ES6初步瞭解
慕課網視訊課程:https://www.imooc.com/learn/955
ES6可以參考資料:
http://es6.ruanyifeng.com/
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004365693?utm_source=tag-newest#articleHeader7
https://www.jianshu.com/p/287e0bb867ae
前端技術教程及文件:https://github.com/cucygh/fe-material
包括Git、Webpack、Paracle、Gulp、Grunt、Rollup、Browserify、Lerna、Eslint、http-server、ast、自動化測試、Vue、React、Angular、Riot、Koala、Express、Mobx、E下JS、Three.js、d3.js、HTML5動畫庫、視訊播放器、CSS教程、JavaScript教程、服務端教程、開源圖示、視訊技術、動畫技術和遊戲方向等等。
1.前言
jquery是es3
angular 、vue、react是es6
IE8不支援ES6,但是可以引入es5-sham.js和es5-shim.js就可以了
環境搭建:
安裝git
安裝完Git後,應該在Git Bash裡執行如下語句:
git clone https://www.github.com/cucygh/es6-webpack.git
克隆完後 cd es6-webpack
執行:npm install / npm i
等待安裝完成
npm i webpack -g
npm i webpack-dev-sever -g
執行:npm start
瀏覽器輸入localhost:9000就可以了。
2.常量
// ES5 中常量的寫法(通過設定writable屬性為false,不可寫來宣告常量)
Object.defineProperty(window, "PI2", {
value: 3.1415926,
writable: false,
})
console.log(window.PI2)
// ES6 的常量寫法(const)
const PI = 3.1415926
console.log(PI)
3.作用域
// ES5 中作用域 const callbacks = [] for (var i = 0; i <= 2; i++) { callbacks[i] = function() { return i * 2 } } console.table([ callbacks[0](), callbacks[1](), callbacks[2](), ])
輸出結果:

因為變數提升,var i宣告放在前面,所以是全域性變數,函式體內i是變數,返回的是變數i與2的乘積,i*2,最後()呼叫時候,i都是為3,所以最後輸出都是6.
或者這樣理解:第一個for迴圈的i,不要先去理解閉包,因為i是var定義,var沒有塊級作用域的改變,所以在for之前還能被訪問,而且for之外訪問的i肯定是for迴圈中最大的值,所以在for之後執行的那幾個callback函式,其實用的都是那個最大的i值
而let有塊級作用域,在for之外,根本就沒有let的存在
const callbacks2 = []
for (let j = 0; j <= 2; j++) {
callbacks2[j] = function() {
return j * 2
}
}
console.table([
callbacks2[0](),
callbacks2[1](),
callbacks2[2](),
])

用let宣告的變數有塊作用域的概念。他會把當前塊作用域的變數的值儲存下來供後面閉包使用,每迴圈一次生成一次新的作用域,閉包就倒向閉包作用域裡面的變數。
宣告一個函式,這個函式只能在這個程式碼塊中執行,ES5中可以用立即執行函式解決:
((function() {
const foo = function() {
return 1
}
console.log("foo()===1", foo() === 1);
((function() {
const foo = function() {
return 2
}
console.log("foo()===2", foo() === 2)
})())
})())
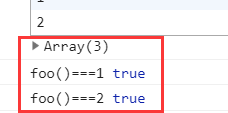
ES6中比較簡單,可以用{}就能指定一個作用域。
{
function foo() {
return 1
}
console.log("foo()===1", foo() === 1)
{
function foo() {
return 2
}
console.log("foo()===2", foo() === 2)
}
console.log("foo()===1", foo() === 1)
}
4.箭頭函式
箭頭函式:
function a(){
}
變成了:
//引數只有一個時候()可以省略,{}中的表示式直接作為返回值,也可以省略{}
()=>{
}
/* eslint-disable */
{
// ES3,ES5
var evens = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
var odds = evens.map(function(v) {
return v + 1
});
console.log(evens, odds);
};
{
// ES6 //引數只有一個時候()可以省略,{}中的表示式直接作為返回值,也可以省略{}
let evens = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let odds = evens.map(v => v + 1); // (v)=>{return v+1}
console.log(evens, odds);
}
//箭頭函式this指向問題
{
// ES3,ES5
var factory = function() {
this.a = 'a';
this.b = 'b';
this.c = {
a: 'a+',
b: function() {
return this.a
}
}
}
console.log(new factory().c.b());
};
{
//ES6
var factory = function() {
this.a = 'a';
this.b = 'b';
this.c = {
a: 'a+',
b: () => {
return this.a
}
}
}
console.log(new factory().c.b());
}
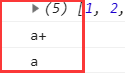
ES3、ES5中this是誰呼叫指向誰,ES6是定義時this的指向,指向new factory()的例項,所以是a。
5.預設引數/可變引數
{
// ES5\ES3 預設引數的寫法(通過判斷語句)
function f(x, y, z) {
if (y === undefined) {
y = 7;
}
if (z === undefined) {
z = 42
}
return x + y + z
}
console.log(f(1, 3));
}
//類似下面也可以
function a(x,y){
x = x||1;
y = y||2;
}
{
// ES6 預設引數
function f(x, y = 7, z = 42) {
return x + y + z
}
console.log(f(1, 3));
}
//對於函式必選引數的校驗
{
function checkParameter() {
throw new Error('can\'t be empty')
}
function f(x = checkParameter(), y = 7, z = 42) { //沒有x時,通過執行預設引數執行checkParameter函式
return x + y + z
}
console.log(f(1));
try {
f()
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
} finally {}
}
{
// ES3,ES5 可變引數
function f() {
var a = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
var sum = 0;
a.forEach(function(item) {
sum += item * 1;
})
return sum
}
console.log(f(1, 2, 3, 6));
}
{
// ES6 可變引數
function f(...a) {
var sum = 0;
a.forEach(item => {
sum += item * 1
});
return sum
}
console.log(f(1, 2, 3, 6));
}
{
// ES5 合併陣列
var params = ['hello', true, 7];
var other = [1, 2].concat(params);
console.log(other);
}
{
// ES6 利用擴充套件運算符合並陣列
var params = ['hello', true, 7];
var other = [
1, 2, ...params
];
console.log(other);
}
6.物件代理
/* eslint-disable */
// es3通過建構函式/this.get/this.set來資料保護
{
// ES3,ES5 資料保護
var Person = function() {
var data = {
name: 'es3',
sex: 'male',
age: 15
}
this.get = function(key) {
return data[key]
}
this.set = function(key, value) {
if (key !== 'sex') {
data[key] = value
}
}
}
// 宣告一個例項
var person = new Person();
// 讀取
console.table({name: person.get('name'), sex: person.get('sex'), age: person.get('age')});
// 修改
person.set('name', 'es3-cname');
console.table({name: person.get('name'), sex: person.get('sex'), age: person.get('age')});
person.set('sex', 'female');
console.table({name: person.get('name'), sex: person.get('sex'), age: person.get('age')});
}
//ES5通過Object.defineProperty定義來保護資料(只讀不寫就可以保護了)
{
// ES5
var Person = {
name: 'es5',
age: 15
};
Object.defineProperty(Person, 'sex', {
writable: false,
value: 'male'
});
console.table({name: Person.name, age: Person.age, sex: Person.sex});
Person.name = 'es5-cname';
console.table({name: Person.name, age: Person.age, sex: Person.sex});
try {
Person.sex = 'female';
console.table({name: Person.name, age: Person.age, sex: Person.sex});
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
}
//ES6通過 Proxy/set/get來資料保護
{
// ES6
let Person = {
name: 'es6',
sex: 'male',
age: 15
};
let person = new Proxy(Person, {
get(target, key) {
return target[key]
},
set(target,key,value){
if(key!=='sex'){
target[key]=value;
}
}
});
console.table({
name:person.name,
sex:person.sex,
age:person.age
});
try {
person.sex='female';
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
} finally {
}
}
ES6進階:解構賦值、模板字串、正則擴充套件、數字擴充套件、函式擴充套件、Class、Module、Symbol、物件擴充套件、Iterator、Set和Map、Generator等等。
