第十七週作業
姓名:鄒豐蔚
學號:201771010138
實驗十七 執行緒同步控制
實驗時間 2018-12-10
1、實驗目的與要求
(1) 掌握執行緒同步的概念及實現技術;
(2) 執行緒綜合程式設計練習
2、實驗內容和步驟
實驗1:測試程式並進行程式碼註釋。
測試程式1:
l 在Elipse環境下除錯教材651頁程式14-7,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 掌握利用鎖物件和條件物件實現的多執行緒同步技術。
package synch; import java.util.*; import java.util.concurrent.locks.*; /** * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses locks for serializing access. * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Bank { private final double[] accounts; private Lock bankLock; private Condition sufficientFunds; /** * Constructs the bank. * @param n the number of accounts * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account*/ public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) { accounts = new double[n]; Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); bankLock = new ReentrantLock(); sufficientFunds = bankLock.newCondition(); } /** * Transfers money from one account to another. * @param from the account to transfer from * @param to the account to transfer to * @param amount the amount to transfer*/ public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException//通過鎖物件生成條件物件 { bankLock.lock();//加鎖 try { while (accounts[from] < amount) sufficientFunds.await();//條件物件如果被註釋會出現死鎖現象不能實現執行緒的有效呼叫 System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); accounts[from] -= amount; System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); accounts[to] += amount; System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); sufficientFunds.signal(); } finally { bankLock.unlock(); } } /** * Gets the sum of all account balances. * @return the total balance */ public double getTotalBalance() { bankLock.lock(); try { double sum = 0; for (double a : accounts) sum += a; return sum; } finally { bankLock.unlock(); } } /** * Gets the number of accounts in the bank. * @return the number of accounts */ public int size() { return accounts.length; } }
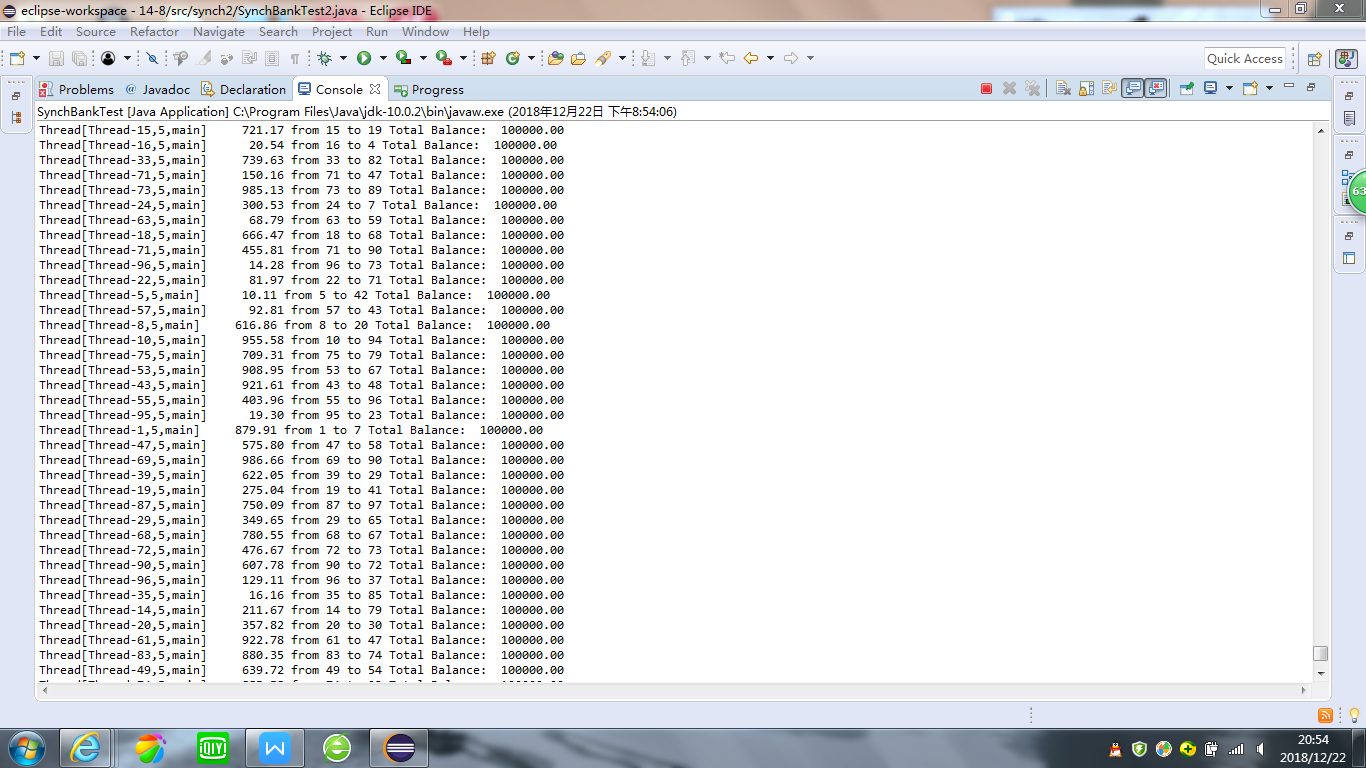
package synch; /** * This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure. * @version 1.31 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class SynchBankTest { public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100; public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000; public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 10; public static void main(String[] args) { Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE); for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) { int fromAccount = i; Runnable r = () -> { try { while (true) { int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random()); double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random(); bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount); Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random())); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }; Thread t = new Thread(r); t.start(); } } }

測試程式2:
l 在Elipse環境下除錯教材655頁程式14-8,結合程式執行結果理解程式;
l 掌握synchronized在多執行緒同步中的應用。
package synch2; import java.util.*; /** * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses synchronization primitives. * @version 1.30 2004-08-01 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Bank { private final double[] accounts; /** * Constructs the bank. * @param n the number of accounts * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account */ public Bank(int n, double initialBalance) { accounts = new double[n]; Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance); } /** * Transfers money from one account to another. * @param from the account to transfer from * @param to the account to transfer to * @param amount the amount to transfer */ public synchronized void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException { while (accounts[from] < amount) wait(); /* 該方法屬於Object的方法,wait方法的作用是使得當前呼叫wait方法所在部分(程式碼塊)的執行緒停止執行, 並釋放當前獲得的呼叫wait所在的程式碼塊的鎖,並在其他執行緒呼叫notify或者notifyAll方法時恢復到競爭鎖狀態(一旦獲得鎖就恢復執行)。*/ System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()); accounts[from] -= amount; System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to); accounts[to] += amount; System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance()); notifyal(); } private void notifyal() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } private void notifyA() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } /** * Gets the sum of all account balances. * @return the total balance */ public synchronized double getTotalBalance() { double sum = 0; for (double a : accounts) sum += a; return sum; } /** * Gets the number of accounts in the bank. * @return the number of accounts */ public int size() { return accounts.length; } }
package synch2; /** * This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure, * using synchronized methods. * @version 1.31 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class SynchBankTest2 { public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100; public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000; public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000; public static final int DELAY = 10; public static void main(String[] args) { Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE); for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++) { int fromAccount = i; Runnable r = () -> { try { while (true) { int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random()); double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random(); bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount); Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random())); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }; Thread t = new Thread(r); t.start(); } } }
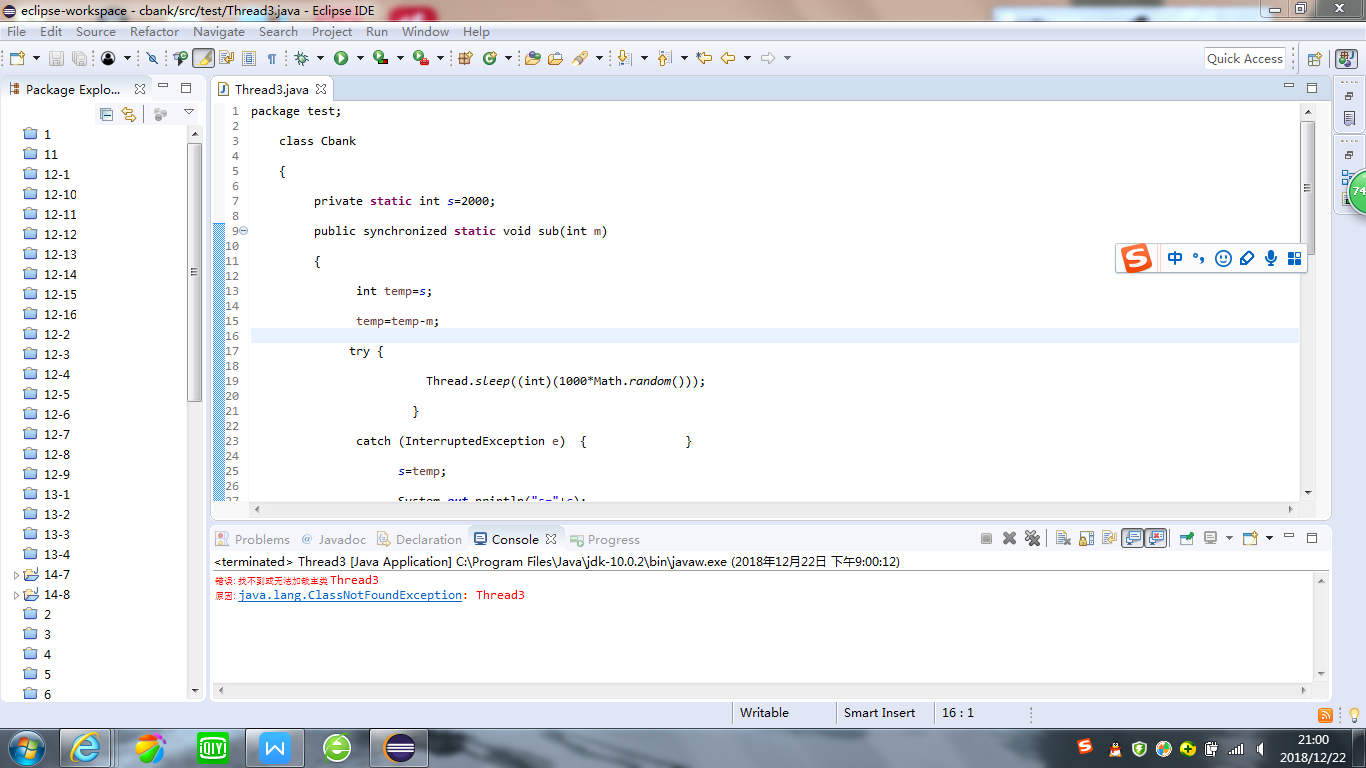
測試程式3:
l 在Elipse環境下執行以下程式,結合程式執行結果分析程式存在問題;
l 嘗試解決程式中存在問題。
class test { private static int s=2000; public static void sub(int m) { int temp=s; temp=temp-m; try { Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } s=temp; System.out.println("s="+s); } } class Customer extends Thread { public void run() { for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) Cbank.sub(100); } } public class Thread3 { public static void main(String args[]) { Customer customer1 = new Customer(); Customer customer2 = new Customer(); customer1.start(); customer2.start(); } }
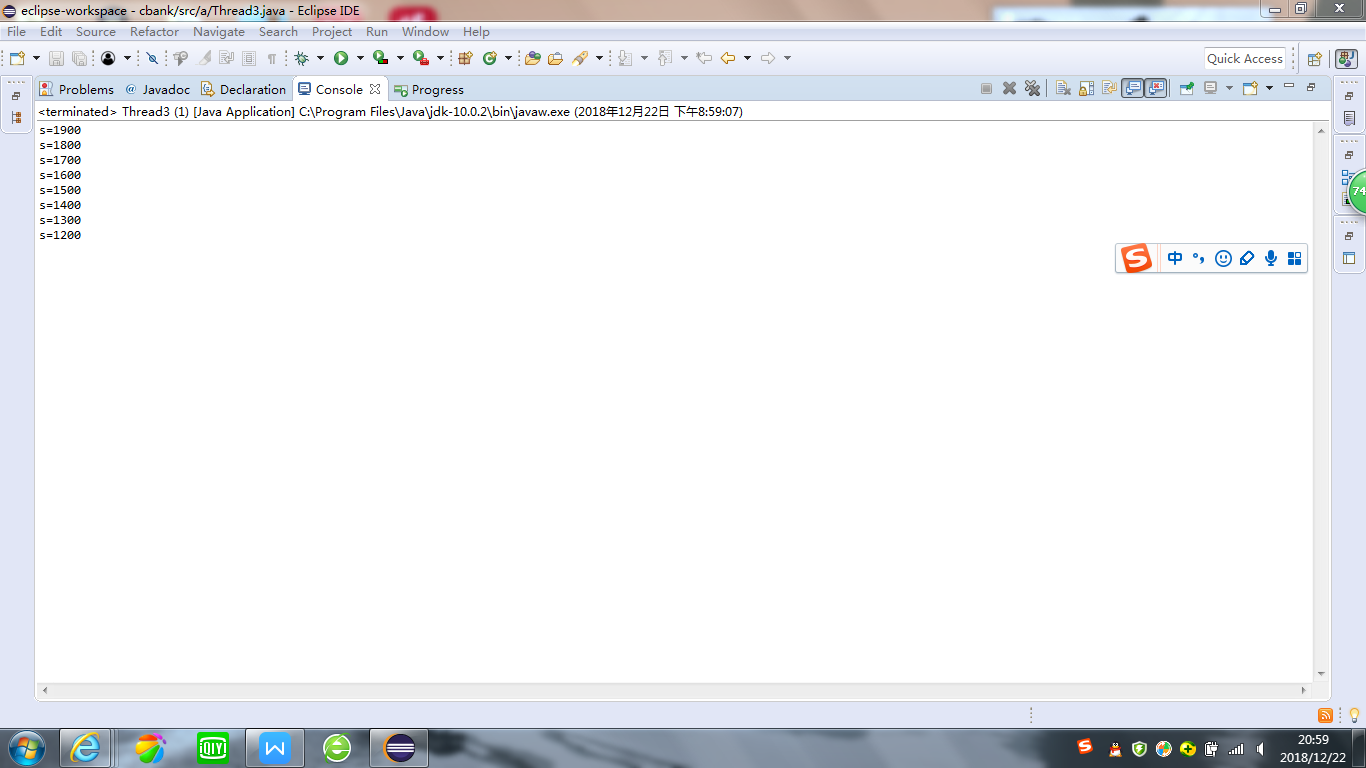
修改之後:
package test; class Cbank { private static int s=2000; public synchronized static void sub(int m) { int temp=s; temp=temp-m; try { Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } s=temp; System.out.println("s="+s); } } class Customer extends Thread { public void run() { for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) Cbank.sub(100); } } public class Thread3 { public static void main(String args[]) { Customer customer1 = new Customer(); Customer customer2 = new Customer(); customer1.start(); customer2.start(); } }
實驗2 程式設計練習
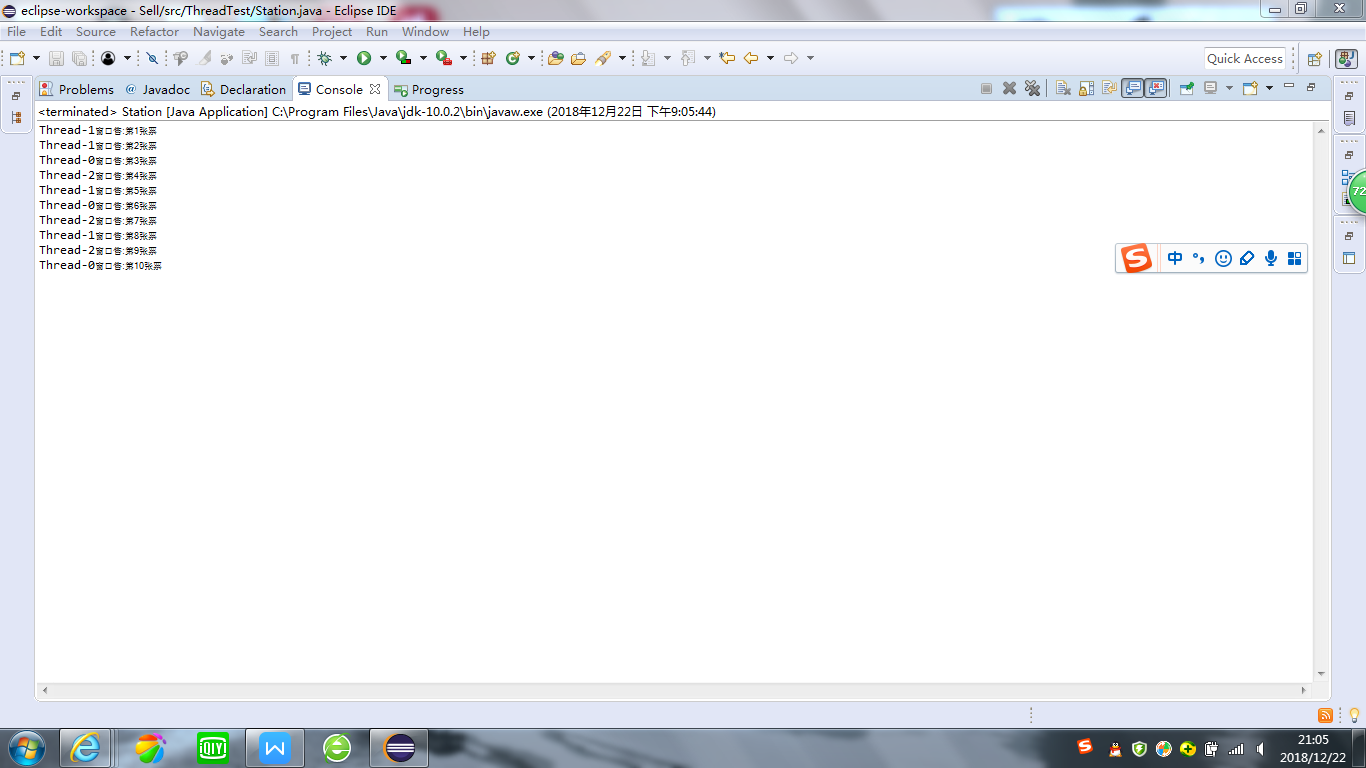
利用多執行緒及同步方法,編寫一個程式模擬火車票售票系統,共3個視窗,賣10張票,程式輸出結果類似(程式輸出不唯一,可以是其他類似結果)。
Thread-0視窗售:第1張票
Thread-0視窗售:第2張票
Thread-1視窗售:第3張票
Thread-2視窗售:第4張票
Thread-2視窗售:第5張票
Thread-1視窗售:第6張票
Thread-0視窗售:第7張票
Thread-2視窗售:第8張票
Thread-1視窗售:第9張票
Thread-0視窗售:第10張票
package ThreadTest; public class Station extends Thread{ public Station(String name) { super(name); } static int tickers=1; static Object ob="a";//指定一個共用物件 //重寫run操作,實現賣票 @Override public void run() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.run(); while(tickers<=10){ synchronized (ob) { if(tickers<=10){ System.out.println(getName()+"視窗售:第"+tickers+"張票"); tickers++; } } try { sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { Station station1=new Station("Thread-0"); Station station2=new Station("Thread-1"); Station station3=new Station("Thread-2"); station1.start(); station2.start(); station3.start(); } }
學習總結:
1.執行緒同步
(1)多執行緒併發執行不確定性問題解決方案:引入線 程同步機制,使得另一執行緒要使用該方法,就只 能等待
(2)在Java中解決多執行緒同步問題的方法有兩種:
解決方案一:鎖物件與條件物件
用ReentrantLock保護程式碼塊的基本結構如下: myLock.lock();
try { critical section }
finally{ myLock.unlock(); }
(3)解決方案二: synchronized關鍵字
synchronized關鍵字作用: ➢ 某個類內方法用synchronized 修飾後,該方 法被稱為同步方法
2.Java通過多執行緒的併發執行提高系統資源利用 率,改善系統性能。
3.假設有兩個或兩個以上的執行緒共享 某個物件,每個執行緒都呼叫了改變該物件類狀態的方法,就會引起的不確定性。
4.多執行緒併發執行中的問題
多個執行緒相對執行的順序是不確定的。
執行緒執行順序的不確定性會產生執行結果的不確定性。
在多執行緒對共享資料操作時常常會產生這種不確定性。
5.多執行緒併發執行不確定性問題解決方案:引入執行緒同步機制。
這次實驗我掌握了利用鎖物件和條件物件實現的多執行緒同步技術。這次實驗是最後一次實驗了,回想一個學期的學習,我學到了很多。感謝老師和學長的幫助。
