大資料多路歸併排序
問題
給你1個檔案bigdata,大小4663M,5億個數,檔案中的資料隨機,如下一行一個整數:
6196302
3557681
6121580
2039345
2095006
1746773
7934312
2016371
7123302
8790171
2966901
...
7005375現在要對這個檔案進行排序,怎麼搞?
內部排序
先嚐試內排,選2種排序方式:
3路快排:
private final int cutoff = 8;
public <T> void perform(Comparable<T>[] a) {
perform(a,0,a.length - 1);
}
private 歸併排序:
/**
* 小於等於這個值的時候,交給插入排序
*/
private final int cutoff = 8;
/**
* 對給定的元素序列進行排序
*
* @param a 給定元素序列
*/
@Override
public <T> void perform(Comparable<T>[] a) {
Comparable<T>[] b = a.clone();
perform(b, a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
private <T> void perform(Comparable<T>[] src,Comparable<T>[] dest,int low,int high) {
if(low >= high)
return;
//小於等於cutoff的時候,交給插入排序
if(high - low <= cutoff) {
SortFactory.createInsertionSort().perform(dest,low,high);
return;
}
int mid = low + ((high - low) >>> 1);
perform(dest,src,low,mid);
perform(dest,src,mid + 1,high);
//考慮區域性有序 src[mid] <= src[mid+1]
if(lessThanOrEqual(src[mid],src[mid+1])) {
System.arraycopy(src,low,dest,low,high - low + 1);
}
//src[low .. mid] + src[mid+1 .. high] -> dest[low .. high]
merge(src,dest,low,mid,high);
}
private <T> void merge(Comparable<T>[] src,Comparable<T>[] dest,int low,int mid,int high) {
for(int i = low,v = low,w = mid + 1; i <= high; i++) {
if(w > high || v <= mid && lessThanOrEqual(src[v],src[w])) {
dest[i] = src[v++];
}else {
dest[i] = src[w++];
}
}
}資料太多,遞迴太深 ->棧溢位?加大Xss?
資料太多,陣列太長 -> OOM?加大Xmx?
耐心不足,沒跑出來.而且要將這麼大的檔案讀入記憶體,在堆中維護這麼大個資料量,還有內排中不斷的拷貝,對棧和堆都是很大的壓力,不具備通用性。
sort命令來跑
sort -n bigdata -o bigdata.sorted跑了多久呢?24分鐘.
為什麼這麼慢?
粗略的看下我們的資源:
- 記憶體
jvm-heap/stack,native-heap/stack,page-cache,block-buffer- 外存
swap + 磁碟資料量很大,函式呼叫很多,系統呼叫很多,核心/使用者緩衝區拷貝很多,髒頁回寫很多,io-wait很高,io很繁忙,堆疊資料不斷交換至swap,執行緒切換很多,每個環節的鎖也很多.
總之,記憶體吃緊,問磁碟要空間,髒資料持久化過多導致cache頻繁失效,引發大量回寫,回寫執行緒高,導致cpu大量時間用於上下文切換,一切,都很糟糕,所以24分鐘不細看了,無法忍受.
點陣圖法
private BitSet bits;
public void perform(
String largeFileName,
int total,
String destLargeFileName,
Castor<Integer> castor,
int readerBufferSize,
int writerBufferSize,
boolean asc) throws IOException {
System.out.println("BitmapSort Started.");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
bits = new BitSet(total);
InputPart<Integer> largeIn = PartFactory.createCharBufferedInputPart(largeFileName, readerBufferSize);
OutputPart<Integer> largeOut = PartFactory.createCharBufferedOutputPart(destLargeFileName, writerBufferSize);
largeOut.delete();
Integer data;
int off = 0;
try {
while (true) {
data = largeIn.read();
if (data == null)
break;
int v = data;
set(v);
off++;
}
largeIn.close();
int size = bits.size();
System.out.println(String.format("lines : %d ,bits : %d", off, size));
if(asc) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (get(i)) {
largeOut.write(i);
}
}
}else {
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (get(i)) {
largeOut.write(i);
}
}
}
largeOut.close();
long stop = System.currentTimeMillis();
long elapsed = stop - start;
System.out.println(String.format("BitmapSort Completed.elapsed : %dms",elapsed));
}finally {
largeIn.close();
largeOut.close();
}
}
private void set(int i) {
bits.set(i);
}
private boolean get(int v) {
return bits.get(v);
}nice!跑了190秒,3分來鍾.
以核心記憶體4663M/32大小的空間跑出這麼個結果,而且大量時間在用於I/O,不錯.
問題是,如果這個時候突然記憶體條壞了1、2根,或者只有極少的記憶體空間怎麼搞?
外部排序
該外部排序上場了.
外部排序幹嘛的?
- 記憶體極少的情況下,利用分治策略,利用外存儲存中間結果,再用多路歸併來排序;
- map-reduce的嫡系.
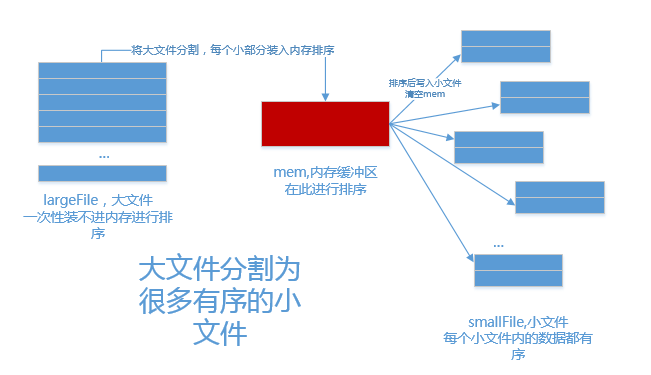
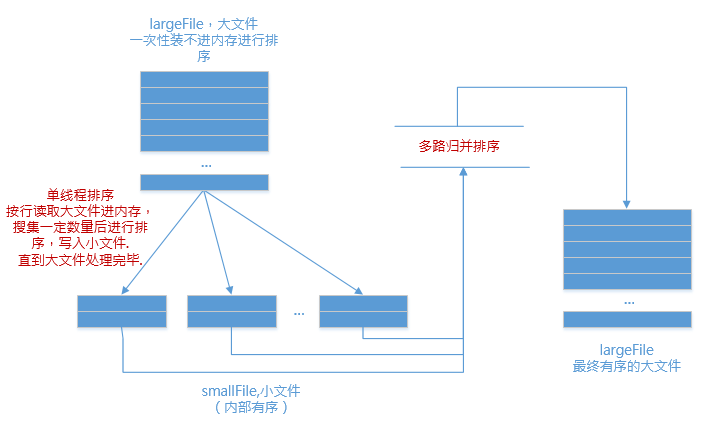
1.分
記憶體中維護一個極小的核心緩衝區memBuffer,將大檔案bigdata按行讀入,蒐集到memBuffer滿或者大檔案讀完時,對memBuffer中的資料呼叫內排進行排序,排序後將有序結果寫入磁碟檔案bigdata.xxx.part.sorted.
迴圈利用memBuffer直到大檔案處理完畢,得到n個有序的磁碟檔案:
2.合
現在有了n個有序的小檔案,怎麼合併成1個有序的大檔案?
把所有小檔案讀入記憶體,然後內排?
(⊙o⊙)…
no!
利用如下原理進行歸併排序:
我們舉個簡單的例子:
檔案1:3,6,9
檔案2:2,4,8
檔案3:1,5,7第一回合:
檔案1的最小值:3 , 排在檔案1的第1行
檔案2的最小值:2,排在檔案2的第1行
檔案3的最小值:1,排在檔案3的第1行
那麼,這3個檔案中的最小值是:min(1,2,3) = 1
也就是說,最終大檔案的當前最小值,是檔案1、2、3的當前最小值的最小值,繞麼?
上面拿出了最小值1,寫入大檔案.
第二回合:
檔案1的最小值:3 , 排在檔案1的第1行
檔案2的最小值:2,排在檔案2的第1行
檔案3的最小值:5,排在檔案3的第2行
那麼,這3個檔案中的最小值是:min(5,2,3) = 2
將2寫入大檔案.也就是說,最小值屬於哪個檔案,那麼就從哪個檔案當中取下一行資料.(因為小檔案內部有序,下一行資料代表了它當前的最小值)
最終的時間,跑了771秒,13分鐘左右.
less bigdata.sorted.text
...
9999966
9999967
9999968
9999969
9999970
9999971
9999972
9999973
9999974
9999975
9999976
9999977
9999978
...