Factorization Machines簡介與程式碼實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-23
介紹
FM是聯合SVM與因式分解模型的優點所得。在有比較大的資料稀疏情況下,也能從中找出聯絡。FM可以線上性時間內優化。
優點
-
可以在非常稀疏的資料中進行合理的引數估計
-
FM模型的時間複雜度是線性的
-
FM是一個通用模型,它可以用於任何特徵為實值的情況
特徵向量例子
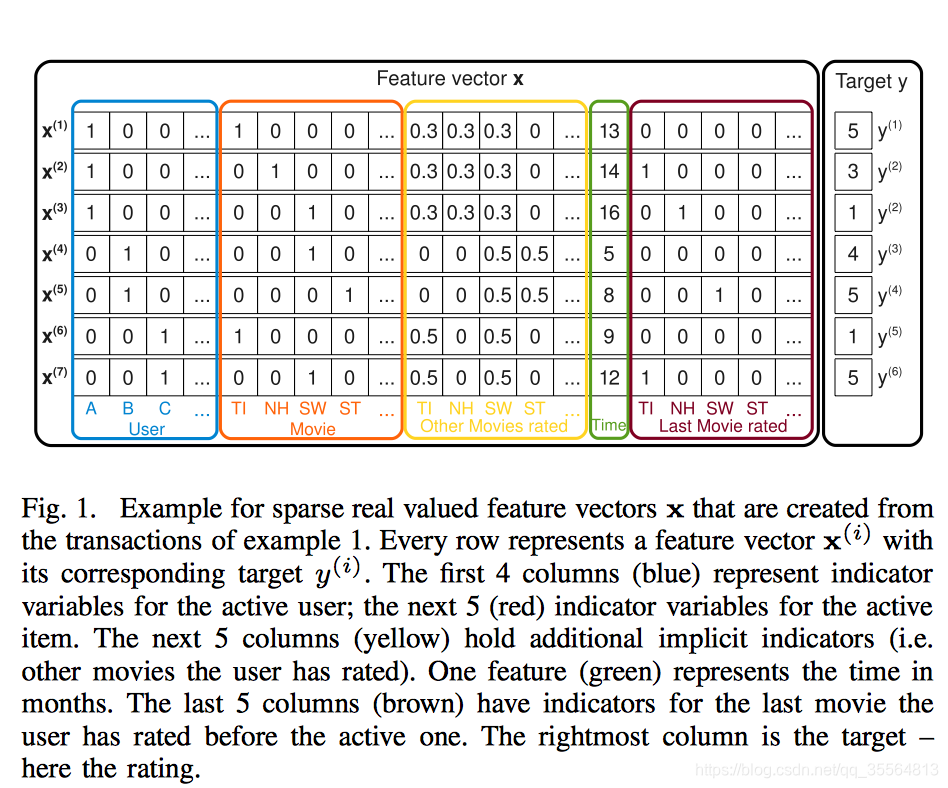
演算法原理
- model equation:
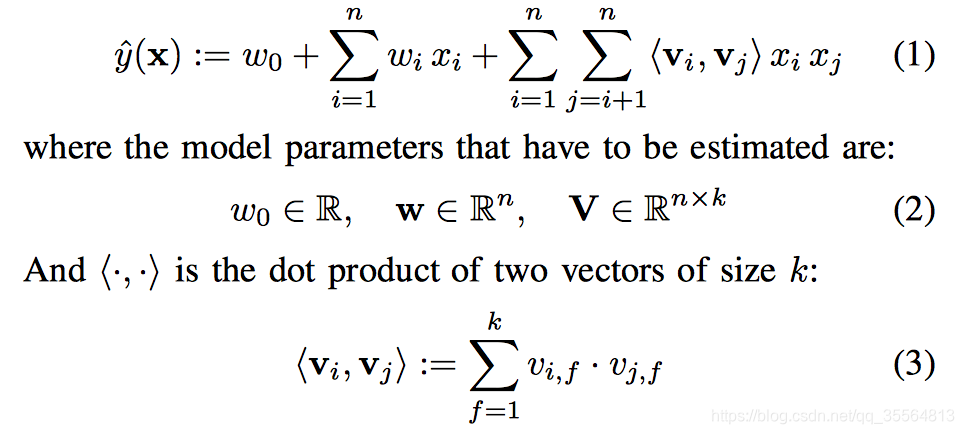
- Expressiveness:
對於一個W總是存在 ,也就說對於任何W只要V的列k取得適當,總是能從 獲得。但是在資料非常稀疏的時候,因為沒有足夠的資料來得到W,那麼就可以通過 ,V的k取得足夠小來得到W。
- Parameter Estimation Under Sparsity:
因為FM的因式分解,打破了變數之間的獨立性,使我們可以通過一個互動來估計相關互動的引數
- Computation:
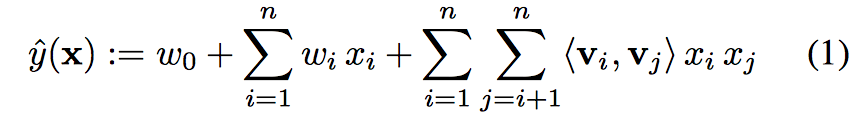
對於上述公式,時間複雜度是O(k )
但是對於上述公式成對互動可以重新化簡為:
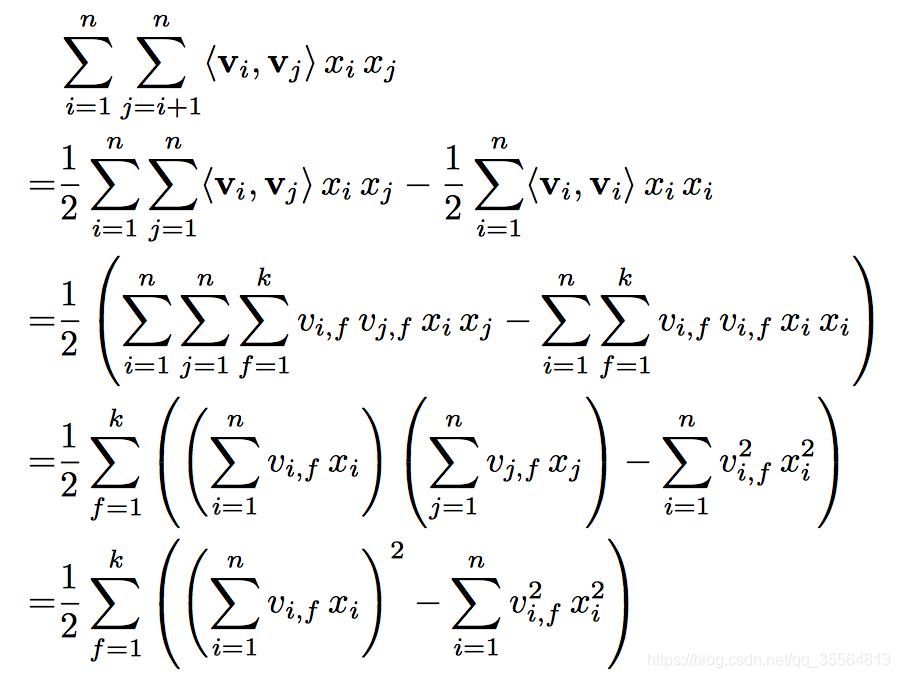
第一步推導可以從下圖得出:
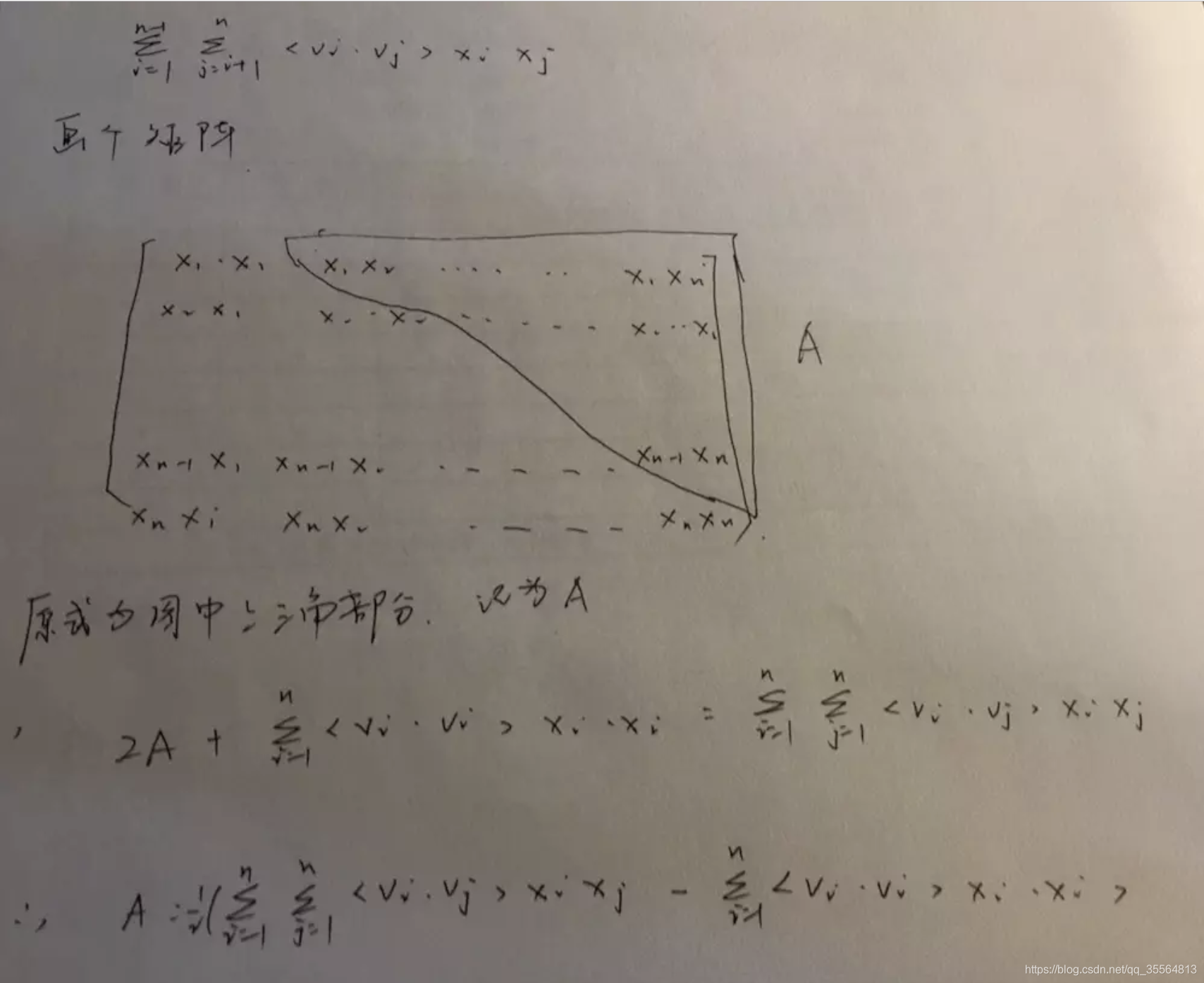
則複雜度變為了O(kn)
FM as Predictor
-
可以做迴歸
-
二分類
-
排序
上述都可以使用L2正則來優化防止過擬合
Learning FM
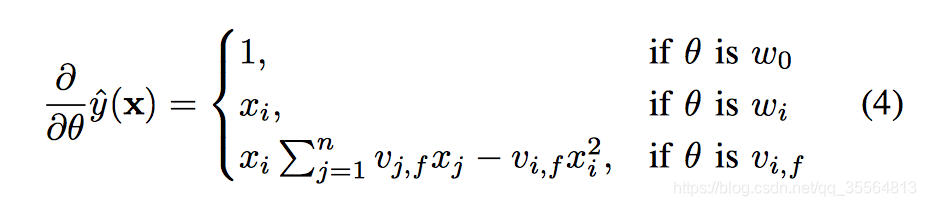
利用梯度來更新
程式碼實現
簡單資料:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
x_data = np.matrix([
# Users | Movies | Movie Ratings | Time | Last Movies Rated
# A B C | TI NH SW ST | TI NH SW ST | | TI NH SW ST
[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0, 13, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0, 14, 1, 0, 0, 0 ],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 0, 16, 0, 1, 0, 0 ],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0.5, 0.5, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0.5, 0.5, 8, 0, 0, 1, 0 ],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0.5, 0, 0.5, 0, 9, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0.5, 0, 0.5, 0, 12, 1, 0, 0, 0 ]
])
# ratings
y_data = np.array([5, 3, 1, 4, 5, 1, 5])
# Let's add an axis to make tensoflow happy.
y_data.shape += (1, )
n, p = x_data.shape
# number of latent factors
k = 5
# design matrix
X = tf.placeholder('float32', [n, p])
# target vector
y = tf.placeholder('float32', [n, 1])
# bias and weights
w0 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([p]))
# interaction factors, randomly initialized
V = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([k, p], stddev=0.01))
# estimate of y, initialized to 0.
y_hat = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n, 1]))
linear_terms = tf.add(w0,
tf.reduce_sum(
tf.multiply(W, X), 1, keepdims=True))
interactions = (tf.multiply(0.5,
tf.reduce_sum(
tf.subtract(
tf.pow(tf.matmul(X, tf.transpose(V)), 2),
tf.matmul(tf.pow(X, 2), tf.transpose(tf.pow(V, 2)))),
1, keepdims=True)))
y_hat = tf.add(linear_terms, interactions)
# L2 regularized sum of squares loss function over W and V
lambda_w = tf.constant(0.001, name='lambda_w')
lambda_v = tf.constant(0.001, name='lambda_v')
l2_norm = (tf.reduce_sum(
tf.add(
tf.multiply(lambda_w, tf.pow(W, 2)),
tf.multiply(lambda_v, tf.pow(V, 2)))))
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(tf.subtract(y, y_hat)))
loss = tf.add(error, l2_norm)
eta = tf.constant(0.1)
optimizer = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(eta).minimize(loss)
# that's a lot of iterations
N_EPOCHS = 1000
# Launch the graph.
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(N_EPOCHS):
# indices = np.arange(n)
# np.random.shuffle(indices)
# x_data, y_data = x_data[indices], y_data[indices]
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={X: x_data, y: y_data})
print('MSE: ', sess.run(error, feed_dict={X: x_data, y: y_data}))
print('Loss (regularized error):', sess.run(loss, feed_dict={X: x_data, y: y_data}))
print('Predictions:', sess.run(y_hat, feed_dict={X: x_data, y: y_data}))
print('Learnt weights:', sess.run(W, feed_dict={X: x_data, y: y_data}))
print('Learnt factors:', sess.run(V, feed_dict={X: x_data, y: y_data}))
複雜資料版:使用資料來自MovieLens100K Dataset
from scipy.sparse import csr
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
def vectorize_dic(dic,ix=None,p=None,n=0,g=0):
"""
dic -- dictionary of feature lists. Keys are the name of features
ix -- index generator (default None)
p -- dimension of feature space (number of columns in the sparse matrix) (default None)
"""
if ix==None:
ix = dict()
nz = n * g
col_ix = np.empty(nz,dtype = int)
i = 0
numofUsers=0
flag=True
for k,lis in dic.items():
for t in range(len(lis)):
if k=='users':
ix[str(lis[t]) + str(k)] = ix.get(str(lis[t]) + str(k),lis[t]-1)
elif k=='items':
if flag==True:
numofUsers=len(ix)
flag=False
ix[str(lis[t]) + str(k)] = lis[t]-1+numofUsers
col_ix[i+t*g] = ix[str(lis[t]) + str(k)]
i += 1
row_ix = np.repeat(np.arange(0,n),g)
data = np.ones(nz)
if p == None:
p = len(ix)
ixx = np.where(col_ix < p)
return csr.csr_matrix((data[ixx],(row_ix[ixx],col_ix[ixx])),shape=(n,p)),ix
#where data, row_ind and col_ind satisfy the relationship a[row_ind[k], col_ind[k]] = data[k].
def batcher(X_, y_=None, batch_size=-1):
n_samples = X_.shape[0]
if batch_size == -1:
batch_size = n_samples
if batch_size < 1:
raise ValueError('Parameter batch_size={} is unsupported'.format(batch_size))
for i in range(0, n_samples, batch_size):
upper_bound = min(i + batch_size, n_samples)
ret_x = X_[i:upper_bound]
if y_ is not None:
ret_y = y_[i:upper_bound]
yield (ret_x, ret_y)
cols = ['user','item','rating','timestamp']
train = pd.read_csv('ua.base',delimiter='\t',names = cols)
test = pd.read_csv('ua.test',delimiter='\t',names = cols)
x_train,ix = vectorize_dic({'users':train['user'].values,
'items':train['item'].values},n=len(train.index),g=2)
x_test,ix = vectorize_dic({'users':test['user'].values,
'items':test['item'].values},ix,x_train.shape[1],n=len(test.index),g=2)
y_train = train['rating'].values
y_test = test['rating'].values
x_train = x_train.todense()
x_test = x_test.todense()
n,p = x_train.shape
k = 10
x = tf.placeholder('float',[None,p])
y = tf.placeholder('float',[None,1])
w0 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
w = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([p]))
v = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([k,p],mean=0,stddev=0.01))
#y_hat = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n,1]))
linear_terms = tf.add(w0,tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(w,x),1,keepdims=True)) # n * 1
pair_interactions = 0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(
tf.subtract(
tf.pow(
tf.matmul(x,tf.transpose(v)),2),
tf.matmul(tf.pow(x,2),tf.transpose(tf.pow(v,2)))
),axis = 1 , keepdims=True)
y_hat = tf.add(linear_terms,pair_interactions)
lambda_w = tf.constant(0.001,name='lambda_w')
lambda_v = tf.constant(0.001,name='lambda_v')
l2_norm = tf.reduce_sum(
tf.add(
tf.multiply(lambda_w,tf.pow(w,2)),
tf.multiply(lambda_v,tf.pow(v,2))
)
)
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_hat))
loss = tf.add(error,l2_norm)
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(loss)
epochs = 10
batch_size = 1000
# Launch the graph
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(epochs):
perm = np.random.permutation(x_train.shape[0])
# iterate over batches
for bX, bY in batcher(x_train[perm], y_train[perm], batch_size):
_,t = sess.run([train_op,loss], feed_dict={x: bX.reshape(-1, p), y: bY.reshape(-1, 1)})
print(t)
print('MSE: ', sess.run(error, feed_dict={x: x_test.reshape(-1, p), y: y_test.reshape(-1, 1)}))
print('Predictions:', sess.run(y_hat, feed_dict={x: x_test.reshape(-1, p), y: y_test.reshape(-1, 1)}))
