6、八大內部排序--Java程式碼
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-09
八大內部排序:
一、直接插入排序:
package algorithm.sort; /** * 插入排序之直接插入排序 * @author baolibin */ public class _04_insertSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] tmpNum={54,23,8,87,56,21,34,17,6,23,4}; insertSort insertSort = new insertSort(tmpNum); insertSort.insert_Sort(); insertSort.fnPrint(); } } class insertSort{ private int[] tmpNum; public insertSort(int[] tmpNum){ this.tmpNum=tmpNum; } /** * 直接插入排序 */ public void insert_Sort(){ int tmp=0,j=0; for (int i = 1; i < tmpNum.length; i++) { // fnPrint(); tmp=tmpNum[i]; j=i; while (j>0&&tmpNum[j-1]>tmp) { tmpNum[j]=tmpNum[j-1]; j--; } tmpNum[j]=tmp; } } /** * 列印函式 */ public void fnPrint(){ for (int i = 0; i < tmpNum.length; i++) { if (i==tmpNum.length-1) { System.out.println(tmpNum[i]); }else { System.out.print(tmpNum[i]+"、"); } } } }
二、希爾排序:
package algorithm.sort; /** * 插入排序之希爾排序 * @author baolibin */ public class _06_shellSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] tmpNum={54,23,8,87,56,21,34,17,6,23,4}; shellSort shellSort = new shellSort(tmpNum); shellSort.shell_Sort(); shellSort.fnPrint(); } } class shellSort{ private int[] tmpNum; public shellSort(int[] tmpNum){ this.tmpNum=tmpNum; } /** * 希爾排序 */ public void shell_Sort(){ int step=tmpNum.length/2; while (1<=step) { this.fnPrint(); //遍歷所有得的組 for (int i = step; i < tmpNum.length; i++) { int j=i-step; //儲存要插入的資料 int tmp=tmpNum[i]; while(j>=0&&tmp<tmpNum[j]){ tmpNum[j+step]=tmpNum[j]; j=j-step; } tmpNum[j+step]=tmp; } step=step/2; } } /** * 列印函式 */ public void fnPrint(){ for (int i = 0; i < tmpNum.length; i++) { if (i==tmpNum.length-1) { System.out.println(tmpNum[i]); }else { System.out.print(tmpNum[i]+"、"); } } } }
三、簡單選擇排序:
package algorithm.sort; /** * 選擇排序之簡單選擇排序 * @author baolibin */ public class _05_selectSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] tmpNum={54,23,8,87,56,21,34,17,6,23,4}; selectSort selectSort = new selectSort(tmpNum); selectSort.select_Sort(); selectSort.fnPrint(); } } class selectSort{ private int[] tmpNum; public selectSort(int[] tmpNum){ this.tmpNum=tmpNum; } /** * 簡單選擇排序 */ public void select_Sort(){ int tmp=0,index=0; for (int i = 0; i < tmpNum.length-1; i++) { index=i; for (int j = i+1; j < tmpNum.length; j++) { if(tmpNum[index]>tmpNum[j]){ index=j; } } tmp=tmpNum[i]; tmpNum[i]=tmpNum[index]; tmpNum[index]=tmp; } } /** * 列印函式 */ public void fnPrint(){ for (int i = 0; i < tmpNum.length; i++) { if (i==tmpNum.length-1) { System.out.println(tmpNum[i]); }else { System.out.print(tmpNum[i]+"、"); } } } }
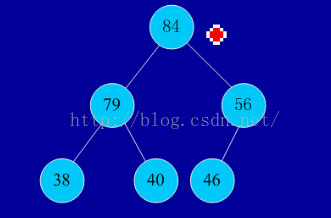
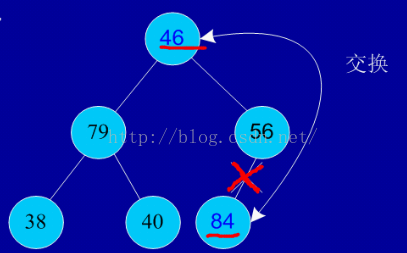
四、堆排序:
package algorithm.sort;
/**
* 選擇排序之堆排序
* @author baolibin
*
* 參考網址:
* http://www.cnblogs.com/jingmoxukong/p/4303826.html
* http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2012/11/30/2796845.html
*/
public class _02_heapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tmpNum={32,5,76,9,23,43,12,4,56}; //宣告的靜態陣列
heapSort heapsort=new heapSort(tmpNum);
heapsort.heapScheduler(tmpNum);
heapsort.sortPtint();
}
}
class heapSort{
private int[] tmpNum;
public heapSort(int[] tmpNum){
this.tmpNum=tmpNum;
}
/**進行堆調整
* @param tmpNum 陣列
* @param parent 選擇開始調整的父節點儲存的陣列下標
* @param length 待排序陣列的下標長度
*/
public void heapAdjust(int[] tmpNum,int parent,int length){
//先儲存當前父節點的值
int tmp=tmpNum[parent];
//選取當前父節點的左孩子
int child=2*parent+1;
while(child<length){
//選取右孩子的條件:存在右節點且右節點的值大於左節點的值
if (child+1<=length&&tmpNum[child]<tmpNum[child+1]) {
child++;
}
//當父節點的值大於孩子節點的時候,直接結束
if (tmp>=tmpNum[child]) {
break;
}
tmpNum[parent]=tmpNum[child];
//從孩子節點的左孩子開始繼續往下篩選
parent=child;
child=2*child+1;
}
tmpNum[parent]=tmp;
}
public void heapScheduler(int[] tmpNum){
//建堆
//本程式建立大頂堆,保證所有的父節點都比孩子節點大
for(int i=tmpNum.length/2;i>=0;i--){
heapAdjust(tmpNum, i, tmpNum.length-1);
}
sortPtint();
//進行排序
int tmp=0;
for (int i=tmpNum.length-1;i>0;i--) {
//最後一個元素和第一個元素進行交換
tmp=tmpNum[i];
tmpNum[i]=tmpNum[0];
tmpNum[0]=tmp;
/**
按堆的定義將陣列R[0..n]調整為堆(這個過程稱為建立初始堆),交換R[0]和R[n];
然後,將R[0..n-1]調整為堆,交換R[0]和R[n-1];
如此反覆,直到交換了R[0]和R[1]為止。
*/
heapAdjust(tmpNum, 0, i);
System.out.println("第"+(tmpNum.length-i)+"趟");
}
}
/**
* 列印堆的資料
* 用陣列儲存的堆
*/
public void sortPtint(){
for(int i=0;i<tmpNum.length;i++){
if(i==tmpNum.length-1){
System.out.print(tmpNum[i]);
}else {
System.out.print(tmpNum[i]+"、");
}
}
}
}
五、氣泡排序:
package algorithm.sort;
/**
* 交換排序之氣泡排序
* @author baolibin
*/
public class _03_bubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tmpNum={54,23,8,87,56,21,34,17,6,23,4};
bubbleSort bubbleSort = new bubbleSort(tmpNum);
bubbleSort.bullble_Sort();
bubbleSort.fnPrint();
}
}
class bubbleSort{
private int[] tmpNum;
public bubbleSort(int[] tmpNum){
this.tmpNum=tmpNum;
}
/**
* 氣泡排序函式
*/
public void bullble_Sort(){
int tmp=0;
for (int i = 0; i < tmpNum.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < tmpNum.length; j++) {
if(tmpNum[j]<tmpNum[i]){
tmp=tmpNum[i];
tmpNum[i]=tmpNum[j];
tmpNum[j]=tmp;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 列印函式
*/
public void fnPrint(){
for (int i = 0; i < tmpNum.length; i++) {
if (i==tmpNum.length-1) {
System.out.println(tmpNum[i]);
}else {
System.out.print(tmpNum[i]+"、");
}
}
}
}
六、快速排序:
package algorithm.sort;
/**
* 8大內部排序演算法之一:交換排序之快速排序
* author:baolibin
*/
public class _01_quickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tmpNum={32,12,76,3,9,26,72,9,2,54,3,23}; //待排序的陣列
Sort sort=new Sort(tmpNum);
sort.sortScheduler(0, tmpNum.length-1, tmpNum);
sort.print();
}
}
class Sort {
private int[] sortTmp;
public Sort(int[] sortTmp) {
this.sortTmp = sortTmp;
}
/**
* 遞迴呼叫進行排序
* @param low 左指標
* @param hight 右指標
* @param tmpNum 陣列
*/
public void sortScheduler(int low, int hight,int[] tmpNum){
if(low<hight){
int middle=sortNum(0, hight, tmpNum);
if(middle>0&&middle<hight){
sortScheduler(0, middle-1, tmpNum);
sortScheduler(middle+1, hight, tmpNum);
}
}
}
/**
* @param low 左指標
* @param hight 右指標
* @param tmpNum 陣列
* @return 基準元素插入的位置
*/
public int sortNum(int low, int hight, int[] tmpNum) {
int tmp = tmpNum[low];
while (low < hight) {
while (low < hight && tmp <= tmpNum[hight]) {
hight--;
}
tmpNum[low] = tmpNum[hight];
while (low < hight && tmpNum[low] <= tmp) {
low++;
}
tmpNum[hight] = tmpNum[low];
}
tmpNum[low] = tmp;
return low;
}
/**
* 進行結果的列印
*/
public void print() {
for (int i = 0; i < sortTmp.length; i++) {
if(i==sortTmp.length-1){
System.out.print(sortTmp[i]);
}else{
System.out.print(sortTmp[i] + "、");
}
}
}
}
七、歸併排序:
package algorithm.sort;
/**
* 歸併排序
* @author baolibin
*/
public class _07_mergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tmpNum={54,23,8,87,56,21,34,17,6,23,4};
mergeSort mergesort = new mergeSort(tmpNum);
mergesort.sortProgress();
mergesort.fnPrint();
}
}
class mergeSort {
private int[] tmpNum;
public mergeSort(int[] tmpNum) {
this.tmpNum=tmpNum;
}
/**
* 歸併排序
* @param tmpNum 待排序的陣列
* @param low 第一段陣列的起始下標
* @param middle 第一段陣列的末尾下標
* @param high 第二段陣列的末尾下標
*/
public void merge_Sort(int[] tmpNum, int low, int middle, int high) {
int first = low; // 存放第一段序列下標
int second = middle + 1; // 存放第二段序列下標
int tmpkey = 0; // 存放合併陣列的下標
int tmp[] = new int[high - low + 1]; // 存放合併陣列用的
while (first <= middle && second <= high) {
if (tmpNum[first] < tmpNum[second]) {
tmp[tmpkey] = tmpNum[first];
first++;
tmpkey++;
} else {
tmp[tmpkey] = tmpNum[second];
second++;
tmpkey++;
}
}
// 第一個段陣列沒有遍歷完
while (first <= middle) {
tmp[tmpkey] = tmpNum[first];
first++;
tmpkey++;
}
// 第二個段陣列沒有遍歷完
while (second <= high) {
tmp[tmpkey] = tmpNum[high];
second++;
tmpkey++;
}
int k=low;
//將合併的陣列拷貝到原始的陣列中
for (int i = 0; i < tmp.length; i++) {
tmpNum[k]=tmp[i];
k++;
}
}
public void sortProgress(){
//進行每趟歸併,改變字表的長度
for (int step = 1; step < tmpNum.length; step=2*step) {
int i=0;
//進行每趟歸併排序,歸併長度為step的兩個相鄰的子表
for(i=0;i+2*step-1<tmpNum.length;i=i+2*step){
merge_Sort(tmpNum, i, i+step-1, i+2*step-1);
}
//剩下單獨的一個子表
if (i+step-1<tmpNum.length) {
merge_Sort(tmpNum, i, i+step-1, tmpNum.length-1);
}
}
}
/**
* 列印函式
*/
public void fnPrint() {
for (int i = 0; i < tmpNum.length; i++) {
if (i == tmpNum.length - 1) {
System.out.println(tmpNum[i]);
} else {
System.out.print(tmpNum[i] + "、");
}
}
}
}
八、基數排序:
package algorithm.sort;
/**
* 基數排序
* @author baolibin
*/
public class _08_radixSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tmpNum={54,23,8,187,56,21,341,17,6,23,4,88,33,40,39,73,15};
radixSort radixsort = new radixSort(tmpNum);
radixsort.radix_Sort(tmpNum,3); //開始基數排序
radixsort.fnPrint();
}
}
/**
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
class radixSort{
private int[] tmpNum; //帶排序的陣列
private int radix=10; //指0~9,像鄰接連結串列的左側豎著顯示的陣列
private int[] bucket_offset_right;//一共10位,每個值代表著,在bucket陣列,的對應桶,的末尾的下標。 以及每個桶儲存的個數
private int[] bucket; ////原本鄰接連結串列的結構用陣列進行儲存,每個桶在對應範圍下標進行儲存。
public radixSort(int[] tmpNum) {
this.tmpNum=tmpNum;
bucket_offset_right=new int[radix]; //代表著每個桶的個數以及在bucket桶陣列中的儲存下標
bucket=new int[tmpNum.length];
}
/**
* 基數排序部分
* @param tmpNum 待排序的陣列
* @param low_index 陣列的開始下標
* @param high_index 陣列的結尾下標
* @param max_Num_length 陣列中最大元素的位置
*/
public void radix_Sort(int[] tmpNum,int max_length){
for (int i = 1; i <= max_length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < radix; j++) { //各個桶儲存的個數置為0
bucket_offset_right[j]=0;
}
int countNum=0;
for (int j = 0; j < tmpNum.length; j++) { //統計每個桶要裝入的資料的個數
countNum=tmpNum[j]/((int) Math.pow(10, i-1))%10;
// System.out.println("countNum="+countNum);
bucket_offset_right[countNum]++;
}
for (int j = 1; j < radix; j++) { //儲存每個桶截止本桶一共裝的個數,存的值對應桶陣列下標,方便進行每個桶快速定位進行儲存
bucket_offset_right[j]=bucket_offset_right[j]+bucket_offset_right[j-1];
}
for (int j = tmpNum.length-1; j >=0; j--) { //將資料依次存入桶中
countNum=tmpNum[j]/((int) Math.pow(10, i-1))%10;
bucket[bucket_offset_right[countNum]-1]=tmpNum[j]; //將資料儲存到對應桶的指定陣列位置,倒著進行儲存
bucket_offset_right[countNum]--; //對應桶儲存位置指標,從桶的末尾往前移一位
}
for (int j = 0; j < tmpNum.length; j++) {
tmpNum[j]=bucket[j];
}
// fnPrint();
}
}
/**
* 列印函式
*/
public void fnPrint() {
for (int i = 0; i < tmpNum.length; i++) {
if (i == tmpNum.length - 1) {
System.out.println(tmpNum[i]);
} else {
System.out.print(tmpNum[i] + "、");
}
}
}
}
八大內部排序的複雜度比較: