libx264 API] 關閉解碼器
if (x4->enc)
x264_encoder_close(x4->enc);
av_frame_free(&avctx->coded_frame);
return 0;
}
可以看出X264_close()呼叫x264_encoder_close()關閉了libx264編碼器。
雷霄驊
[email protected]
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020