react-navigation 原始碼簡單分析以及徒手擼react-navigation簡易版
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-07
目標簡單做個導航效果的Navigator
在接觸ReactNative中 渲染檢視最重要即render方法去渲染,對於react-navigation如何快取之前的檢視物件,以及如何在一個容器裡面做到跳轉效果(Acitvity 的概念),以及回退了 之前物件還是快取資料 有了興趣,在閱讀原始碼後簡單模仿了低配版的Navigator
首先我們初始化專案後加入react-navigation
import React, { Component } from 'react' import { Button, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native' export default class PageA extends Component { static navigationOptions = { headerTitle: 'PageA' } constructor (props) { super(props) this.state = { number: 0 } } render () { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <Text>PageA</Text> <Button onPress={() => { this.setState({ number: ++this.state.number }) }} title={'計數器:'+this.state.number+''} /> <Button onPress={() => { this.props.navigation.navigate('PageB') }} title='go to pageB' /> </View> ) } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF' } })
import React, {Component} from 'react'; import {Platform, StyleSheet, Text, View} from 'react-native'; export default class PageB extends Component{ static navigationOptions = { headerTitle:'PageB', }; render() { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <Text>PageB</Text> </View> ); } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', }, });
import {StackNavigator} from 'react-navigation'; //這裡是我們之後要低配版導航 // import StackNavigator from './animatorCustomerNavigator/StackNavigator'; import PageA from './PageA' import PageB from './PageB' export default StackNavigator({ PageA: { screen: PageA }, PageB: { // 詳情頁 screen: PageB }, }, { headerMode: 'screen', // 標題導航 initialRouteName: 'PageA', // 預設先載入的頁面元件 mode: 'card' // 定義跳轉風格(card、modal) });
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { Text } from 'react-native'
import Naviagtor from './src/Naviagtor'
import PageA from './src/PageA'
export default class App extends Component {
render () {
return <Naviagtor/>
}
}
這個時候 以及跑起來專案了,首先我們先解決 react-navigation 如何做到元件的快取
StackNavigator 為例 定位程式碼
StackNavigator=>
require('react-navigation-stack').createStackNavigator=>
require('./navigators/createContainedStackNavigator').default
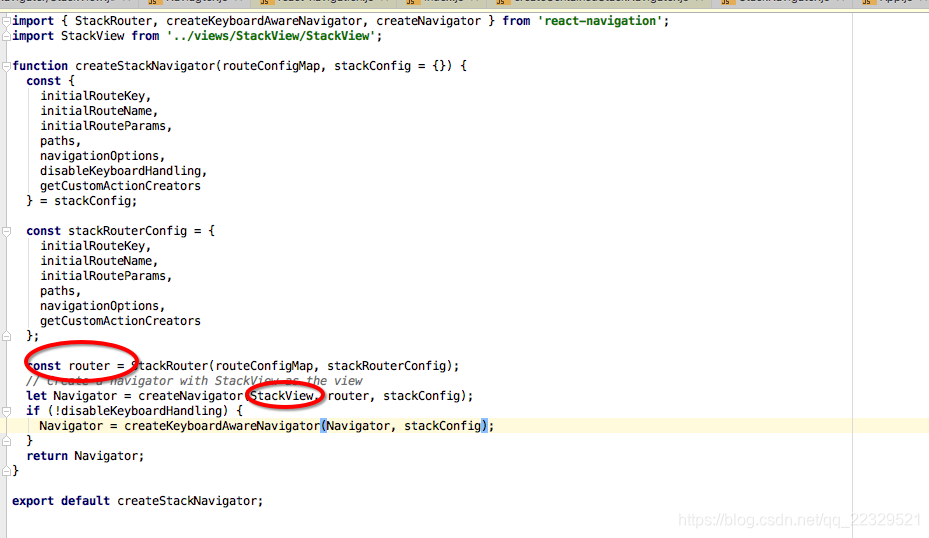
呼叫navigateor 需要兩個 stackView 和router,router是個控制器內部包含了檢視棧的配置,控制,StackView就是一個容器根據router控制來顯示view
createNavigator 原始碼
....
routes.forEach(route => {
if (
prevDescriptors &&
prevDescriptors[route.key] &&
route === prevDescriptors[route.key].state &&
screenProps === prevState.screenProps
) {
descriptors[route.key] = prevDescriptors[route.key];
return;
}
const getComponent = router.getComponentForRouteName.bind(
null,
route.routeName
);
const childNavigation = navigation.getChildNavigation(route.key);
const options = router.getScreenOptions(childNavigation, screenProps);
descriptors[route.key] = {
key: route.key,
getComponent,
options,
state: route,
navigation: childNavigation,
};
});
return { descriptors, screenProps };
render() {
return (
//這個NavigatorView 就是外部傳進來的StackView
<NavigatorView
{...this.props}
screenProps={this.state.screenProps}
navigation={this.props.navigation}
navigationConfig={navigationConfig}
//這個就是router進行相應的具體配置如設定了key,getComponent,等
descriptors={this.state.descriptors}
/>
);
}
StackRouter 大致就是定義了pop push actions等狀態
接下來我們看StackView
_render = (transitionProps, lastTransitionProps) => {
const { screenProps, navigationConfig } = this.props;
return <StackViewLayout {...navigationConfig} onGestureBegin={this.props.onGestureBegin} onGestureCanceled={this.props.onGestureCanceled} onGestureEnd={this.props.onGestureEnd} screenProps={screenProps} descriptors={this.props.descriptors} transitionProps={transitionProps} lastTransitionProps={lastTransitionProps} />;
};
其實內部還是呼叫了StackViewLayout
StackViewLayout 中的render 方法
render() {
....
const {
transitionProps: { scene, scenes }
} = this.props;
const { options } = scene.descriptor;
....
return <View {...handlers} style={containerStyle}>
<ScreenContainer style={styles.scenes}>
//這裡scenes map 實際上就是組建疊上去疊上去的
{scenes.map(s => this._renderCard(s))}
</ScreenContainer>
{floatingHeader}
</View>;
}
我們追蹤transitionProps
StackView transitionProps 實際上 Transitioner組建裡面呼叫 的
render() {
return <Transitioner render={this._render} configureTransition={this._configureTransition} screenProps={this.props.screenProps} navigation={this.props.navigation} descriptors={this.props.descriptors} onTransitionStart={this.props.onTransitionStart || this.props.navigationConfig.onTransitionStart} onTransitionEnd={(transition, lastTransition) => {
const { navigationConfig, navigation } = this.props;
const onTransitionEnd = this.props.onTransitionEnd || navigationConfig.onTransitionEnd;
if (transition.navigation.state.isTransitioning) {
navigation.dispatch(StackActions.completeTransition({
key: navigation.state.key
}));
}
onTransitionEnd && onTransitionEnd(transition, lastTransition);
}} />;
}
Transitioner 原始碼
this._transitionProps = buildTransitionProps(props, this.state);
function buildTransitionProps(props, state) {
const { navigation } = props;
const { layout, position, progress, scenes } = state;
const scene = scenes.find(isSceneActive);
invariant(scene, 'Could not find active scene');
return {
layout,
navigation,
position,
progress,
scenes,
scene,
index: scene.index
};
}
到這裡我們也能看出棧的實現就是一個個組建疊上去的 同時瀏覽了Transitioner 原始碼大致也能猜出實際介面跳轉就是一個元件動畫實現的流程然後疊上去 在StackView 中有_configureTransition方法-》呼叫 StackViewTransitionConfigs.getTransitionConfig方法
//android 預設實現的動畫配置,StackViewTransitionConfigs StackViewStyleInterpolator 這兩個js中程式碼能找到
function defaultTransitionConfig(transitionProps, prevTransitionProps, isModal) {
if (Platform.OS === 'android') {
// Use the default Android animation no matter if the screen is a modal.
// Android doesn't have full-screen modals like iOS does, it has dialogs.
if (prevTransitionProps && transitionProps.index < prevTransitionProps.index) {
// Navigating back to the previous screen
return FadeOutToBottomAndroid;
}
return FadeInFromBottomAndroid;
}
// iOS and other platforms
if (isModal) {
return ModalSlideFromBottomIOS;
}
return SlideFromRightIOS;
}
簡易版react-navigation 實現
import React, {Component} from 'react'
import {View, Dimensions, Text, Image, TouchableOpacity,DeviceEventEmitter} from 'react-native'
import createStackView from './StackView'
var width = Dimensions.get('window').width
var height = Dimensions.get('window').height
export default (createNavigationContainer = (routeConfigs, config = {}) => {
class NavigationContainer extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
const navigation = {
navigate: name => {
this.state.stack.push({
config: routeConfigs[name].screen,
screen: createStackView(routeConfigs[name].screen, navigation, true,this.state.stack.length),
index: this.state.stack.length
})
this.forceUpdate()
},
pop: () => {
let str='pop'
str=str+String(this.state.stack.length-1)+''
DeviceEventEmitter.emit(str)
this.timer = setTimeout(
() => { this.state.stack.pop()
this.forceUpdate() },
500
);
}
}
this.state = {
routeConfigs,
config,
stack: [{
config: routeConfigs[config.initialRouteName].screen,
screen: createStackView(routeConfigs[config.initialRouteName].screen, navigation, false,0),
index: 0
}],
navigation,
}
}
render() {
return (
<View style={{flex: 1}}>
{this.state.stack.map((d) =>
<View style={{position: 'absolute', width, height}}>
{d.screen}
</View>)}
</View>
)
}
// render(){
// let Page = this.state.stack[this.state.stack.length - 1].screen
// return (
// <View style={{flex: 1}}>
// {Page}
// </View>
// )
// }
}
return NavigationContainer
})
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import {
View,
Dimensions,
Text,
Image,
TouchableOpacity,
Animated,
Easing,
DeviceEventEmitter
} from 'react-native'
var width = Dimensions.get('window').width
var height = Dimensions.get('window').height
//考慮到快取 就用方法去建立然後塞到數組裡面
export default (createStackView = (Page, navigation, back,index) => {
class StackView extends React.Component {
constructor (props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
active: false,
opacity: new Animated.Value(0),
transformX: new Animated.Value(0),
transformY: new Animated.Value(0)
}
console.warn('pop'+index)
this.subscription = DeviceEventEmitter.addListener('pop'+index,() =>{
console.warn('fadoOutAnimator')
this.fadoOutAnimator()
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// 移除
this.subscription.remove();
}
componentDidMount () {
Animated.parallel([
Animated.timing(
this.state.opacity,
{
toValue: 1,
duration: index==0?10:500,
easing: Easing.in(Easing.poly(4)),
timing: Animated.timing
}
),
Animated.timing(this.state.transformY, {
toValue: 1,
duration: index==0?10:500,
easing: Easing.in(Easing.poly(4)),
timing: Animated.timing
})
]).start(() => {})
}
fadoOutAnimator(){
Animated.parallel([
Animated.timing(
this.state.opacity,
{
toValue: 0,
duration: index==0?10:500,
easing: Easing.in(Easing.poly(4)),
timing: Animated.timing
}
),
Animated.timing(this.state.transformY, {
toValue: 0,
duration: index==0?10:500,
easing: Easing.in(Easing.poly(4)), // accelerate
timing: Animated.timing
})
]).start(() => {})
}
render () {
return (
<Animated.View
style={{
flex: 1,
opacity: this.state.opacity,
transform: [
{
translateY: this.state.transformY.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, 1],
outputRange: [height, 0]
})
}
]
}}
>
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<View
style={{
width,
height: 50,
backgroundColor: 'blue',
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center'
}}
>
{back &&
<TouchableOpacity
onPress={() => {
navigation.pop()
}}
style={{ position: 'absolute', left: 10 }}
>
<Image
source={require('./back-icon.png')}
style={{ tintColor: 'white' }}
/>
</TouchableOpacity>}
<Text style={{ color: 'white' }}>
{Page.navigationOptions.headerTitle}
</Text>
</View>
<Page navigation={navigation} />
</View>
</Animated.View>
)
}
}
return <StackView />
})
福利圖

