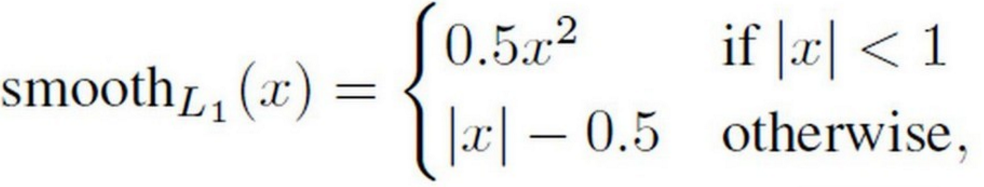【目標檢測】SSD演算法--損失函式的詳解(tensorflow實現)
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-01
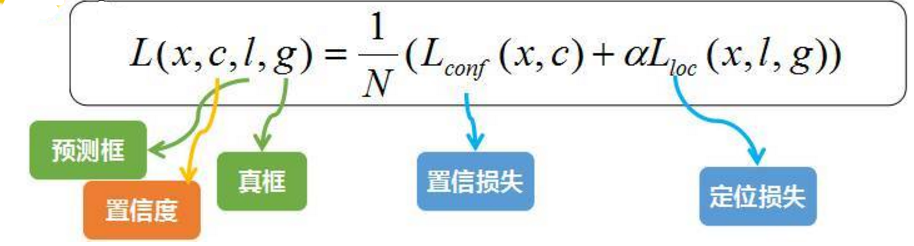
SSD的損失函式包含用於分類的log loss 和用於迴歸的smooth L1,並對正負樣本比例進行了控制,可以提高優化速度和訓練結果的穩定性。
總的損失函式是分類和迴歸的誤差的帶權加和。α表示兩者的權重,N表示匹配到default box的數量
1 loc的損失函式:smooth L1
y_true:shape: (batch_size,n_boxes,4) ,最後一個維度包括(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
y_pred的shape應該和y_true保持一致。
但是一張圖片中的ground truth就幾個到幾十個,如何和y_pred保持統一形狀
def smooth_L1_loss(self, y_true, y_pred): absolute_loss = tf.abs(y_true - y_pred) square_loss = 0.5 * (y_true - y_pred)**2 l1_loss = tf.where(tf.less(absolute_loss, 1.0), square_loss, absolute_loss - 0.5) return tf.reduce_sum(l1_loss, axis=-1)
2 conf的損失函式:Log loss
y_true shape:(batch_size, n_boxes, n_classes)
def log_loss(self, y_true, y_pred): # 確保y_pred中不含0,否則會使log函式崩潰的 y_pred = tf.maximum(y_pred, 1e-15) # Compute the log loss log_loss = -tf.reduce_sum(y_true * tf.log(y_pred), axis=-1) return log_loss
3 hard negative mining
主要思路:
1.根據正樣本的個數和正負比例,確定負樣本的個數,negative_keep
2.找到confidence loss最大的negative_keep個負樣本,計算他們的分類損失之和
3.計算正樣本的分類損失之和,分類損失是正樣本和負樣本的損失和
4.計算正樣本的位置損失localization loss.無法計算負樣本位置損失 %>_<%
5. 對迴歸損失和位置損失之和
def compute_loss(self, y_true, y_pred): self.neg_pos_ratio = tf.constant(self.neg_pos_ratio) self.n_neg_min = tf.constant(self.n_neg_min) self.alpha = tf.constant(self.alpha) batch_size = tf.shape(y_pred)[0] # Output dtype: tf.int32 n_boxes = tf.shape(y_pred)[1] # Output dtype: tf.int32, note that `n_boxes` in this context denotes the total number of boxes per image, not the number of boxes per cell. ## 計算每個box的類別和框的損失 classification_loss = tf.to_float(self.log_loss(y_true[:,:,:-12], y_pred[:,:,:-12])) # Output shape: (batch_size, n_boxes) localization_loss = tf.to_float(self.smooth_L1_loss(y_true[:,:,-12:-8], y_pred[:,:,-12:-8])) # Output shape: (batch_size, n_boxes) ## 為正的和負的groud truth 製作mask #此時需要對y_true提前進行編碼。 #對於類別只有所屬的類別是1,其他全是0,對於出ground truth之外的box的類別,背景設為1,其餘全設為0 negatives = y_true[:,:,0] # Tensor of shape (batch_size, n_boxes) positives = tf.to_float(tf.reduce_max(y_true[:,:,1:-12], axis=-1)) # Tensor of shape (batch_size, n_boxes) #統計正樣本的個數 n_positive = tf.reduce_sum(positives) # 掩蓋負的box,計算正樣本box的損失之和 pos_class_loss = tf.reduce_sum(classification_loss * positives, axis=-1) # Tensor of shape (batch_size,) # 計算所有負樣本的box的損失之和 neg_class_loss_all = classification_loss * negatives # Tensor of shape (batch_size, n_boxes) #計算損失非零的負樣本的個數 n_neg_losses = tf.count_nonzero(neg_class_loss_all, dtype=tf.int32) # The number of non-zero loss entries in `neg_class_loss_all` # Compute the number of negative examples we want to account for in the loss. # 至多保留 `self.neg_pos_ratio` 倍於 y_true中正樣本的數量, 至少保留 n_neg_min個負樣本 per batch. n_negative_keep = tf.minimum(tf.maximum(self.neg_pos_ratio * tf.to_int32(n_positive), self.n_neg_min), n_neg_losses) def f1(): ''' 當不存在負樣本的ground truth時,直接返回0 ''' return tf.zeros([batch_size]) def f2(): ''' 獲得confidence loss最高的k(n_negative_keep)個負樣本。 損失越大說明,越難訓練,也就是尋找hard negative ''' # To do this, we reshape `neg_class_loss_all` to 1D neg_class_loss_all_1D = tf.reshape(neg_class_loss_all, [-1]) # Tensor of shape (batch_size * n_boxes,) # ...and then we get the indices for the `n_negative_keep` boxes with the highest loss out of those... values, indices = tf.nn.top_k(neg_class_loss_all_1D, k=n_negative_keep, sorted=False) # We don't need them sorted. # 對這些選擇出來的保留負樣本,做一個掩碼mask negatives_keep = tf.scatter_nd(indices=tf.expand_dims(indices, axis=1), updates=tf.ones_like(indices, dtype=tf.int32), shape=tf.shape(neg_class_loss_all_1D)) # Tensor of shape (batch_size * n_boxes,) negatives_keep = tf.to_float(tf.reshape(negatives_keep, [batch_size, n_boxes])) # Tensor of shape (batch_size, n_boxes) # 計算保留的負樣本的損失之和 neg_class_loss = tf.reduce_sum(classification_loss * negatives_keep, axis=-1) # Tensor of shape (batch_size,) return neg_class_loss neg_class_loss = tf.cond(tf.equal(n_neg_losses, tf.constant(0)), f1, f2) class_loss = pos_class_loss + neg_class_loss # Tensor of shape (batch_size,) # 3: 計算正樣本的位置損失之和 # 我們不能計算對於那些預測為負樣本的box計算座標損失,你可能會問,為啥呢? #因為根本不存在標準的負樣本box的座標啊。對於正樣本可以計算是因為存在對應的ground truth loc_loss = tf.reduce_sum(localization_loss * positives, axis=-1) # Tensor of shape (batch_size,) total_loss = (class_loss + self.alpha * loc_loss) / tf.maximum(1.0, n_positive) # In case `n_positive == 0` total_loss = total_loss * tf.to_float(batch_size) return total_loss
完整程式碼,在這裡
剛開始啃這一塊,如果有理解的不對的地方,歡迎指出