HDU 6000 Wash (雙二分+貪心)
Wash
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 64000/64000 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2613 Accepted Submission(s): 700
Problem Description
Mr.Panda is about to engage in his favourite activity doing laundry! He’s brought L indistinguishable loads of laundry to his local laundromat, which has N washing machines and M dryers.The ith washing machine takes Wi minutes to wash one load of laundry, and the ith dryer takes Di minutes to dry a load of laundry.
At any point in time, each machine may only be processing at most one load of laundry.
As one might expect, Panda wants to wash and then dry each of his L loads of laundry. Each load of laundry will go through the following steps in order:
1. A non-negative amount of time after Panda arrives at the laundromat, Panda places the load in an unoccupied washing machine i.
2. Wi minutes later, he removes the load from the washing machine, placing it in a temporary holding basket (which has unlimited space)
3. A non-negative amount of time later, he places the load in an unoccupied dryer j
4. Dj minutes later, he removes the load from the dryer Panda can instantaneously add laundry to or remove laundry from a machine. Help Panda minimize the amount of time (in minutes after he arrives at the laundromat) after which he can be done washing and drying all L loads of laundry!
Input
The first line of the input gives the number of test cases, T.
T test cases follow. Each test case consists of three lines. The first line contains three integer L, N, and M.
The second line contains N integers W1,W2,...,WN representing the wash time of each wash machine.
The third line contains M integers D1,D2,...,DM representing the dry time of each dryer.
Output
For each test case, output one line containing “Case #x: y”, where x is the test case number (starting from 1) and y is the minimum time it will take Panda to finish his laundry.
limits
∙1≤T≤100.
∙1≤L≤106.
∙1≤N,M≤105.
∙1≤Wi,Di≤109.
Sample Input
2 1 1 1 1200 34 2 3 2 100 10 1 10 10
Sample Output
Case #1: 1234 Case #2: 12
題意:
給你n(n<=1e6)件衣服,m(m<=1e5)臺洗衣機,n(n<=1e5)臺烘乾機。每臺洗衣機有洗一件衣服的時間a[i],每臺烘乾機有烘乾一件衣服的時間b[j],問你最快多長時間洗完n件衣服。時限10000ms
思路:
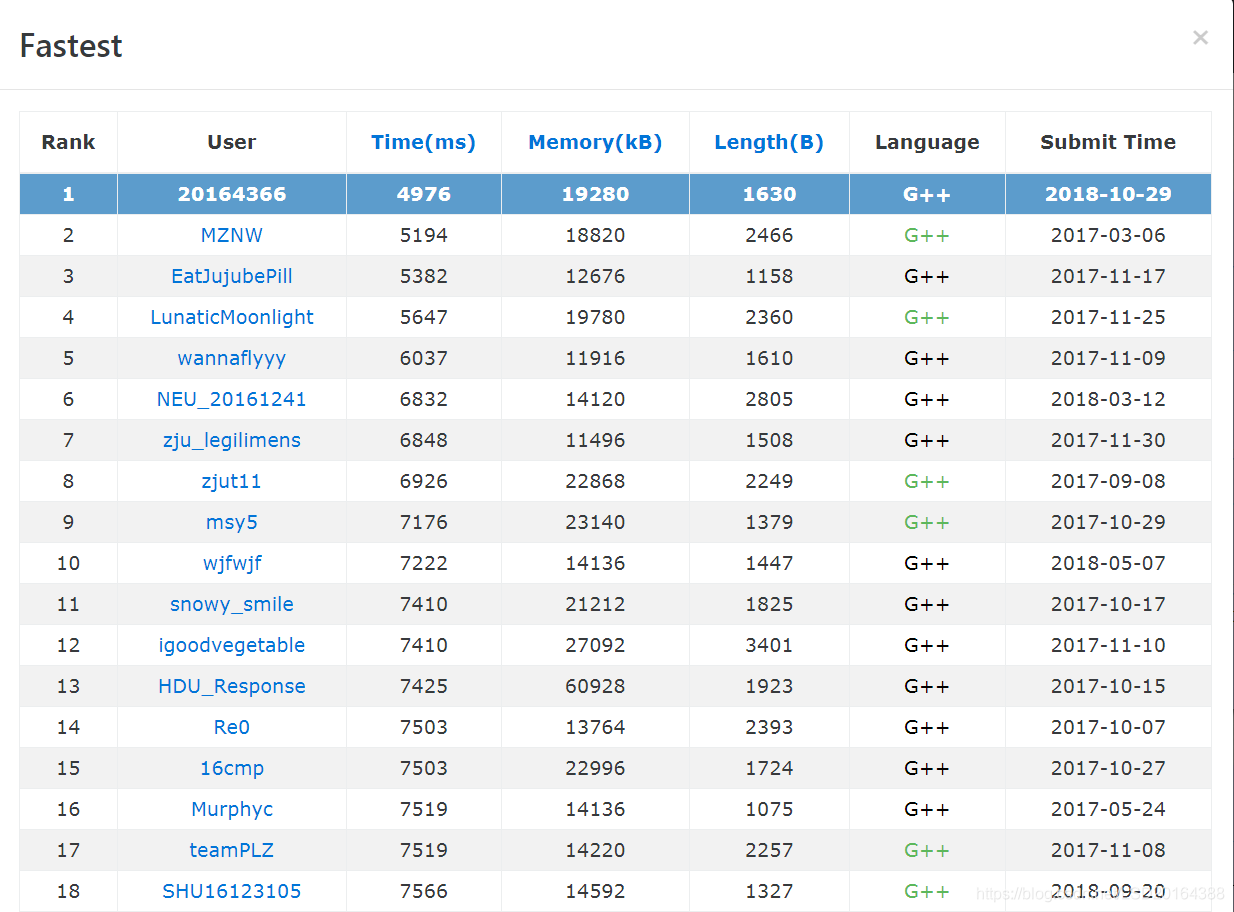
網上題解給的全都是優先佇列+貪心的做法,然而這種做法效率比較低,為8000~10000ms之間,因此這裡我給出一種效率極好,程式碼比較短,又好理解,時間僅需5000ms左右的雙二分+貪心的演算法。目前我的程式碼已經在vj上效率排第一。
貪心的思想還是一樣,求出每件衣服的洗完時間和烘乾時間之後,用洗衣服最短時間的和烘乾最長時間的匹配,次短和次長匹配,自己畫一畫,想一想,這樣肯定是最優的。但是求最短多長時間洗完、烘乾n件衣服的時間,網上都說用優先佇列求的。
然而其實提高結束時間,所有洗衣機洗完的衣服數量一定是單調遞增的。所以滿足二分的性質。
因此程式碼變得極簡單:二分求出最早的能洗完n件衣服的結束時間,再二分求出最早的能烘乾n件衣服的結束時間。再求出每件衣服的洗完、烘乾時間,進行一一貪心匹配取最大值即可。思想很簡單,程式碼也很好寫。
注意:統計每件衣服的洗完、烘乾時間的陣列要開大一些,因為二分結果可能洗、烘乾多餘的衣服,我們只取前n小的即可。
程式碼:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define inf 10000000000000000LL
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100010;
ll n,m,k;
ll a[maxn],b[maxn];
ll c[10000010],d[10000010],now;
bool jud(ll x)
{
ll sum=0;
for(ll i=0;i<m&&(x>=a[i]);i++)
{
sum+=(x/a[i]);
if(sum>=n) return 1;
}
return 0;
}
bool judd(ll x)
{
ll sum=0;
for(ll i=0;i<k&&(x>=b[i]);i++)
{
sum+=(x/b[i]);
if(sum>=n) return 1;
}
return 0;
}
ll go()
{
ll l=0,r=inf;
while(l<r)
{
ll mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(jud(mid)) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
ll cnt=0;
for(ll i=0;i<m;i++)
{
ll num=r/a[i],kk=1;
while(num)
{
c[++cnt]=a[i]*kk;
kk++;
num--;
}
}
sort(c+1,c+cnt+1);
l=0,r=inf;
while(l<r)
{
ll mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(judd(mid)) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
cnt=0;
for(ll i=0;i<k;i++)
{
ll num=r/b[i],kk=1;
while(num)
{
d[++cnt]=b[i]*kk;
kk++;
num--;
}
}
sort(d+1,d+cnt+1);
ll ans=c[1]+d[1];
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
ans=max(ans,c[i]+d[n-i+1]);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int T,cas=1;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&n,&m,&k);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
scanf("%lld",&b[i]);
sort(a,a+m);
sort(b,b+k);
printf("Case #%d: %lld\n",cas++,go());
}
return 0;
}
/*
2
1 1 1
1200
34
2 3 2
100 10 1
10 10
*/
附:效率截圖: