Keras官方示例程式碼解釋(1):variational autoencoder
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-03
前言
Keras原始碼中附有一個examples的資料夾,裡面包含一些使用Keras進行編寫的常用的神經網路模型,如CNN、LSTM、ResNet等。這些例子基本上是Keras學習入門必看的,作為Keras的學習者,就在這裡記錄一下examples中的程式碼解析,一為自身記憶,二為幫助他人。
原始碼
這裡解析的原始碼是變分自動編碼器(variational autoencoder,VAE),其是標準自動編碼器的一個升級版本。與標準自動編碼器相比,VAE在編碼器階段添加了一個約束,使產生的code服從單位高斯分佈。關於VAE的介紹可參考這裡。
VAE的示意圖如下:
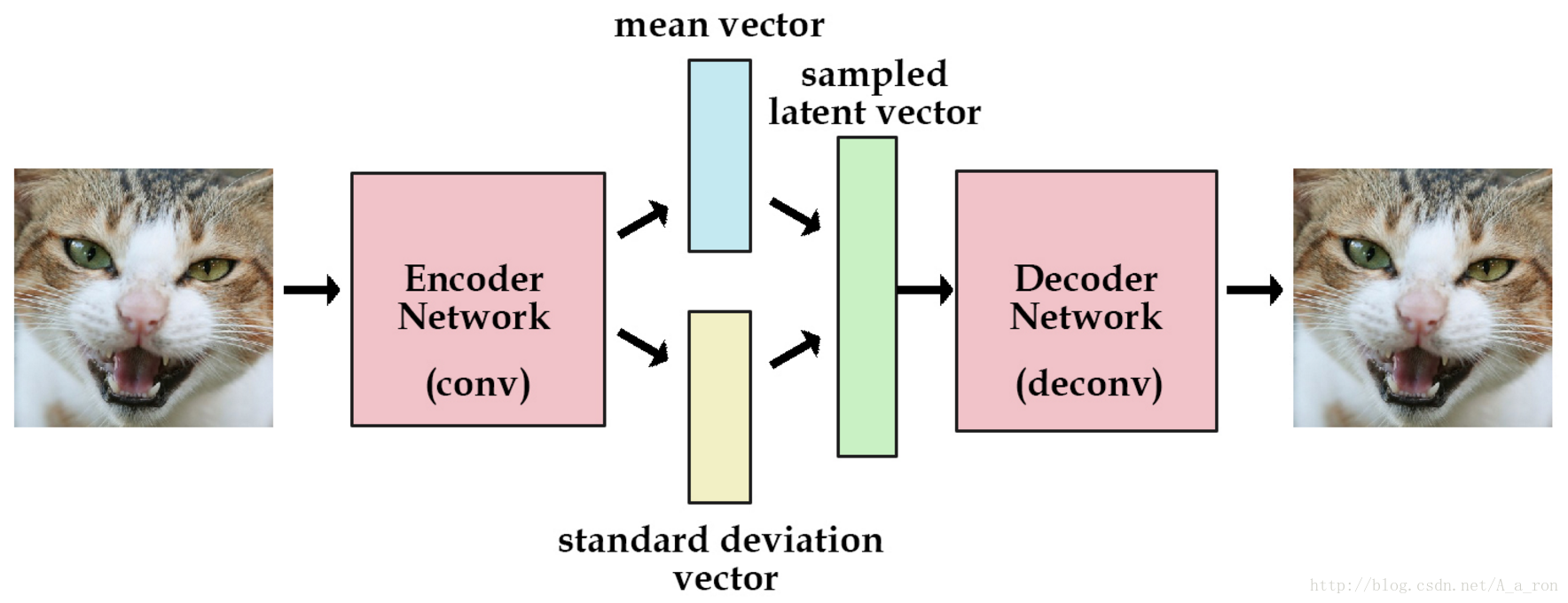
VAE的示例程式碼在Keras中的路徑為Keras/examples/variational_autoencoder.py
examples中的variational_autoencoder_deconv.py檔案中的程式碼是VAE的卷積網路實現的形式,兩者執行的結果很類似,程式碼上也很接近,大家可以參照這個來理解卷積網路版本的VAE。
#匯入相關包
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import norm
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Lambda, Layer
from #整個網路的維度變化為:784->256->2->256->784
batch_size = 100
#原始輸入維度,28*28=784
original_dim = 784
#編碼後的code的維度
latent_dim = 2
#中間隱藏層的維度
intermediate_dim = 256
#迭代50次
epochs = 50
#初始化時的標準差 #編碼器的結構
x = Input(shape=(original_dim,))
h = Dense(intermediate_dim, activation='relu')(x)
# mean vector
z_mean = Dense(latent_dim)(h)
# standard deviation vector
z_log_var = Dense(latent_dim)(h)#使用均值變數(mean vector)和標準差變數(standard deviation vector)合成隱變數
def sampling(args):
z_mean, z_log_var = args
#使用標準正態分佈初始化
epsilon = K.random_normal(shape=(K.shape(z_mean)[0], latent_dim), mean=0.,stddev=epsilon_std)
#合成公式
return z_mean + K.exp(z_log_var / 2) * epsilon
# note that "output_shape" isn't necessary with the TensorFlow backend
#z即為所要求得的隱含變數
z = Lambda(sampling, output_shape=(latent_dim,))([z_mean, z_log_var])# we instantiate these layers separately so as to reuse them later
# 解碼器的結構
decoder_h = Dense(intermediate_dim, activation='relu')
decoder_mean = Dense(original_dim, activation='sigmoid')
h_decoded = decoder_h(z)
#x_decoded_mean 即為解碼器輸出的結果
x_decoded_mean = decoder_mean(h_decoded)# Custom loss layer
#自定義損失層,損失包含兩個部分:圖片的重構誤差(均方差Square Loss)以及隱變數與單位高斯分割之間的差異(KL-散度KL-Divergence Loss)。
class CustomVariationalLayer(Layer):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.is_placeholder = True
super(CustomVariationalLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def vae_loss(self, x, x_decoded_mean):
xent_loss = original_dim * metrics.binary_crossentropy(x, x_decoded_mean)#Square Loss
kl_loss = - 0.5 * K.sum(1 + z_log_var - K.square(z_mean) - K.exp(z_log_var), axis=-1)#KL-Divergence Loss
return K.mean(xent_loss + kl_loss)
def call(self, inputs):
x = inputs[0]
x_decoded_mean = inputs[1]
loss = self.vae_loss(x, x_decoded_mean)
self.add_loss(loss, inputs=inputs)
# We won't actually use the output.
return x有關損失函式的推導,感興趣的可看這篇論文的推導
#將損失層加入網路
y = CustomVariationalLayer()([x, x_decoded_mean])
vae = Model(x, y)
vae.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss=None)# train the VAE on MNIST digits
#使用MNIST資料集進行訓練
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
#影象資料歸一化
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
#將影象資料轉換為784維的向量
x_train = x_train.reshape((len(x_train), np.prod(x_train.shape[1:])))
x_test = x_test.reshape((len(x_test), np.prod(x_test.shape[1:])))#模型訓練設定
vae.fit(x_train,
shuffle=True,
epochs=epochs,
batch_size=batch_size,
validation_data=(x_test, None))至此,整個網路的構建和訓練都結束,下面為測試的程式碼。
# build a model to project inputs on the latent space
#編碼器的網路結構,將輸入圖形對映為code,即隱含變數
encoder = Model(x, z_mean)
# display a 2D plot of the digit classes in the latent space
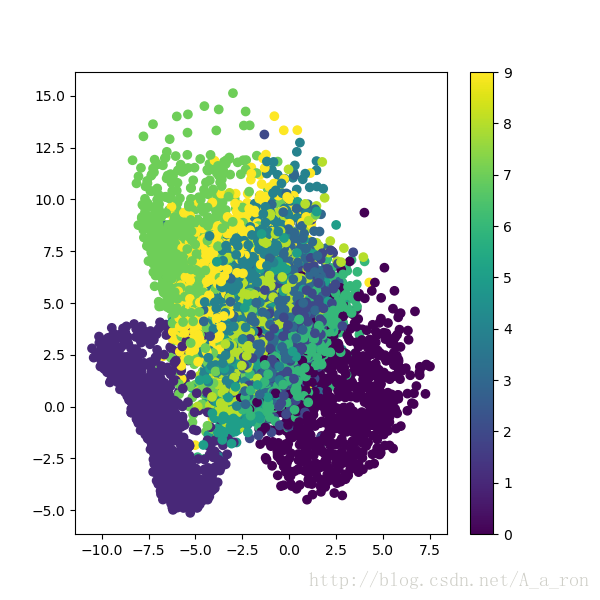
#將所有測試集中的圖片通過encoder轉換為隱含變數(二維變數),並將其在二維空間中進行繪圖
x_test_encoded = encoder.predict(x_test, batch_size=batch_size)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.scatter(x_test_encoded[:, 0], x_test_encoded[:, 1], c=y_test)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()測試集影象經過encoder之後在二維空間中的分佈如下:
# build a digit generator that can sample from the learned distribution
#構建一個解碼器,用於將隱變數解碼層圖片
decoder_input = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
_h_decoded = decoder_h(decoder_input)
_x_decoded_mean = decoder_mean(_h_decoded)
generator = Model(decoder_input, _x_decoded_mean)# display a 2D manifold of the digits
#繪製一個15個影象*15個影象的圖
n = 15 # figure with 15x15 digits
#每個影象的大小為28*28
digit_size = 28
#初始化為0
figure = np.zeros((digit_size * n, digit_size * n))
# linearly spaced coordinates on the unit square were transformed through the inverse CDF (ppf) of the Gaussian
# to produce values of the latent variables z, since the prior of the latent space is Gaussian
# 生成因變數空間(二維)中的資料,資料滿足高斯分佈。這些資料構成隱變數,用於影象的生成。
#ppf為累積分佈函式(cdf)的反函式,累積分佈函式是概率密度函式(pdf)的積分。np.linspace(0.05, 0.95, n)為累計分佈函式的輸出值(y值),現在我們需要其對應的x值,所以使用cdf的反函式,這些x值構成隱變數。
grid_x = norm.ppf(np.linspace(0.05, 0.95, n))
grid_y = norm.ppf(np.linspace(0.05, 0.95, n))有關scipy中的ppf函式可檢視這裡
#繪圖
for i, yi in enumerate(grid_x):
for j, xi in enumerate(grid_y):
z_sample = np.array([[xi, yi]])#add by weihao: 1*2
x_decoded = generator.predict(z_sample)
digit = x_decoded[0].reshape(digit_size, digit_size)#add by weihao: the generated image
figure[i * digit_size: (i + 1) * digit_size,
j * digit_size: (j + 1) * digit_size] = digit
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(figure, cmap='Greys_r')
plt.show()使用構建的隱含變數解碼出的影象如下圖所示:
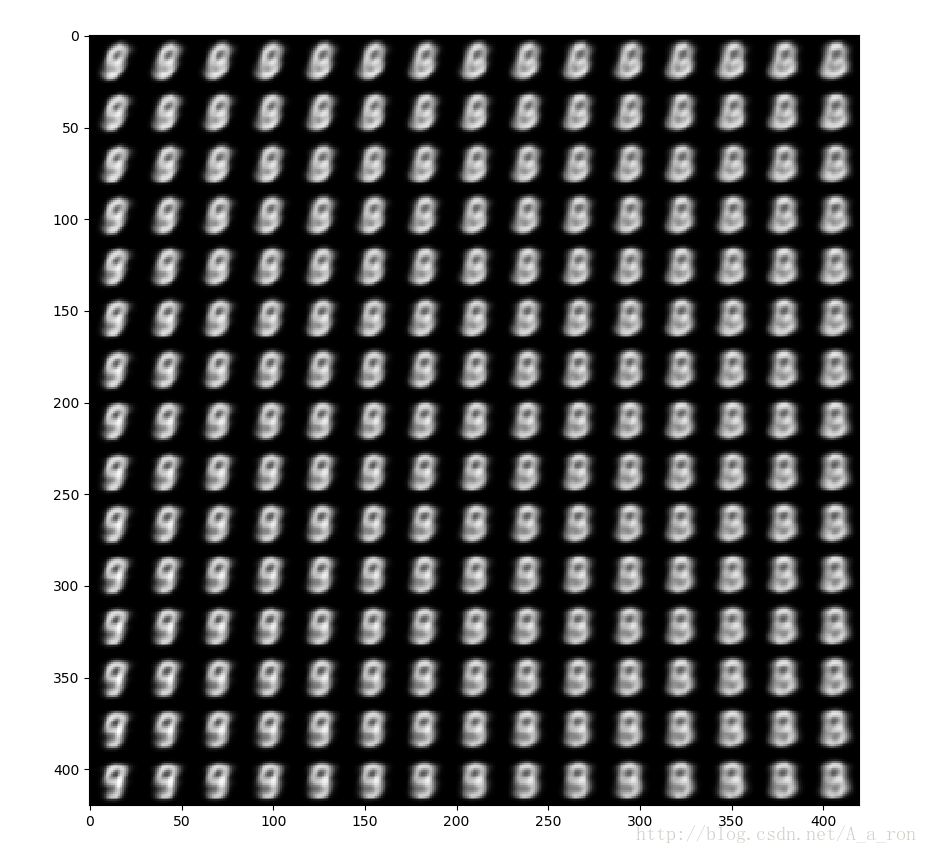
可以看出,還是有一定的誤差的。