Stanford Machine Learning 公開課筆記(1) Linear Regression
最近在Coursera上學習Stanford的Andrew Ng的Machine Learning公開課,也做筆記,寫作業。記錄一下我的筆記。大部分是課堂視訊截圖,形式比較醜,主要用來幫助自己回憶一些內容。
寫完程式設計作業(主要用octave來實現,和matlab語法很像)之後,發現寫作業並且在系統中提交通過才能給你帶來真正地學會了的感覺,推薦認真聽課並且獨立完成作業。
課程引入
1 Regression和Classification的區別
Regression: to predict the continuous valued output.
Classification: to predict the discrete valued output.
2 如何用ML algorithm處理有infinite number of features?
SVM會有mathematical trick to allow computer to deal with infinite number of features without exhausting the memory.
3 Cocktail Party Algorithm 問題
Microphone1 有speaker1和speaker2的聲音的混合,Microphone2也有speaker1和speaker2的聲音的混合,如何從中清晰地分離出speaker1和 speaker2的聲音呢?可以使用ML演算法。
4選什麼工具
Trust Professor,在學習Machine Learning時候使用的工具是 Octave or Matlab,比Java/C++更快
5 Supervised Learning和Unsupervised Learning的區別
Supervised Learning有labeled data,但是Unsupervised Learning沒有
Cost Function, 求最小值,區域性最優和全域性最優
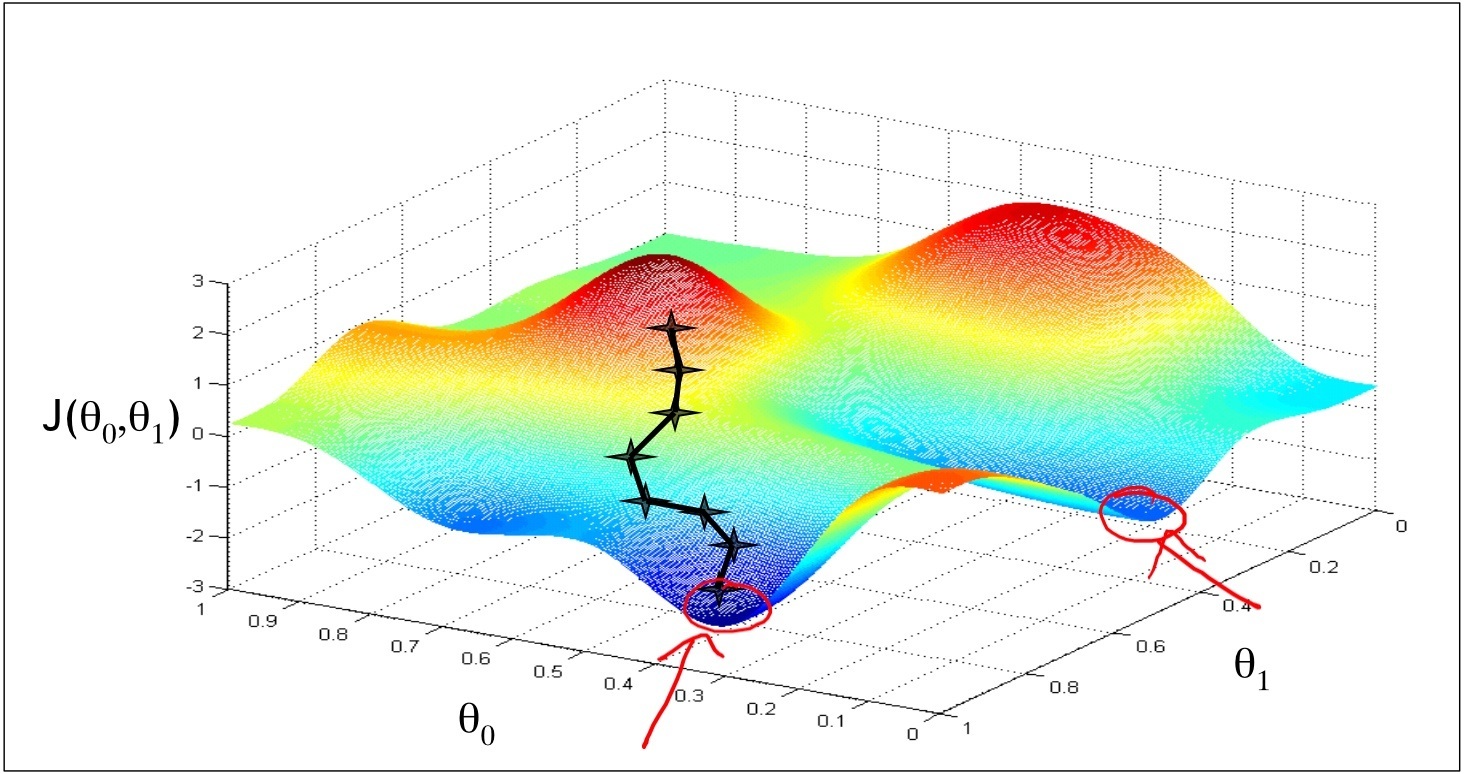
1 如下圖,是線性迴歸(假設只有兩個引數)cost function的視覺化圖形表達,是個(bowl)碗型平面
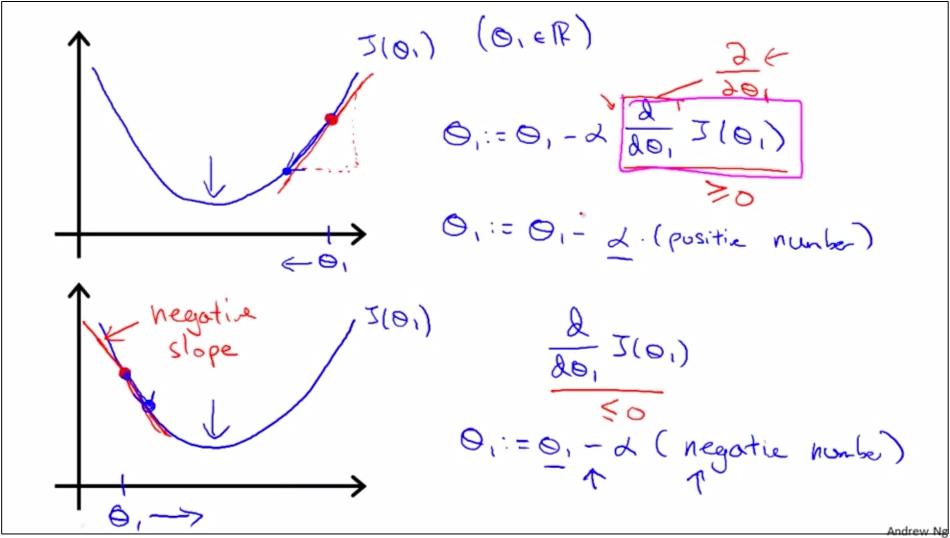
2 關於求導數的複習



3 有沒有可能gradient descent找到的是區域性最優? 有可能。
Gradient Descent(梯度下降的)方法可能跳不出區域性最優。 但是,對只有2個變數的線性函式的模型而言,由於cost function是一個凸函式,所以只有一個最優點,所以區域性最優就是全域性最優。
Contour Plot
如下,把bowl壓扁了就是contour plot,每個圈圈上的點都有相同的J(θ₀,θ₁)取值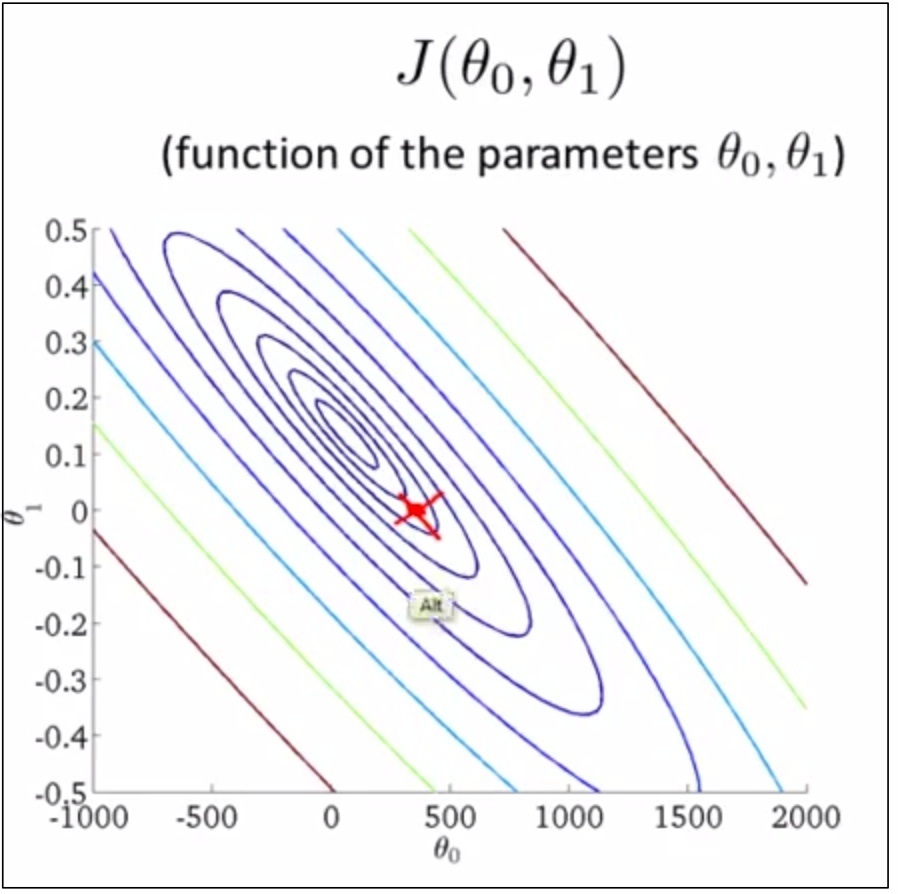
Gradient Descent
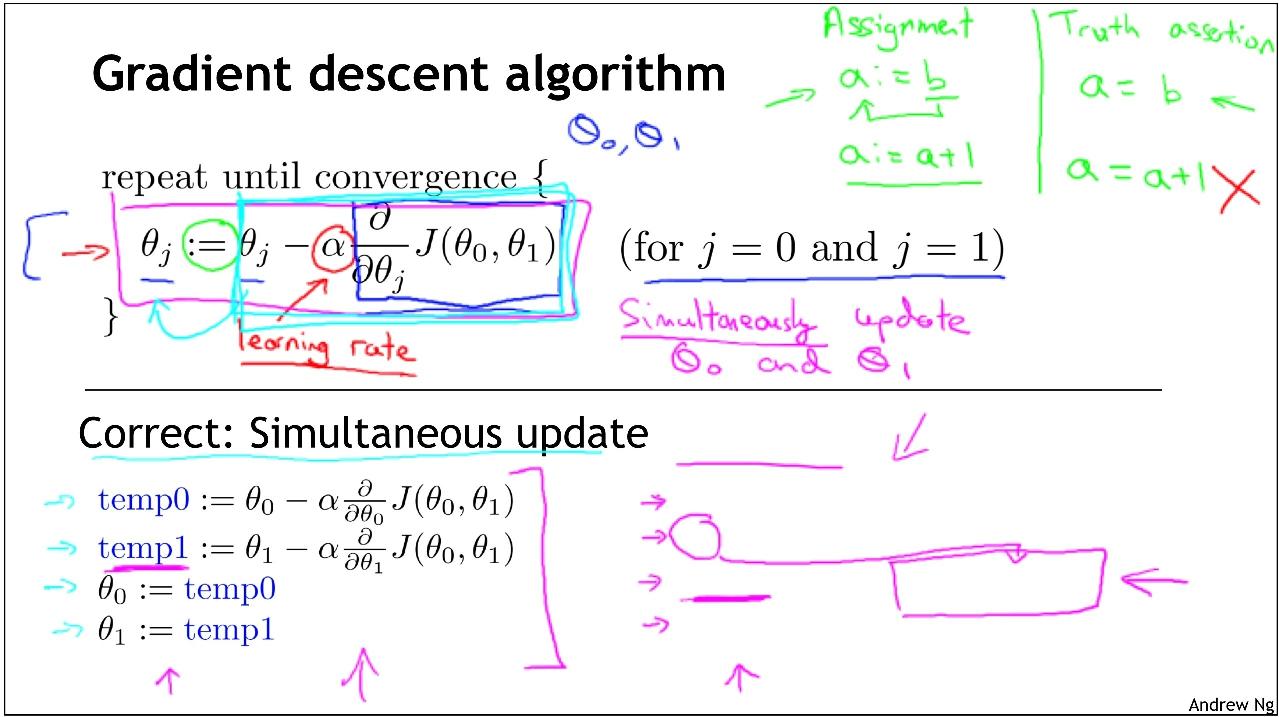
如上面2圖,θ0減去α*偏導數的目的是為了使得θ,向著bowl平面的最低點聚攏,也就是向著二次函式的中間點聚攏。
區域性最優
如上圖,是公式的含義,Gradient Descent的工作機制是,as we approach a local minimum, Learning rate α will automatically take smaller steps, thus no need to decrease α over time.
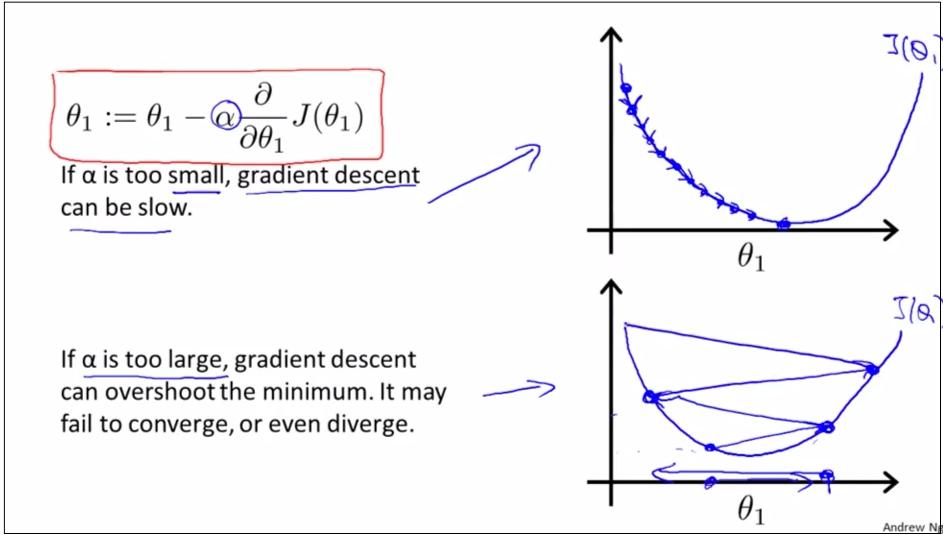
如上圖,如果learning rate α過大過小會怎樣?
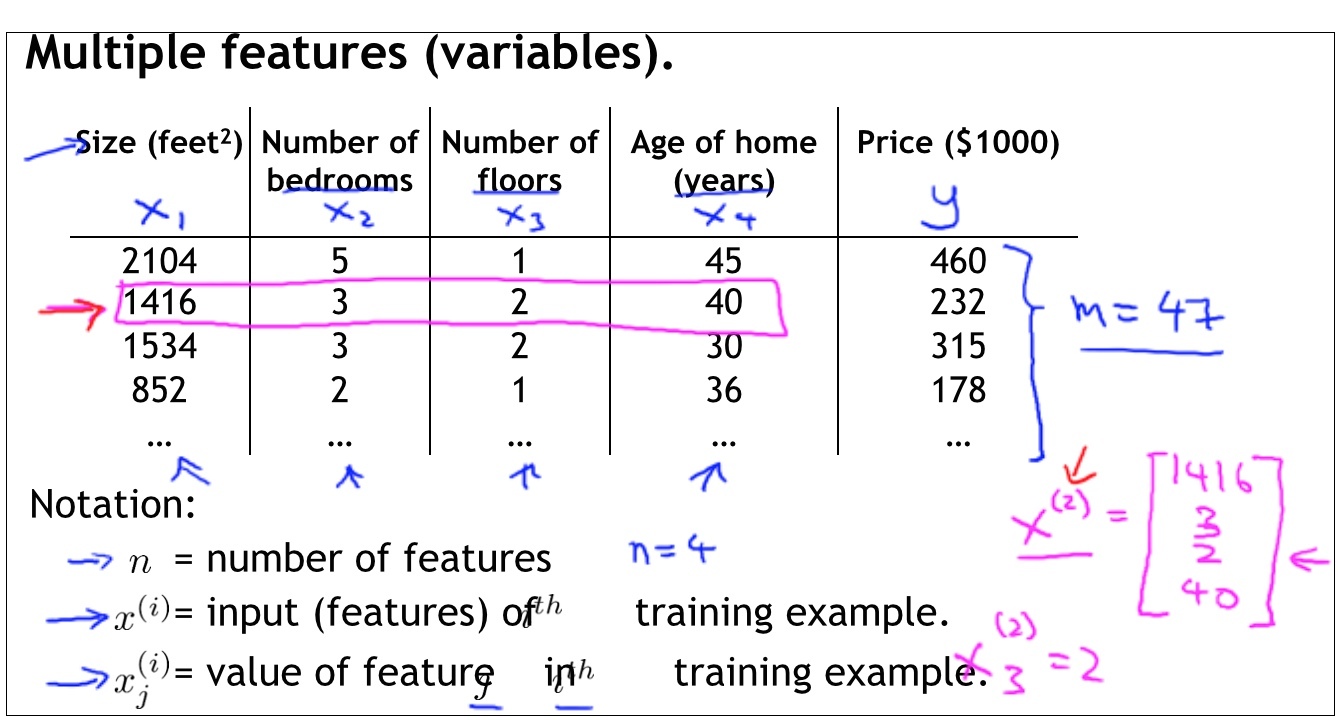
Linear Regression with Multiple Variables
如上圖,各種變數的含義

如上圖,說明了在多變數的情況下,如何在每步使用Gradient Descent對進行更新。
Feature Scaling make sure that features are on a similar scale
如上圖,做Feature Scaling的好處是,可以儘可能低使得contour長得像個circle,所以gradient descent在找尋global minimun的過程中就會有更加直接的路徑(右圖),而不是像左圖那樣。
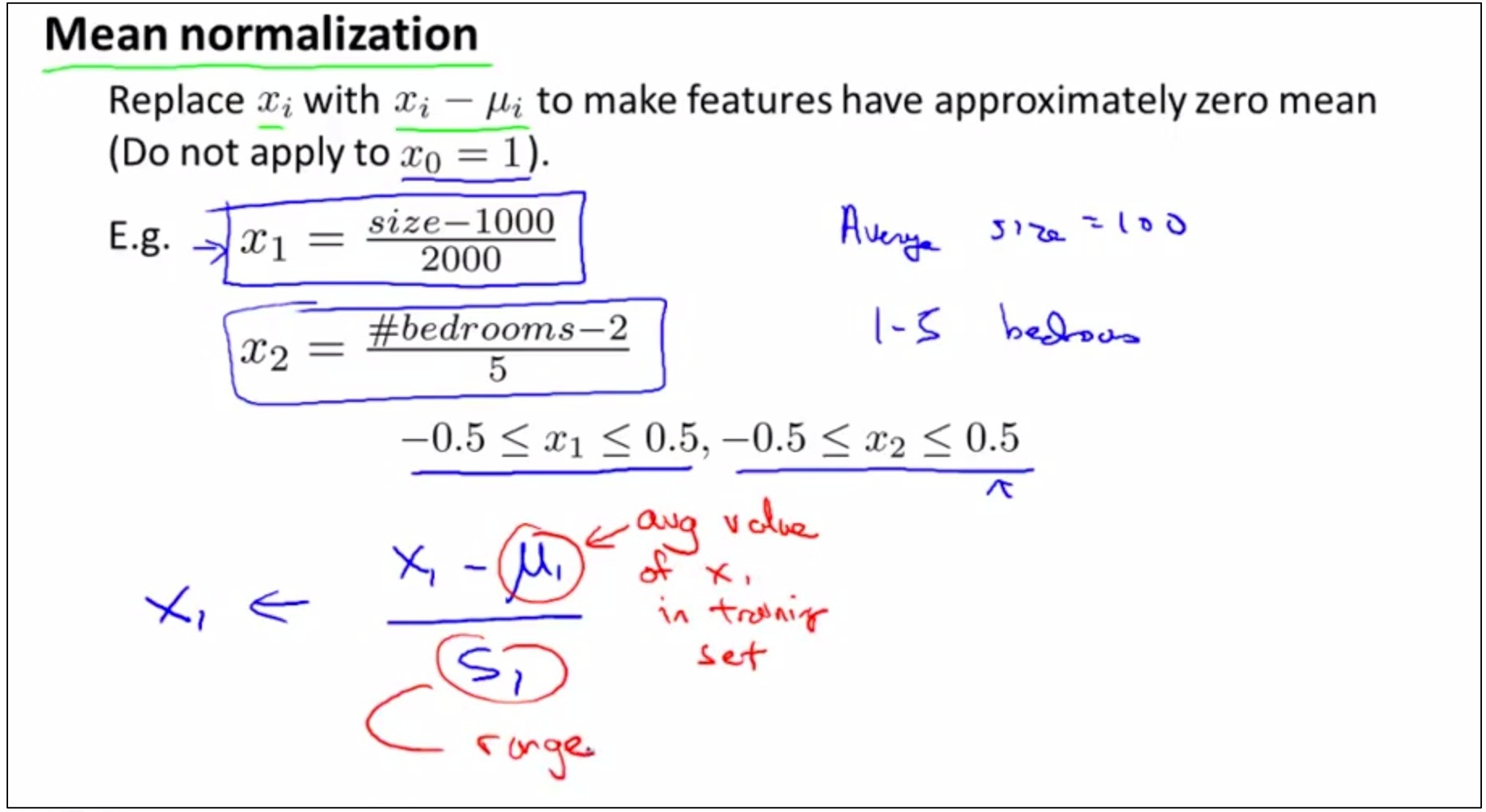
如上圖,對feature的取值做處理通常包含兩件事情,1 feature scaling 2 mean normalization
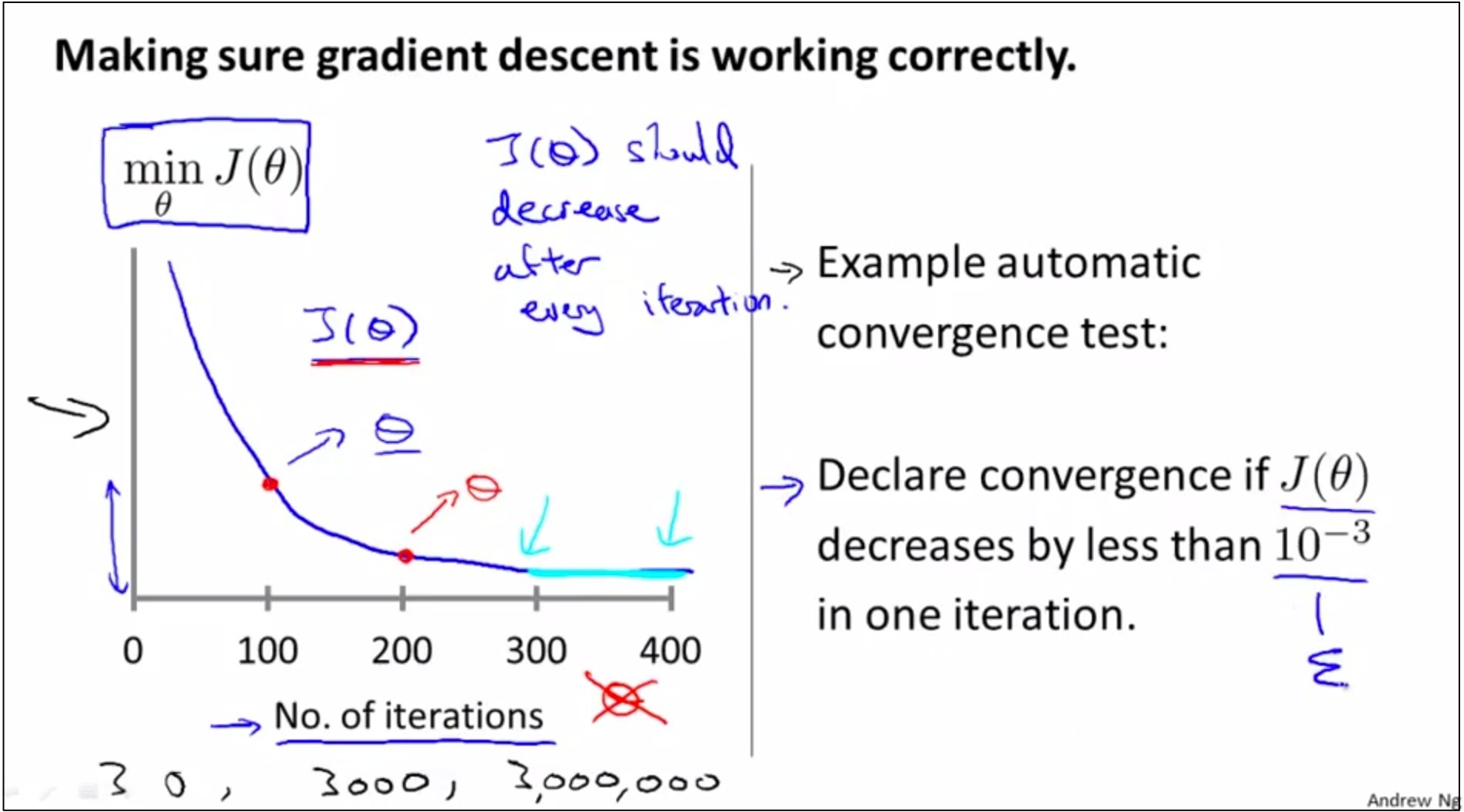
Debugging and make sure that gradient descent works well
如上圖,有兩種辦法,分別在豎線左邊和豎線右邊。
第一種: 作圖,看看是否隨著iteration的進行,min J(θ)是先減小然後逐漸flatten的趨勢
第二種: automatic convergence test,難點是很難找到合適的threshold
常見錯誤 learning rate α 取值過大