JavaEE框架——Spring入門基礎(控制反轉Ioc和切面技術Aop)
一.簡介:
Spring在英語中含義是春天,對於JavaEE開發者來說,Spring框架出現確實帶來了一股全新的春天的氣息。早在2002年,Rod Johson在其編著的《Expert one to one J2EE design anddevelopment》書中,對Java EE框架臃腫、低效、脫離現實的種種現狀提出了很多質疑,並積極尋求探索革新之道。由他主導編寫了interface21框架,從實際需求出發,著眼於輕便、靈巧,易於開發、測試和部署的輕量級開發框架。以interface21框架為基礎,並集成了其它許多開源成果,於2004年3月24日,釋出了1.0正式版取名為Spring。
Spring的核心是個
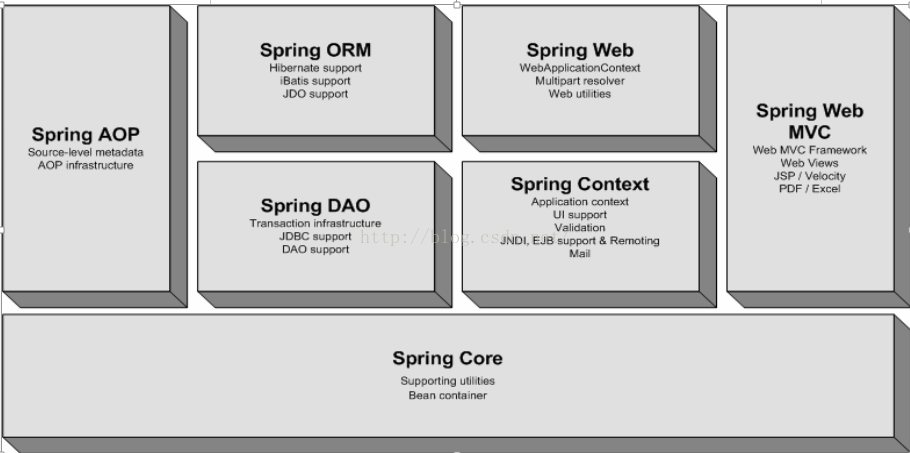
輕量級容器,實現了IoC(控制翻轉)模式的容器,基於此核心容器所建立的應用程式,可以達到程式元件的鬆散耦合。這些特性都使得整個應用程式維護簡化。Spring框架核心由下圖所示的七個模組組成。
1、核心容器(Core)
這是Spring框架最基礎的部分,它提供了依賴注入(Dependency Injection)特徵來實現容器對Bean的管理。這裡最基本的概念是BeanFactory,它是任何Spring應用的核心。BeanFactory是工廠模式的一個實現,它使用IoC將應用配置和依賴說明從實際的應用程式碼中分離出來。
2、AOP模組
AOP即面向切面程式設計技術,Spring在它的AOP
模組中提供了對面向切面程式設計的豐富支援。AOP允許通過分離應用的業務邏輯與系統級服務(例如安全和事務管理)進行內聚性的開發。應用物件只實現它們應該做的——完成業務邏輯——僅此而已。它們並不負責其它的系統級關注點,例如日誌或事務支援。3、物件/關係對映整合模組ORM
Hibernate是成熟的ORM產品,Spring並沒有自己實現ORM框架而是集成了幾個流行的ORM產品如Hibernate、JDO和iBATIS等。可以利用Spring對這些模組提供事務支援等。
4、JDBC抽象和DAO模組
Spring雖然集成了幾個ORM產品,但也可以不選擇這幾款產品,因為Spring提供了JDBC和DAO模組
。該模組對現有的JDBC技術進行了優化。你可以保持你的資料庫訪問程式碼乾淨簡潔,並且可以防止因關閉資料庫資源失敗而引起的問題。5、Spring的Web模組
Web上下文模組建立於應用上下文模組之上,提供了一個適合於Web應用的上下文。另外,這個模組還提供了一些面向服務支援。例如:實現檔案上傳的multipart請求,它也提供了Spring和其它Web框架的整合,比如Struts、WebWork。
6、應用上下文(Context)模組
核心模組的BeanFactory使Spring成為一個容器,而上下文模組使它成為一個框架。Web上下文模組建立於應用上下文模組之上,提供了一個適合於Web應用的上下文。該模組還提供了一些面向服務支援這個模組擴充套件了BeanFactory的概念,增加了對國際化(I18N)訊息、事件傳播以及驗證的支援。
另外,這個模組還提供了許多企業服務,例如電子郵件、JNDI訪問、EJB整合、遠端以及時序排程(scheduling)服務。也包括對模版框架例如Velocity和FreeMarker整合的支援。
7、Spring的MVC框架
Spring為構建Web應用提供了一個功能全面的MVC框架。雖然Spring可以很容易地與其它MVC框架整合,例如Struts2,但Spring的MVC框架使用IoC對控制邏輯和業務物件提供了完全的分離。
二.Spring入門示例
spring2.5基礎包:spring.jar和commons-logging.jar
spring3.x基礎包:
- commons-logging.jar
- org.springframework.asm-3.1.1.RELEASE.jar
- org.springframework.beans-3.1.1.RELEASE.jar
- org.springframework.context.support-3.1.1.RELEASE.jar
- org.springframework.context-3.1.1.RELEASE.jar
- org.springframework.core-3.1.1.RELEASE.jar
- org.springframework.expression-3.1.1.RELEASE.jar
建立好web工程或Java工程後在MyEclipse中可以加入Spring的支援,匯入Spring的核心包。如果是Eclipse則在Spring網站上下載Spring的核心包並加入到工程中。1、編寫一個普通的Java類(JavaBean)
package cn.hncu.s25.domain; public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public Person() { System.out.println("這是建構函式"); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }2、在Spring配置檔案applicationContext.xml。將JavaBean由Spring容器來管理。(2.5和3.x版本不一致,這裡一2.5版本為例)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="p" class="cn.hncu.s25.domain.Person" scope="singleton"></bean> </beans>3、如何使用Spring容器配置的Bean
BeanFactory factory=new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"));//這是2.5版本的方法 Person p=(Person) factory.getBean("p"); System.out.println(p.hashCode());
三、Spring配置檔案詳解:
這個配置檔案
這是Bean物件<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="p" class="cn.hncu.s3x.domain.Person"> <property name="name" value="Jack"></property> <property name="age" value="23"></property> </bean> <bean id="user" class="cn.hncu.s3x.demo2.User"> <property name="name" value="Jack" /> <property name="age" value="20" /> <property name="cat" ref="cat" /> <property name="pets"> <list> <value>Tom</value> <value>dog</value> <value>pig</value> </list> </property> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="name" value="中國"> </entry> </map> </property> <property name="set"> <set> <value>aaa</value> <value>bbb</value> </set> </property> <property name="objs"> <array> <value>222</value> <ref bean="cat2" /> <list> <ref bean="cat2" /> <ref bean="cat" /> </list> <bean class="cn.hncu.s3x.demo2.Cat"> <property name="name" value="我的貓" /> </bean> </array> </property> <property name="list"> <list> <map> <entry key-ref="p" value-ref="cat"></entry> <entry value-ref="cat2"> <key> <bean class="cn.hncu.s3x.domain.Person"> <property name="name" value="王建安" /> <property name="age" value="25" /> </bean> </key> </entry> </map> </list> </property> </bean> <bean id="cat" class="cn.hncu.s3x.demo2.Cat"> <property name="name" value="Tom貓" /> </bean> <bean id="cat2" class="cn.hncu.s3x.demo2.Cat"> <property name="name" value="黑貓" /> </bean> </beans>package cn.hncu.s3x.demo2; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; public class User { private String name; private Integer age; private Cat cat; private List<String> pets; private Map<String,Object> map; private Set<String> set; private Object objs[]; private List<Map<Object, Cat>> list; public List<Map<Object, Cat>> getList() { return list; } public void setList(List<Map<Object, Cat>> list) { this.list = list; } public Set<String> getSet() { return set; } public void setSet(Set<String> set) { this.set = set; } public Object[] getObjs() { return objs; } public void setObjs(Object[] objs) { this.objs = objs; } public Map<String, Object> getMap() { return map; } public void setMap(Map<String, Object> map) { this.map = map; } public List<String> getPets() { return pets; } public void setPets(List<String> pets) { this.pets = pets; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Cat getCat() { return cat; } public void setCat(Cat cat) { this.cat = cat; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", cat=" + cat + ", pets=" + pets + ", map=" + map + ", set=" + set + ", objs=" + Arrays.toString(objs) + ", list=" + list + "]"; } } package cn.hncu.s3x.demo2; public class Cat { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Cat [name=" + name + "]"; } } package cn.hncu.s3x.domain; public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
這是測試程式碼package cn.hncu.s3x.demo2; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Demo2 { @Test public void demo1(){ ApplicationContext act=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app2.xml"); User user=act.getBean("user", User.class); System.out.println(user); } }
四、Spring IOC 控制反轉
IoC(Inversion of Control)中文譯為控制反轉也可以叫做DI(Dependency Injection,依賴注入)。
控制反轉模式的基本概念是:不直接建立物件,但是在xml配置檔案中描述建立它們的方式。在工程中使用該Bean時由Spring容器建立Bean的例項。在程式碼中不直接與物件和服務連線,但在配置檔案中描述哪一個元件需要哪一項服務。
第1步、Spring注入(又稱依賴注入DI):其目的是為其中bean的屬性賦值
第2步:在配置檔案中注入屬性的初始值
五、Spring Bean的作用域
在Spring2.0之前bean只有2種作用域即:singleton(單例)、non-singleton(也稱prototype), Spring2.0以後,增加了session、request、global session三種專用於Web應用程式上下文的Bean。
因此,預設情況下Spring2.0現在有五種型別的Bean。當然,Spring2.0對Bean的型別的設計進行了重構,並設計出靈活的Bean型別支援,理論上可以有無數多種型別的Bean,使用者可以根據自己的需要,增加新的Bean型別,滿足實際應用需求。
1、singleton單例項
當一個bean的作用域設定為singleton,那麼Spring IOC容器中只會存在一個共享的bean例項,並且所有對bean的請求,只要id與該bean定義相匹配,則只會返回bean的同一例項。換言之,當把一個bean定義設定為singleton作用域時,Spring IOC容器只會建立該bean定義的唯一例項。這個單一例項會被儲存到單例快取(singletoncache)中,並且所有針對該bean的後續請求和引用都將返回被快取的物件例項。
<beanid="userdao"class="com.bean.UserDao"scope="singleton"/>
或<beanid=" userdao" class="com.bean.UserDao"singleton="true"/>
UserDaobean1=( UserDao)factory.getBean("userdao");
UserDaobean2=( UserDao)factory.getBean("userdao");
2、prototype多例項
每個Spring容器中,一個bean對應多個例項. prototype作用域部署的bean,每一次請求(將其注入到另一個bean中,或者以程式的方式呼叫容器的getBean()方法)都會產生一個新的bean例項,相當一個new的操作。
<beanid="userdao"class="com.bean.UserDao"
scope="prototype"/>
或<beanid=" userdao" class="com.bean.UserDao"
singleton="false"/>
UserDao bean1=(UserDao)factory.getBean("userdao");
UserDao bean2=(UserDao)factory.getBean("userdao");
Bean1與bean2的引用不相同。每次使用getBean()重新產生一個例項
3、request
request表示該針對每一次HTTP請求都會產生一個新的bean,同時該bean僅在當前HTTP request內有效。
<bean id="userdao"class="com.bean.UserDao"
scope="request"/>
4、session
session作用域表示該針對每一次HTTP請求都會產生一個新的bean,同時該bean僅在當前HTTP session內有效.
Spring AOP程式設計
切面(Aspect):簡單的理解就是把那些與核心業務無關的程式碼提取出來,進行封裝成一個或幾個模組用來處理那些附加的功能程式碼。(如日誌,事務,安全驗證)我們把這個模組的作用理解為一個切面,其實切面就是我們寫一個類,這個類中的程式碼原來是在業務模組中完成的,現在單獨成一個或幾個類。在業務模組需要的時候才織入。
連線點(Joinpoint):在程式執行過程中某個特定的點,比如某方法呼叫的時候或者處理異常的時候。 在Spring AOP中,一個連線點總是代表一個方法的執行。通過宣告一個JoinPoint型別的引數可以使通知(Advice)的主體部分獲得連線點資訊。
切入點(Pointcut):本質上是一個捕獲連線點的結構。在AOP中,可以定義一個pointcut,來捕獲相關方法的呼叫
織入(Weaving):把切面(aspect)連線到其它的應用程式型別或者物件上,並建立一個被通知(advised)的物件。這些可以在編譯時,類載入時和執行時完成。Spring和其它純Java AOP框架一樣,在執行時完成織入。
通知(Advice):在切面的某個特定的連線點(Joinpoint)上執行的動作。通知有各種型別,其中包括“around”、“before”和“after”等通知。通知的型別將在後面部分進行討論。許多AOP框架,包括Spring,都是以攔截器做通知模型,並維護一個以連線點為中心的攔截器鏈。
通知的型別:
前置通知(Before advice):在某連線點(join point)之前執行的通知,但這個通知不能阻止連線點前的執行(除非它丟擲一個異常)。
返回後通知(After returning advice):在某連線點(join point)正常完成後執行的通知:例如,一個方法沒有丟擲任何異常,正常返回。
丟擲異常後通知(After throwing advice):在方法丟擲異常退出時執行的通知。
後置通知(After (finally)advice):當某連線點退出的時候執行的通知(不論是正常返回還是異常退出)。
環繞通知(Around Advice):包圍一個連線點(join point)的通知,如方法呼叫。這是最強大的一種通知型別。 環繞通知可以在方法呼叫前後完成自定義的行為。它也會選擇是否繼續執行連線點或直接返回它們自己的返回值或丟擲異常來結束執行。
下面演示程式碼:
純Java方式寫AOP(攔截技術)
package cn.hncu.spring4x.aop; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.aopalliance.aop.Advice; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.aop.Advisor; import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice; import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice; import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory; import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean; import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor; import org.springframework.aop.support.JdkRegexpMethodPointcut; import cn.hncu.spring4x.domain.Person; public class AopDemo { @Test//純Java的方式實現切面(攔截)技術 public void demo1(){ Person p=new Person(); ProxyFactory factory=new ProxyFactory(); //該類的功能沒有ProxyFactoryBean強 factory.setTarget(p);//1 給代理工廠一個原型物件 //切面 = 切點 + 通知 //切點 JdkRegexpMethodPointcut pointcut=new JdkRegexpMethodPointcut(); pointcut.setPattern("cn.hncu.spring4x.domain.Person.run"); // pointcut.setPattern(".*run.*");ProxyFactory對setPattern無效 Advice advice=new MethodInterceptor() { @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("前面攔截"); Object obj=invocation.proceed(); System.out.println("後面攔截"); return obj; } }; //切面 = 切點 + 通知 Advisor advisor=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, advice); factory.addAdvice(advice); Person p2=(Person) factory.getProxy(); // p2.run(); // p2.run(5); p2.say(); } @Test//純Java的方式實現切面(攔截)技術 public void demo2(){ ProxyFactoryBean factoryBean=new ProxyFactoryBean(); factoryBean.setTarget(new Person()); //切面 = 切點 + 通知 //切點 JdkRegexpMethodPointcut pointcut=new JdkRegexpMethodPointcut(); pointcut.setPattern(".*run.*"); //通知 前切面---不需要放行,原方法也能執行 Advice beforeAdvice=new MethodBeforeAdvice() { @Override public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println("beforeAdvice攔截");//正則表示式有效 } }; Advice afterReturning=new AfterReturningAdvice() { @Override public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println("afterReturning"); } }; Advice aroundAdvice=new MethodInterceptor() { public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("前面攔截"); Object obj=invocation.proceed(); System.out.println("後面攔截"); return obj; } }; Advisor advisor1=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, beforeAdvice); Advisor advisor2=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, afterReturning); Advisor advisor3=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, aroundAdvice); factoryBean.addAdvisors(advisor1,advisor2,advisor3); //2 給代理工廠一個切面 ---注意,新增的順序的攔截動作執行的順序是有關係的!!! //先加的切面,如果攔前面,就攔在最前面,如果攔後面,就攔在最後面. Person p = (Person) factoryBean.getObject(); //3 從代理工廠中獲取一個代理後的物件 //p.run(); //p.run(0); p.say(); } }
下面演示5種理由配置檔案AOP通知:AroundAdvice.java
package cn.hncu.spring4x.aop; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation; public class AroundAdvice implements MethodInterceptor { @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("前面攔攔...."); Object resObj = invocation.proceed();//放行 System.out.println("後面攔攔....."); return resObj; } }
測試程式碼,
1.xmlpackage cn.hncu.spring4x.aop; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AopXmlDemo { @Test//採用配置檔案的方式使用切面攔截 public void demo1(){ ApplicationContext act=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/hncu/spring4x/aop/1.xml"); Cat cat=act.getBean("catProxide",Cat.class);//要從catProxide返回 cat.run(); cat.say(); cat.run(6); } @Test//把切點和通知配置成 切面的內部bean public void demo2(){ ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/hncu/spring4x/aop/2.xml"); Cat cat = ctx.getBean("catProxide",Cat.class); cat.run(); cat.say(); cat.run(7); } @Test//直接在切面bean中配置“切點的正則表示式”,省去“切點bean”的配置 public void demo3(){ ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/hncu/spring4x/aop/3.xml"); Cat cat = ctx.getBean("catProxide",Cat.class); cat.run(); cat.say(); cat.run(7); } @Test//自動代理 public void demo4(){ ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/hncu/spring4x/aop/4.xml"); Cat cat = ctx.getBean(Cat.class); cat.run(); cat.say(); cat.run(7); } @Test//自己寫的自動代理 public void demo5(){ ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/hncu/spring4x/aop/5.xml"); Cat cat = ctx.getBean("cat",Cat.class); // cat.run(); // cat.say(); // cat.run(7); } }<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd"> <bean id="cat" class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.Cat"></bean> <!-- 切點 --> <bean id="pointcut" class="org.springframework.aop.support.JdkRegexpMethodPointcut"> <property name="pattern" value=".*run.*"></property> </bean> <!-- 通知 ,要自己寫--> <bean id="advice" class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.AroundAdvice"></bean> <!-- 切面=切點+通知 --> <bean id="advisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor"> <property name="advice" ref="advice"></property> <property name="pointcut" ref="pointcut"></property> </bean> <bean id="catProxide" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean"> <property name="target" ref="cat"></property> <property name="interceptorNames"> <list> <value>advisor</value> </list> </property> </bean> </beans>
2.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd"> <bean id="cat" class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.Cat"></bean> <!-- 切面=切點+通知 (把切點和通知寫成內部bean)--> <bean id="advisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor"> <property name="advice"> <bean class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.AroundAdvice"></bean> </property> <property name="pointcut"> <bean class="org.springframework.aop.support.JdkRegexpMethodPointcut"> <property name="patterns"> <list> <value>.*run.*</value> <value>.*say.*</value> </list> </property> </bean> </property> </bean> <bean id="catProxide" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean"> <property name="target" ref="cat"></property> <property name="interceptorNames"> <list> <value>advisor</value> </list> </property> </bean> </beans>3.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd"> <bean id="cat" class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.Cat"></bean> <!--//直接在切面bean中配置“切點的正則表示式”,省去“切點bean”的配置 用到這個類 org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor --> <bean id="advisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor"> <property name="advice"> <bean class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.AroundAdvice"></bean> </property> <property name="patterns"> <list> <value>.*run.*</value> </list> </property> </bean> <bean id="catProxide" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean"> <property name="target" ref="cat"></property> <property name="interceptorNames"> <list> <value>advisor</value> </list> </property> </bean> </beans>4.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd"> <bean id="cat" class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.Cat"></bean> <!--//直接在切面bean中配置“切點的正則表示式”,省去“切點bean”的配置 用到這個類 org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor --> <bean id="advisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor"> <property name="advice"> <bean class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.AroundAdvice"></bean> </property> <property name="patterns"> <list> <value>.*run.*</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 自動代理 --> <bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"></bean> </beans>5.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.3.xsd"> <bean id="cat" class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.Cat"></bean> <!--//直接在切面bean中配置“切點的正則表示式”,省去“切點bean”的配置 用到這個類 org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor --> <bean id="advisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor"> <property name="advice"> <bean class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.AroundAdvice"></bean> </property> <property name="patterns"> <list> <value>.*run.*</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 自動代理 --> <bean class="cn.hncu.spring4x.aop.MyAutoProxy"></bean> </beans>
第五種方法,模擬自動代理MyAutoProxy.java
package cn.hncu.spring4x.aop; import org.springframework.aop.Advisor; import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; public class MyAutoProxy implements BeanPostProcessor,ApplicationContextAware{ private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext=applicationContext;//保證是同一個容器 } @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println(bean+"postProcessBeforeInitialization"); return bean; //直接放行(一定要) } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println(bean+"postProcessAfterInitialization"); ProxyFactoryBean factoryBean=new ProxyFactoryBean(); factoryBean.setTarget(bean); Advisor advisor=applicationContext.getBean("advisor", Advisor.class); factoryBean.addAdvisor(advisor); return factoryBean.getObject(); } }
相關推薦
JavaEE框架——Spring入門基礎(控制反轉Ioc和切面技術Aop)
一.簡介: Spring在英語中含義是春天,對於JavaEE開發者來說,Spring框架出現確實帶來了一股全新的春天的氣息。早在2002年,Rod Johson在其編著的《Expert one to one J2EE design anddevelopment》書中,對J
筆記——spring基本使用(控制反轉IOC、面向切面程式設計AOP、宣告式事務,事務隔離級別、事務傳播)
spring溫習筆記 Spring是一個開放原始碼的設計層面框架,他解決的是業務邏輯層和其他各層的鬆耦合問題,因此它將面向介面的程式設計思想貫穿整個系統應用。 Spring 的控制反轉IOC、面向切面程式設計AOP等特性不多說。 本文核心內容:搭建一個Spring Dem
深入理解spring容器中的控制反轉(IOC)和依賴注入(DI)
首先在開篇之前我們一定一定要明確的就是:DI和IOC並不是兩個概念,DI是IOC思想在應用上的具體例子。 什麼是控制反轉(IOC)? “控制”就是指一件事物對另一件事物進行一種管理,而另一件事物處在一件事物的管理之下,這就叫控制。 在面向物件程式設計的時候,每一個程式的
JavaEE框架---Spring---入門
Spring開源框架 Spring在英語中含義是春天,對於Java EE開發者來說,Spring框架出現確實帶來了一股全新的春天的氣息。早在2002年,Rod Johson在其編著的《Expert one to one J2EE design and development
Spring -- 依賴注入(控制反轉)
依賴注入 Spring框架的核心功能有兩個: Spring容器作為超級大工廠,負責建立、管理所有的Java物件,這些Java物件被稱為Bean。 Spring容器管理容器中Bean之間的依
小白學 Python 爬蟲(33):爬蟲框架 Scrapy 入門基礎(一)
人生苦短,我用 Python 前文傳送門: 小白學 Python 爬蟲(1):開篇 小白學 Python 爬蟲(2):前置準備(一)基本類庫的安裝 小白學 Python 爬蟲(3):前置準備(二)Linux基礎入門 小白學 Python 爬蟲(4):前置準備(三)Docker基礎入門 小白學 Pyth
小白學 Python 爬蟲(34):爬蟲框架 Scrapy 入門基礎(二)
人生苦短,我用 Python 前文傳送門: 小白學 Python 爬蟲(1):開篇 小白學 Python 爬蟲(2):前置準備(一)基本類庫的安裝 小白學 Python 爬蟲(3):前置準備(二)Linux基礎入門 小白學 Python 爬蟲(4):前置準備(三)Docker基礎入門 小白學 Pyth
小白學 Python 爬蟲(35):爬蟲框架 Scrapy 入門基礎(三) Selector 選擇器
人生苦短,我用 Python 前文傳送門: 小白學 Python 爬蟲(1):開篇 小白學 Python 爬蟲(2):前置準備(一)基本類庫的安裝 小白學 Python 爬蟲(3):前置準備(二)Linux基礎入門 小白學 Python 爬蟲(4):前置準備(三)Docker基礎入門 小白學 Pyth
小白學 Python 爬蟲(36):爬蟲框架 Scrapy 入門基礎(四) Downloader Middleware
人生苦短,我用 Python 前文傳送門: 小白學 Python 爬蟲(1):開篇 小白學 Python 爬蟲(2):前置準備(一)基本類庫的安裝 小白學 Python 爬蟲(3):前置準備(二)Linux基礎入門 小白學 Python 爬蟲(4):前置準備(三)Docker基礎入門 小白學 Pyth
小白學 Python 爬蟲(37):爬蟲框架 Scrapy 入門基礎(五) Spider Middleware
人生苦短,我用 Python 前文傳送門: 小白學 Python 爬蟲(1):開篇 小白學 Python 爬蟲(2):前置準備(一)基本類庫的安裝 小白學 Python 爬蟲(3):前置準備(二)Linux基礎入門 小白學 Python 爬蟲(4):前置準備(三)Docker基礎入門 小白學 Pyth
小白學 Python 爬蟲(40):爬蟲框架 Scrapy 入門基礎(七)對接 Selenium 實戰
人生苦短,我用 Python 前文傳送門: 小白學 Python 爬蟲(1):開篇 小白學 Python 爬蟲(2):前置準備(一)基本類庫的安裝 小白學 Python 爬蟲(3):前置準備(二)Linux基礎入門 小白學 Python 爬蟲(4):前置準備(三)Docker基礎入門 小白學 Pyth
小白學 Python 爬蟲(41):爬蟲框架 Scrapy 入門基礎(八)對接 Splash 實戰
人生苦短,我用 Python 前文傳送門: 小白學 Python 爬蟲(1):開篇 小白學 Python 爬蟲(2):前置準備(一)基本類庫的安裝 小白學 Python 爬蟲(3):前置準備(二)Linux基礎入門 小白學 Python 爬蟲(4):前置準備(三)Docker基礎入門 小白學 Pyth
JS入門基礎(if else 與 switch case / node安裝)
json health 案例 js文件 動作 require 步驟 *** 命令 在 JavaScript 中,為不同的決定來執行不同的動作,我們可使用以下條件語句: if 語句 - 只有當指定條件為 true 時,使用該語句來執行代碼 if...else 語句 - 當條
Spring的控制反轉IOC和依賴注入DI
首先想說說IoC(Inversion of Control,控制反轉)。這是spring的核心,貫穿始終。所謂IoC,對於spring框架來說,就是由spring來負責控制物件的生命週期和物件間的關係: 誰控制誰,控制什麼:傳統Java SE程式設計,我們直接在物件內部通過new進行
Nodejs入門基礎(events事件模組、事件抽獎demo)
events,用於宣告事件呼叫,無需打包events1.js基本事件呼叫介紹 var events=require("events");//導events包 var eventsEmitter=new events.EventEmitter();//例項化events模組 /*d
Nodejs入門基礎(使用express建立jade或ejs模板)
建立index.jade(約等於新型的html編碼格式)建立index.ejs(基本跟html沒區別)jade1.js var express = require("express");//匯入express var app = express();//例項化 app.set("view en
spring系統學習之控制反轉 ioc
這學期的課程安排,我們可以系統的學習spring框架了。 相比較自己看部落格筆記,系統的在課堂上學習還是很有必要。 spring是一個開源框架,是為了解決企業應用程式開發複雜性而建立的。 框架的主要優勢之一就是利用其分層架構。 分層架構允許選擇使用哪一個元件,同時
Spring入門學習(基於XML檔案的方式配置事務) 第二十一節
Spring入門學習(基於XML檔案的方式配置事務) XML方式配置事務 XML方式配置事務 複製之前的包,去掉相關的註解,新建Spring配置檔案如下:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?&
控制反轉(IoC)和依賴注入(DI)
容器,字面上理解就是裝東西的東西。常見的變數、物件屬性等都可以算是容器。一個容器能夠裝什麼,全部取決於你對該容器的定義。當然,有這樣一種容器,它存放的不是文字、數值,而是物件、物件的描述(類、介面)或者是提供物件的回撥,通過這種容器,我們得以實現許多高階的功能,其中最常提到的,就是 “解耦” 、“依
Java基礎(適合新學者和架構師閱讀)
近日為了複習CoreJava故自己收集了很多書籍彙編成以下java最核心的內容:參考出處(Java從入門到精通,Java學習手冊(app))備註:我不留對別人毫無用處的博文,所以如果對你有用處請評論。否則,一個月過後沒有超過500我會自行刪除。 Java的誕生與發展