最短尋道時間優先演算法(SSTF)&&掃描演算法(SCAN)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-26
最短尋道時間優先演算法(SSTF)
- SSTF問題描述:SSTF演算法選擇排程處理的磁軌是與當前磁頭所在磁軌距離最近的磁軌,以使每次的尋找時間最短。當然,總是選擇最小尋找時間並不能保證平均尋找時間最小,但是能提供比FCFS演算法更好的效能。這種演算法會產生“飢餓”現象。
-
1、演算法思想:優先選擇距當前磁頭最近的訪問請求進行服務,主要考慮尋道優先。
2、優點:改善了磁碟平均服務時間。
3、缺點:造成某些訪問請求長期等待得不到服務。
-
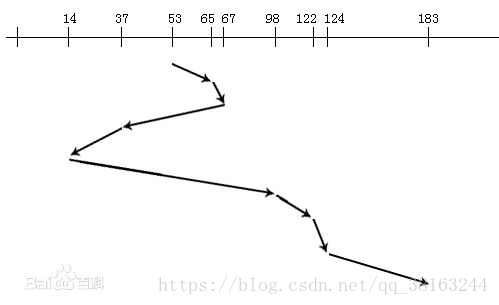
本演算法是對輸入的磁軌首先進行非遞減排序,然後判斷當前磁頭所在的磁軌是否在將要尋找的磁軌中,分別進行最短尋道時間計算。(如下圖示,表示SSTF示意圖)
-
-
//最短尋道時間優先SSTF #include "pch.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; //快速排序 int Partition(int *p, int low, int high) { int i = low, j = high, pivot = p[low]; while (i < j) { while (i < j&&p[j] >= pivot) { j--; } if (i < j) { p[i] = p[j]; i++; } while (i < j&&p[i] <= pivot) { i++; } if (i < j) { p[j] = p[i]; j--; } } p[i] = pivot; return i; } void QuickSort(int *q, int left, int right) { if (left < right) { int pivotpos = Partition(q, left, right); QuickSort(q, left, pivotpos - 1); QuickSort(q, pivotpos + 1, right); } } int main() { int count = 0;//輸入磁碟請求的個數 int currentStair;//當前所在的磁軌 int n; int temp_1, temp_2; int size = 0;//步數計數變數 int temp_3, temp_4; cout << "請輸入要尋到的數量:" << endl; cin >> count; n = count; int *arr = new int[count]; cout << "請輸入要尋得磁軌:" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { cin >> arr[i];//輸入樓梯數 } cout << "please input currentstars:" << endl; cin >> currentStair; QuickSort(arr, 0, count - 1); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)//當前磁軌在要尋磁軌中 { if (currentStair == arr[i]) { currentStair = arr[i]; temp_1 = i - 1; temp_2 = temp_1 + 1; while (temp_1 >= 0 && temp_2 < count) { if (abs(currentStair - arr[temp_1]) < abs(arr[temp_2] - currentStair)) { size += abs(currentStair - arr[temp_1]); currentStair = arr[temp_1]; if (temp_1 > 0) temp_1 -= 1; if (currentStair == arr[temp_1]) { while (temp_2 < count) { size += abs(arr[temp_2] - currentStair); currentStair = arr[temp_2]; temp_2++; } } } else { size += abs(arr[temp_2] - currentStair); if (temp_2 < count) temp_2 += 1; if (currentStair == arr[temp_2]) { while (temp_1 > 0) { size += abs(arr[temp_1] - currentStair); currentStair = arr[temp_1]; temp_1--; } } } } } } for (int h = 0; h < count; h++)//當前所在的位置不在要尋的磁軌中 { if (currentStair > arr[h - 1] && currentStair < arr[h])//定位當前的位置 { temp_3 = h - 1; temp_4 = h; while (temp_3 >= 0 && temp_4 < count) { if (abs(currentStair - arr[temp_3]) < abs(arr[temp_4] - currentStair)) { size += abs(currentStair - arr[temp_3]); currentStair = arr[temp_3]; if (temp_3 > 0) temp_3 -= 1; if (currentStair == arr[temp_3]) { while (temp_4 < count) { size += arr[temp_4] - currentStair; currentStair = arr[temp_4]; temp_4++; } } } else { size += abs(arr[temp_4] - currentStair); currentStair = arr[temp_4]; if (temp_4 < count) temp_4 += 1; if (currentStair == arr[temp_4]) { while (temp_3 > 0) { size += arr[temp_3] - currentStair; currentStair = arr[temp_3]; temp_3--; } } } } } else if (currentStair < arr[0]) { int i = 0; while (i < count) { size += abs(arr[i] - currentStair); currentStair = arr[i]; i++; } } else if (currentStair > arr[count - 1]) { int j = count - 1; while (j > 0) { size += abs(arr[j] - currentStair); currentStair = arr[j]; j--; } } } int average = size / count; cout << "最少尋磁軌數是:"<<size<<"平均尋磁軌數是:"<<average<< endl; }掃描演算法(又稱電梯演算法)
掃描演算法問題描述:SCAN演算法在磁頭當前移動方向上選擇與當前磁頭所在磁軌距離最近的請求作為下一次服務的物件。由於磁頭移動規律與電梯執行相似,故又稱為電梯排程演算法。SCAN演算法對最近掃描過的區域不公平,因此,它在訪問區域性性方面不如FCFS演算法和SSTF演算法好。
演算法思想:當裝置無訪問請求時,磁頭不動;當有訪問請求時,磁頭按一個方向移動,在移 [2] 動過程中對遇到的訪問 請 求 進行服務,然後判斷該方向上是否還有訪問請求,如果有則繼續掃描;否則改變移動方向,併為經過的訪問請求服務,如此反覆 。
優點:克服了最短尋道優先的缺點,既考慮了距離,同時又考慮了方向。(如下圖表示SCAN圖示)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test_louti {
//本演算法我假設樓梯最大到200層,
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("please input your scan from 1 to 200:");
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
int []arr=new int[200];//200樓電梯
System.out.println("請輸入你要輸入的樓層數:");
int number=input.nextInt();//number記錄當前所在樓梯
int b=0;
System.out.println("請輸入樓梯:");
for(int i=0;i<=200;i++)
{
if(b<number){
int num=input.nextInt();
arr[num]=num;//記住樓梯,從小到大
b++;
i++;
}
if(b==number)
break;
}
System.out.println("請輸入當前樓梯號碼:");
int currentScan=input.nextInt();//當前樓梯
int i=currentScan,team=0,j=0,a=currentScan;
arr[currentScan]=currentScan;
while(i<200)//i記住當前判斷的樓梯號碼
{
if(arr[i]!=0)
{
team+=(arr[i]-arr[currentScan]);
currentScan=i;
j=i;//記住最後的樓梯號碼
}
i+=1;
}
//下半層
while(a>0)
{
if(arr[a]!=0)
{
team+=Math.abs((arr[a]-arr[j]));
j=a;
}
a-=1;
}
System.out.println("總的移動量是:"+team);
}
}
未完..............