Tensorflow之基於slim訓練自己的模型
假如我們需要從頭開始訓練一個影象識別的模型,我們可以使用tensorflow構建自己的圖片分類模型,並將圖片轉換成tfrecord格式的檔案。
tfrecord是tensorflow官方提供的一種檔案型別。
這裡補充下,關於tensorflow讀取資料,官網給出了三種方法:
1、供給資料:在tensorflow程式執行的每一步,讓python程式碼來供給資料
2、從檔案讀取資料:建立輸入管線從檔案中讀取資料
3、預載入資料:如果資料量不太大,可以在程式中定義常量或者變數來儲存所有的資料。
這裡主要介紹一種比較通用、高效的資料讀取方法,就是tensorflow官方推薦的標準格式:tfrecord。
tfrecord資料檔案
tfrecord資料檔案是一種將影象資料和標籤統一儲存的二進位制檔案,能更好的利用記憶體,在tensorflow中快速的複製,移動,讀取,儲存等。
tfrecord檔案包含了tf.train.Example 協議緩衝區(protocol buffer,協議緩衝區包含了特徵 Features)。
你可以寫一段程式碼獲取你的資料, 將資料填入到Example協議緩衝區(protocol buffer),將協議緩衝區序列化為一個字串,並且通過tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter class寫入到TFRecords檔案。tensorflow/g3doc/how_tos/reading_data/convert_to_records.py就是這樣的一個例子。
tf.train.Example的定義如下:
message Example{Features features =1;};
message Features{
map<string,Feature> featrue =1;};
message Feature{
oneof kind{BytesList bytes_list =1;FloatList float_list =2;Int64List int64_list =3;}};從上述程式碼可以看出,tf.train.Example中包含了屬性名稱到取值的字典,其中屬性名稱為字串,屬性的取值可以為字串(BytesList)、實數列表(FloatList)或者整數列表(Int64List)。
將資料儲存為tfrecord格式
具體來說,首先需要給定tfrecord檔名稱,並建立一個檔案:
tfrecords_filename ='./tfrecords/train.tfrecords'
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tfrecords_filename)# 建立.tfrecord檔案,準備寫入之後就可以建立一個迴圈來依次寫入資料:
for i in range(100):
img_raw = np.random.random_integers(0,255,size=(7,30))# 建立7*30,取值在0-255之間隨機陣列
img_raw = img_raw.tostring()
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(
feature={'label': tf.train.Feature(int64_list = tf.train.Int64List(value=[i])),'img_raw':tf.train.Feature(bytes_list = tf.train.BytesList(value=[img_raw]))}))
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()example = tf.train.Example()這句將資料賦給了變數example(可以看到裡面是通過字典結構實現的賦值),然後用writer.write(example.SerializeToString()) 這句實現寫入。
值得注意的是賦值給example的資料格式。從前面tf.train.Example的定義可知,tfrecord支援整型、浮點數和二進位制三種格式,分別是
tf.train.Feature(int64_list = tf.train.Int64List(value=[int_scalar]))
tf.train.Feature(bytes_list = tf.train.BytesList(value=[array_string_or_byte]))
tf.train.Feature(bytes_list = tf.train.FloatList(value=[float_scalar]))例如圖片等陣列形式(array)的資料,可以儲存為numpy array的格式,轉換為string,然後儲存到二進位制格式的feature中。對於單個的數值(scalar),可以直接賦值。這裡value=[×]的[]非常重要,也就是說輸入的必須是列表(list)。當然,對於輸入資料是向量形式的,可以根據資料型別(float還是int)分別儲存。並且在儲存的時候還可以指定資料的維數。
slim框架訓練模型
下載slim 和inception v4模型
將slim下載後拷貝到project目錄下,然後進行以下準備工作。
1.將圖片放置到指定的目錄下:
圖片需要按照資料夾進行分類,資料夾名就是分類的名稱,具體可以參考下圖:
2.執行程式碼,轉換格式
#匯入相應的模組
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import random
import math
import sys
#劃分驗證集訓練集
_NUM_TEST = 500
#random seed
_RANDOM_SEED = 0
#資料塊
_NUM_SHARDS = 2
#資料集路徑
DATASET_DIR = 'E:/SVN/Gavin/Learn/Python/pygame/slim/images/'
#標籤檔案
LABELS_FILENAME = 'E:/SVN/Gavin/Learn/Python/pygame/slim/images/labels.txt'
#定義tfrecord 的路徑和名稱
def _get_dataset_filename(dataset_dir,split_name,shard_id):
output_filename = 'image_%s_%05d-of-%05d.tfrecord' % (split_name,shard_id,_NUM_SHARDS)
return os.path.join(dataset_dir,output_filename)
#判斷tfrecord檔案是否存在
def _dataset_exists(dataset_dir):
for split_name in ['train','test']:
for shard_id in range(_NUM_SHARDS):
#定義tfrecord的路徑名字
output_filename = _get_dataset_filename(dataset_dir,split_name,shard_id)
if not tf.gfile.Exists(output_filename):
return False
return True
#獲取圖片以及分類
def _get_filenames_and_classes(dataset_dir):
#資料目錄
directories = []
#分類名稱
class_names = []
for filename in os.listdir(dataset_dir):
#合併檔案路徑
path = os.path.join(dataset_dir,filename)
#判斷路徑是否是目錄
if os.path.isdir(path):
#加入資料目錄
directories.append(path)
#加入類別名稱
class_names.append(filename)
photo_filenames = []
#迴圈分類的資料夾
for directory in directories:
for filename in os.listdir(directory):
path = os.path.join(directory,filename)
#將圖片加入圖片列表中
photo_filenames.append(path)
#返回結果
return photo_filenames ,class_names
def int64_feature(values):
if not isinstance(values,(tuple,list)):
values = [values]
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=values))
def bytes_feature(values):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[values]))
#圖片轉換城tfexample函式
def image_to_tfexample(image_data,image_format,class_id):
return tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/encoded': bytes_feature(image_data),
'image/format': bytes_feature(image_format),
'image/class/label': int64_feature(class_id)
}))
def write_label_file(labels_to_class_names,dataset_dir,filename=LABELS_FILENAME):
label_filename = os.path.join(dataset_dir,filename)
with tf.gfile.Open(label_filename,'w') as f:
for label in labels_to_class_names:
class_name = labels_to_class_names[label]
f.write('%d:%s\n' % (label, class_name))
#資料轉換城tfrecorad格式
def _convert_dataset(split_name,filenames,class_names_to_ids,dataset_dir):
assert split_name in ['train','test']
#計算每個資料塊的大小
num_per_shard = int(len(filenames) / _NUM_SHARDS)
with tf.Graph().as_default():
with tf.Session() as sess:
for shard_id in range(_NUM_SHARDS):
#定義tfrecord的路徑名字
output_filename = _get_dataset_filename(dataset_dir,split_name,shard_id)
with tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(output_filename) as tfrecord_writer:
#每個資料塊開始的位置
start_ndx = shard_id * num_per_shard
#每個資料塊結束的位置
end_ndx = min((shard_id+1) * num_per_shard,len(filenames))
for i in range(start_ndx,end_ndx):
try:
sys.stdout.write('\r>> Converting image %d/%d shard %d '% (i+1,len(filenames),shard_id))
sys.stdout.flush()
#讀取圖片
image_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(filenames[i],'rb').read()
#獲取圖片的類別名稱
#basename獲取圖片路徑最後一個字串
#dirname是除了basename之外的前面的字串路徑
class_name = os.path.basename(os.path.dirname(filenames[i]))
#獲取圖片的id
class_id = class_names_to_ids[class_name]
#生成tfrecord檔案
example = image_to_tfexample(image_data,b'jpg',class_id)
#寫入資料
tfrecord_writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
except IOError as e:
print ('could not read:',filenames[1])
print ('error:' , e)
print ('skip it \n')
sys.stdout.write('\n')
sys.stdout.flush()
if __name__ == '__main__':
#判斷tfrecord檔案是否存在
if _dataset_exists(DATASET_DIR):
print ('tfrecord exists')
else:
#獲取圖片以及分類
photo_filenames,class_names = _get_filenames_and_classes(DATASET_DIR)
#將分類的list轉換成dictionary{‘animal':0,'flowers:1'}
class_names_to_ids = dict(zip(class_names,range(len(class_names))))
#切分資料為測試訓練集
random.seed(_RANDOM_SEED)
random.shuffle(photo_filenames)
training_filenames = photo_filenames[_NUM_TEST:]
testing_filenames = photo_filenames[:_NUM_TEST]
#資料轉換
_convert_dataset('train',training_filenames,class_names_to_ids,DATASET_DIR)
_convert_dataset('test',testing_filenames,class_names_to_ids,DATASET_DIR)
#輸出lables檔案
#與前面的 class_names_to_ids中的元素位置相反{0:'animal',1:'flowers'}
labels_to_class_names = dict(zip(range(len(class_names)),class_names))
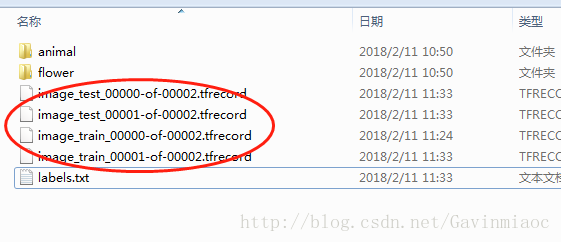
write_label_file(labels_to_class_names,DATASET_DIR)完成後,生成了以下檔案,包括訓練集資料塊和測試集資料塊,另外有個label標籤檔案
驗證模型
接下來就是本文的重點了,上一步完成後我們已經得到tfrecord格式的檔案了。下一步我們就要用這些檔案進行分類驗證測試。
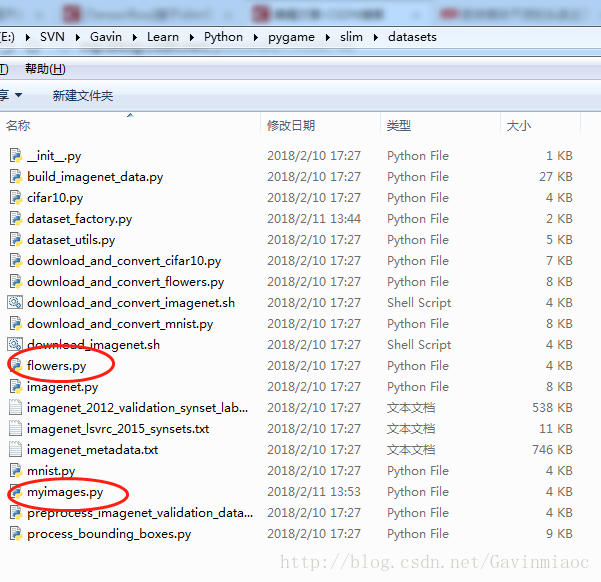
1.在slim/datasets資料夾下,找到訓練的資料集,由於寫法比較 一致,我們只需要拷貝其中一個,比如訓練flowers用的資料來源,新建一個我們自己訓練使用的資料集,命名為myimages(可自由命名),將程式碼拷貝到新檔案中,最後修改。
程式碼如下,需要修改的幾個地方我作了中文標記。程式碼實現的其實就是讀取tfrecord檔案。
# Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Provides data for the flowers dataset.
The dataset scripts used to create the dataset can be found at:
tensorflow/models/research/slim/datasets/download_and_convert_flowers.py
"""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from datasets import dataset_utils
slim = tf.contrib.slim
_FILE_PATTERN = 'image_%s_*.tfrecord' # 這裡修改pattern,格式和生成tfrecord檔案下的格式一致
SPLITS_TO_SIZES = {'train': 1026, 'validation': 50} #修改訓練集和驗證集圖片數量
_NUM_CLASSES = 2 # 這裡修改資料塊個數
_ITEMS_TO_DESCRIPTIONS = {
'image': 'A color image of varying size.',
'label': 'A single integer between 0 and 4',
}
def get_split(split_name, dataset_dir, file_pattern=None, reader=None):
"""Gets a dataset tuple with instructions for reading flowers.
Args:
split_name: A train/validation split name.
dataset_dir: The base directory of the dataset sources.
file_pattern: The file pattern to use when matching the dataset sources.
It is assumed that the pattern contains a '%s' string so that the split
name can be inserted.
reader: The TensorFlow reader type.
Returns:
A `Dataset` namedtuple.
Raises:
ValueError: if `split_name` is not a valid train/validation split.
"""
if split_name not in SPLITS_TO_SIZES:
raise ValueError('split name %s was not recognized.' % split_name)
if not file_pattern:
file_pattern = _FILE_PATTERN
file_pattern = os.path.join(dataset_dir, file_pattern % split_name)
# Allowing None in the signature so that dataset_factory can use the default.
if reader is None:
reader = tf.TFRecordReader
keys_to_features = {
'image/encoded': tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, default_value=''),
'image/format': tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, default_value='png'),
'image/class/label': tf.FixedLenFeature(
[], tf.int64, default_value=tf.zeros([], dtype=tf.int64)),
}
items_to_handlers = {
'image': slim.tfexample_decoder.Image(),
'label': slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor('image/class/label'),
}
decoder = slim.tfexample_decoder.TFExampleDecoder(
keys_to_features, items_to_handlers)
labels_to_names = None
if dataset_utils.has_labels(dataset_dir):
labels_to_names = dataset_utils.read_label_file(dataset_dir)
return slim.dataset.Dataset(
data_sources=file_pattern,
reader=reader,
decoder=decoder,
num_samples=SPLITS_TO_SIZES[split_name],
items_to_descriptions=_ITEMS_TO_DESCRIPTIONS,
num_classes=_NUM_CLASSES,
labels_to_names=labels_to_names)
注意,我們還需要修改 dataset_factory.py檔案下的datasets_map字典,如下
datasets_map = {
'cifar10': cifar10,
'flowers': flowers,
'imagenet': imagenet,
'mnist': mnist,
'myimages': myimages, # 這裡新增個人訓練的資料集
}3.在slim資料夾下新建一個model資料夾,用於儲存訓練生成的模型
4.如果標籤是中文,修改slim/datasets/dataset_utils.py
sys.setdefaultencoding("utf-8") #中文標籤,增加utf-8 5.在slim目錄下編寫執行訓練資料的指令碼。
python E:/SVN/Gavin/Learn/Python/pygame/slim/train_image_classifier.py ^
--dataset_name=myimages ^
--dataset_split_name=train ^
--train_dir= E:\SVN\Gavin\Learn\Python\pygame\slim\models ^
--dataset_dir=E:\SVN\Gavin\Learn\Python\pygame\slim\images ^
--batch_size=10 ^
--max_number_of_steps=10000 ^
--model_name=inception_v3 ^
pause簡單解釋下:
train_dir 訓練生成的模型存放位置dataset_split_name=train 代表使用的是訓練集,之前拆分為訓練集和測試集dataset_dir 訓練圖片存放位置6.執行預測指令碼,使用eval_image_classifier.py檔案
如果使用的CPU,那麼訓練時間是比較漫長的。