吳恩達Coursera深度學習課程 deeplearning.ai (5-1) 迴圈序列模型--程式設計作業(一):構建迴圈神經網路
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-30
Part 1: 構建神經網路
歡迎來到本週的第一個作業,這個作業我們將利用numpy實現你的第一個迴圈神經網路。
迴圈神經網路(Recurrent Neural Networks: RNN) 因為有”記憶”,所以在自然語言處理(Natural Language Processing) 和其他序列化任務中非常有效。RNN每次讀取序列中的一個輸入 (比如一個單詞), 通過啟用函式記住一些資訊和上下文,然後傳遞到下一個實踐部。這使得單向RNN可以攜帶資訊想前傳播,而雙向RNN更是可以攜帶過去的和未來的上下文資訊。
符號說明
- 上標 表示第l層
- 上標 表示第i個樣本
- 上標 表示輸入x在第t個時間步上的值
- 下標 表示一個向量的第i個維度
- 和 分別表示輸入和輸出的時間步數
導包
import numpy as np
from rnn_utils import *下面是 rnn_utils 中包含的程式:
import numpy as np
def softmax(x):
e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x))
return e_x / e_x.sum(axis=0)
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 基本迴圈神經網路的前向傳播
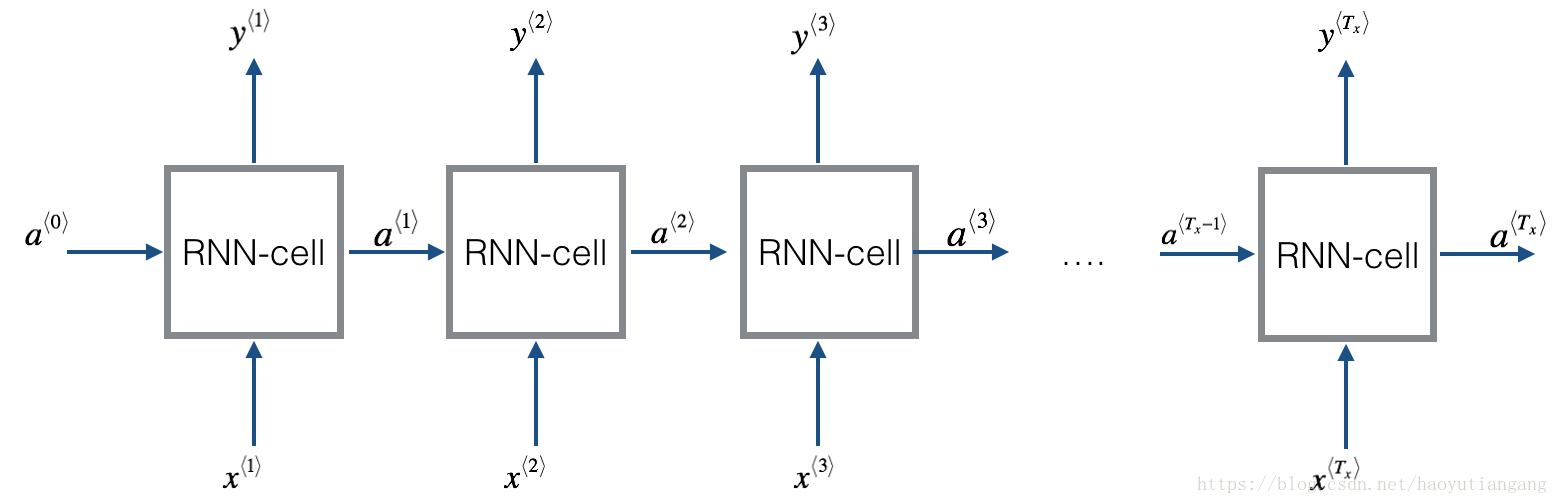
基本的RNN結構如下:(這裡Tx = Ty)
實現迴圈神經網路
- 實現 RNN 單時間步運算
- 按時間迴圈Tx的每個時間步運算
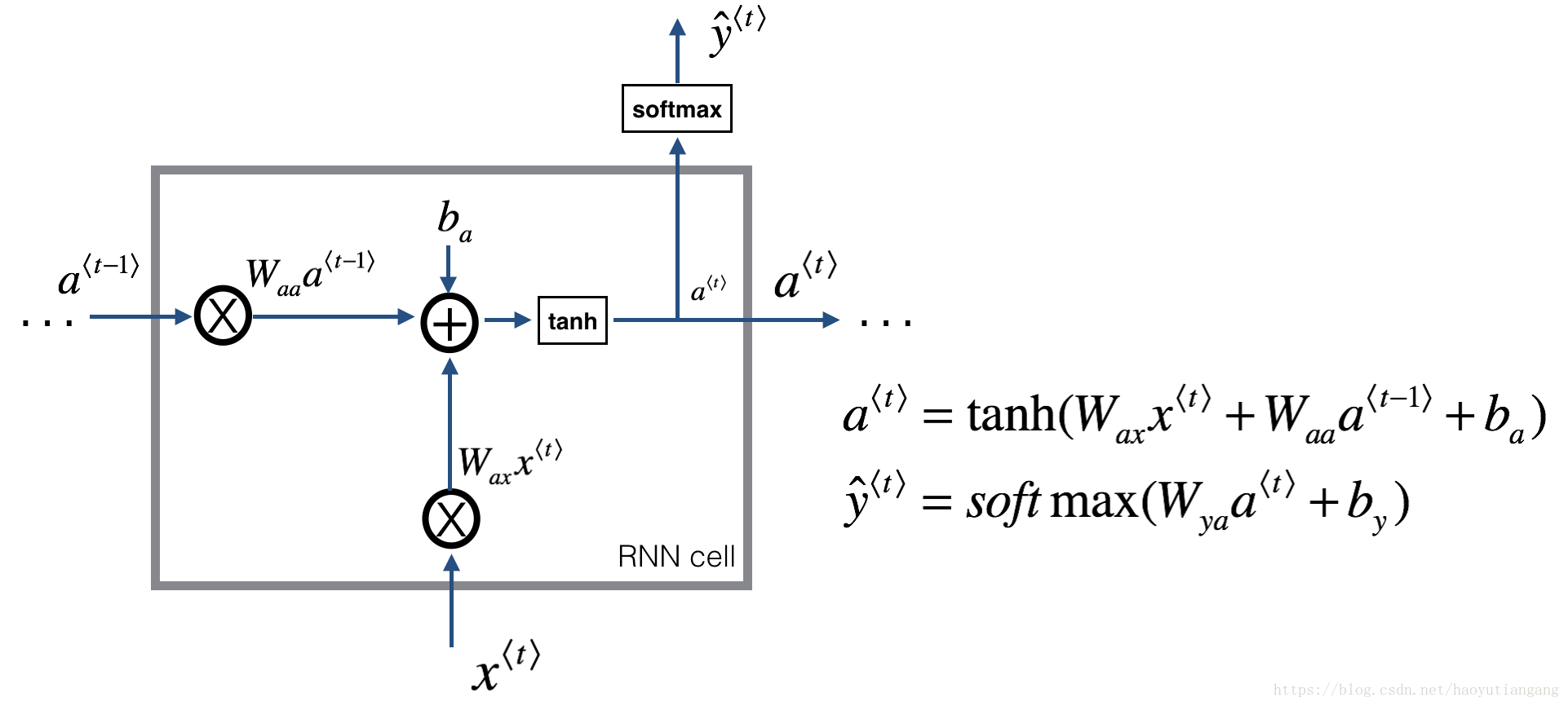
1.1 RNN 單元
一個迴圈神經網路可以看成是單個RNN單元的重複。首先我們將實現一個單時間步的RNN單元的計算,下圖描述了單步RNN 的操作。
練習:實現上圖描述的單步RNN單元
- 利用tanh啟用函式計算隱藏層的狀態
- 使用新的隱藏層狀態 計算預測值 (已提供函式softmax)
- 在cache中儲存引數
- 返回 , 和 cache
我們的輸入是m個向量。所以: 維度:(, m) ; 維度:(, m)
# GRADED FUNCTION: rnn_cell_forward
def rnn_cell_forward(xt, a_prev, parameters):
"""
Implements a single forward step of the RNN-cell as described in Figure (2)
Arguments:
xt -- your input data at timestep "t", numpy array of shape (n_x, m).
a_prev -- Hidden state at timestep "t-1", numpy array of shape (n_a, m)
parameters -- python dictionary containing:
Wax -- Weight matrix multiplying the input, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_x)
Waa -- Weight matrix multiplying the hidden state, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a)
Wya -- Weight matrix relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, n_a)
ba -- Bias, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1)
by -- Bias relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, 1)
Returns:
a_next -- next hidden state, of shape (n_a, m)
yt_pred -- prediction at timestep "t", numpy array of shape (n_y, m)
cache -- tuple of values needed for the backward pass, contains (a_next, a_prev, xt, parameters)
"""
# Retrieve parameters from "parameters"
Wax = parameters["Wax"]
Waa = parameters["Waa"]
Wya = parameters["Wya"]
ba = parameters["ba"]
by = parameters["by"]
### START CODE HERE ### (≈2 lines)
# compute next activation state using the formula given above
a_next = np.tanh(np.dot(Waa, a_prev) + np.dot(Wax, xt) + ba)
# compute output of the current cell using the formula given above
yt_pred = softmax(np.dot(Wya, a_next) + by)
### END CODE HERE ###
# store values you need for backward propagation in cache
cache = (a_next, a_prev, xt, parameters)
return a_next, yt_pred, cache
#########################################################
np.random.seed(1)
xt = np.random.randn(3,10)
a_prev = np.random.randn(5,10)
Waa = np.random.randn(5,5)
Wax = np.random.randn(5,3)
Wya = np.random.randn(2,5)
ba = np.random.randn(5,1)
by = np.random.randn(2,1)
parameters = {"Waa": Waa, "Wax": Wax, "Wya": Wya, "ba": ba, "by": by}
a_next, yt_pred, cache = rnn_cell_forward(xt, a_prev, parameters)
print("a_next[4] = ", a_next[4])
print("a_next.shape = ", a_next.shape)
print("yt_pred[1] =", yt_pred[1])
print("yt_pred.shape = ", yt_pred.shape)
# a_next[4] = [ 0.59584544 0.18141802 0.61311866 0.99808218 0.85016201 # 0.99980978
# -0.18887155 0.99815551 0.6531151 0.82872037]
# a_next.shape = (5, 10)
# yt_pred[1] = [ 0.9888161 0.01682021 0.21140899 0.36817467 0.98988387 # 0.88945212
# 0.36920224 0.9966312 0.9982559 0.17746526]
# yt_pred.shape = (2, 10)期待輸出
| key | value |
|---|---|
| a_next[4]: | [ 0.59584544 0.18141802 0.61311866 0.99808218 0.85016201 0.99980978 -0.18887155 0.99815551 0.6531151 0.82872037] |
| a_next.shape: | (5, 10) |
| yt[1]: | [ 0.9888161 0.01682021 0.21140899 0.36817467 0.98988387 0.88945212 0.36920224 0.9966312 0.9982559 0.17746526] |
| yt.shape: | (2, 10) |