UVA 11178 Morley's Theorem
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-08
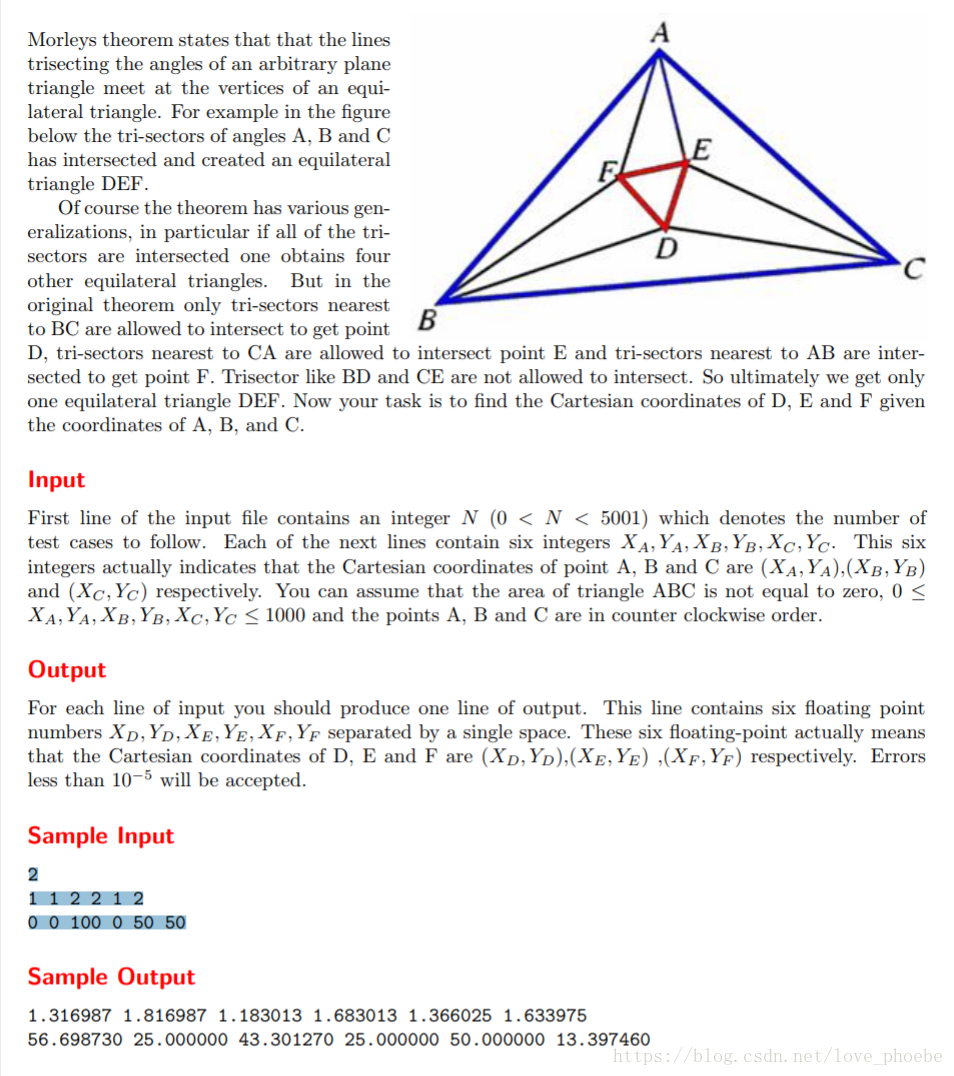
由等邊三角形的頂點與外圍三角形兩角的三分之一作為底部向量的偏轉角,兩偏轉向量的交點就是一個所求點
根據對稱性原理求出另外兩點
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> using namespace std; const double eps=1e-10; struct Point{ double x,y; Point(double x=0,double y=0):x(x),y(y){} }; typedef Point Vector; Vector operator + (Vector A,Vector B){return Vector(A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y);} Vector operator - (Vector A,Vector B){return Vector(A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y);} Vector operator * (Vector A,double B){return Vector(A.x*B,A.y*B);} Vector operator / (Vector A,double B){return Vector(A.x/B,A.y/B);} int dcmp(double x){if(fabs(x)<eps)return 0;return (x>0)?1:-1;} bool operator == (Vector A,Vector B){return dcmp(A.x-B.x)==0 && dcmp(A.y-B.y)==0 ;} double Dot(Vector A,Vector B){return A.x*B.x+A.y*B.y;} double Length(Vector A){return sqrt(Dot(A,A));} double Angle(Vector A,Vector B){return acos(Dot(A,B)/Length(A)/Length(B));} double Cross(Vector A,Vector B){return A.x*B.y-B.x*A.y;} Vector Rotate(Vector A,double rad){//逆時針 return Vector(A.x*cos(rad)-A.y*sin(rad) , A.x*sin(rad)+A.y*cos(rad)); } Point GetLineIntersection(Point P,Vector v,Point Q,Vector w){ Vector u=P-Q; double t=Cross(w,u)/Cross(v,w); return P+v*t; } Point GetPoint(Point A,Point B,Point C){ Vector v1=C-B; double a1=Angle(A-B,v1); v1=Rotate(v1,a1/3); Vector v2=B-C; double a2=Angle(A-C,v2); v2=Rotate(v2,-a2/3); return GetLineIntersection(B,v1,C,v2); } Point read_point(){ int a,b; scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); return Point(a,b); } int main(){ int N; scanf("%d",&N); while(N--){ Point A=read_point(); Point B=read_point(); Point C=read_point(); Point D=GetPoint(A,B,C); Point E=GetPoint(B,C,A); Point F=GetPoint(C,A,B); printf("%.6lf %.6lf %.6lf %.6lf %.6lf %.6lf\n",D.x,D.y,E.x,E.y,F.x,F.y); } return 0; }