什麼是LMS演算法(Least mean square)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-30
LMS演算法可認為是機器學習裡面最基本也比較有用的演算法,神經網路中對引數的學習使用的就是LMS的思想,在通訊訊號處理領域LMS也非常常見,比如自適應濾波器。
其它就是利用梯度下降的演算法來實現的,具體推導如下:
最後這條公式,就是LMS演算法的實現基礎,可以使用python程式碼實現如下:
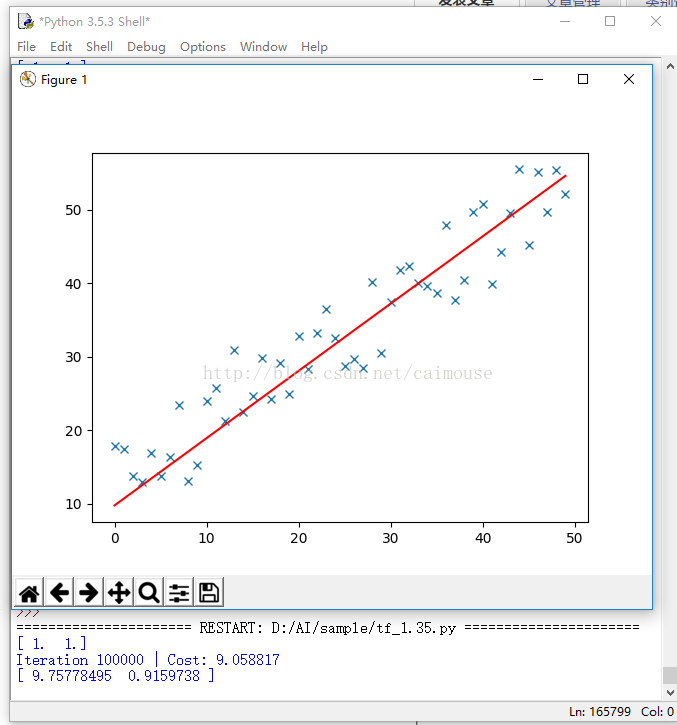
import numpy as np import random from matplotlib import pyplot as plt # m是點的數量 def gradientDescent(x, y, theta, alpha, m, numIterations): #矩陣轉置 xTrans = x.transpose() cost = None for i in range(0, numIterations): #點積 hypothesis = np.dot(x, theta) #計算最小平方數 loss = hypothesis - y cost = np.sum(loss ** 2) / (2 * m) #print("Iteration %d | Cost: %f" % (i, cost)) # 計算梯度 gradient = np.dot(xTrans, loss) / m # 更新值 theta = theta - alpha * gradient print("Iteration %d | Cost: %f" % (numIterations, cost)) return theta def genData(numPoints, bias, variance): x = np.zeros(shape=(numPoints, 2)) y = np.zeros(shape=numPoints) # 構造一條直線左右的點 for i in range(0, numPoints): # 偏移 x[i][0] = 1 x[i][1] = i # 目標值 y[i] = bias + i * variance + random.uniform(0, 1) * 15 return x, y def plotModel(x, y, w): plt.plot(x[:,1], y, "x") plt.plot(x[:,1], [i+j for i, j in x * w], "r-") plt.show() # 生成 100個點,截距為6, 斜率為0.8 x, y = genData(50, 6, 0.8) #獲取x矩陣的行列 m, n = np.shape(x) #迭代次數 numIterations = 100000 #學習步伐 alpha = 0.00005 #計算迴歸引數 theta = np.ones(n) print(theta) theta = gradientDescent(x, y, theta, alpha, m, numIterations) print(theta) plotModel(x, y, theta)
輸出結果如下:
從這個程式碼裡,可以理解前面學習梯度的作用,以及梯度求解,就是最優化的方法。通過這個例子,也明白了什麼叫做LMS演算法,以及它的實現方法,同時也可以理解TensorFlow梯度優化器的原理,為什麼需要不斷對它進行迭代執行,以及更新梯度和應用梯度的過程。