PAT A1086 Tree Traversals Again 樹的遍歷[由前序和中序求後序遍歷]
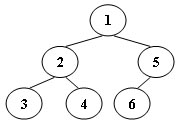
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Figure 1
一箇中序二叉樹遍歷可以用非遞迴方式用棧來實現。比如,假設遍歷一個有6個節點的二叉樹(鍵值從1-6),棧的操作如下:push 1;push 2;push 3;pop();pop();push 4; pop();pop(); push 5; push 6; pop(); pop(). 然後通過這一系列操作就可以構造出如圖1的二叉樹,你的任務是給出這棵樹的後序遍歷
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
第一行包含一個正整數N,表示這棵樹的總節點數(節點從1-N進行編號)。之後有2N行,每一行描述了一個棧操作
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
打印出正確的二叉樹的後序遍歷序列,所有數字用空格隔開,最後一個數字之後沒有空格
思路:通過棧操作構造二叉樹再進行後序遍歷。
Push的次序就是先序遍歷序列中元素的順序。Pop則是中序遍歷序列中元素的順序。
即知道先序遍歷和中序遍歷求後序遍歷。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 50;
struct node{
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};
int pre[maxn],in[maxn],post[maxn];
int n;
//------根據前序遍歷和中序遍歷構造二叉樹------
node* create(int preL,int preR,int inL,int inR){
if(preL>preR) return NULL;
node* root = new node;
root ->data = pre[preL];
int k;
for(k=inL;k<inR;k++){
if(in[k]==pre[preL]){
break;
}
}
int numLeft = k-inL;
root->lchild=create(preL+1,preL+numLeft,inL,k-1);
root->rchild=create(preL+numLeft+1,preR,k+1,inR);
return root;
}
int num=0;
//-------後序遍歷----------
void postorder(node* root){
if(root== NULL) return;
postorder(root->lchild);
postorder(root->rchild);
printf("%d",root->data);
num++;
if(num<n) printf(" ");
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
char str[5];
stack<int> st;
int x,preIndex=0,inIndex=0;
for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++){
scanf("%s",str);
if(strcmp(str,"Push")==0){//如果是Push,入棧,放入前序遍歷陣列
scanf("%d",&x);
pre[preIndex++]=x;
st.push(x);
}else{//如果是Pop 出棧,放入中序遍歷陣列
in[inIndex++]=st.top();
st.pop();
}
}
node* root = create(0,n-1,0,n-1);
postorder(root);
return 0;
}