VINS-Mono程式碼解讀——狀態估計器流程 estimator
前言
本文主要介紹VINS的狀態估計器模組(estimator),從ROS角度說是estimator節點。
這個模組可以說是VINS的最核心模組,從論文的內容上來說,裡面的內容包括了VINS的估計器初始化、基於滑動視窗的非線性優化實現緊耦合,即論文第五章(V. ESTIMATOR INITIALIZATION)第六章(VI. TIGHTLY-COUPLED MONOCULAR VIO)。
程式碼放在資料夾vins_estimator中,可以看到,除了上述內容外,還包括有外參標定、視覺化等其他功能的實現,內容實在是太多了!所以本文主要是對vins_estimator資料夾內每個檔案的程式碼功能進行簡單整理,並從estimator_node.cpp開始,對狀態估計器的具體流程進行程式碼解讀,初始化以及緊耦合的理論知識和具體實現將放在以後進行詳細說明
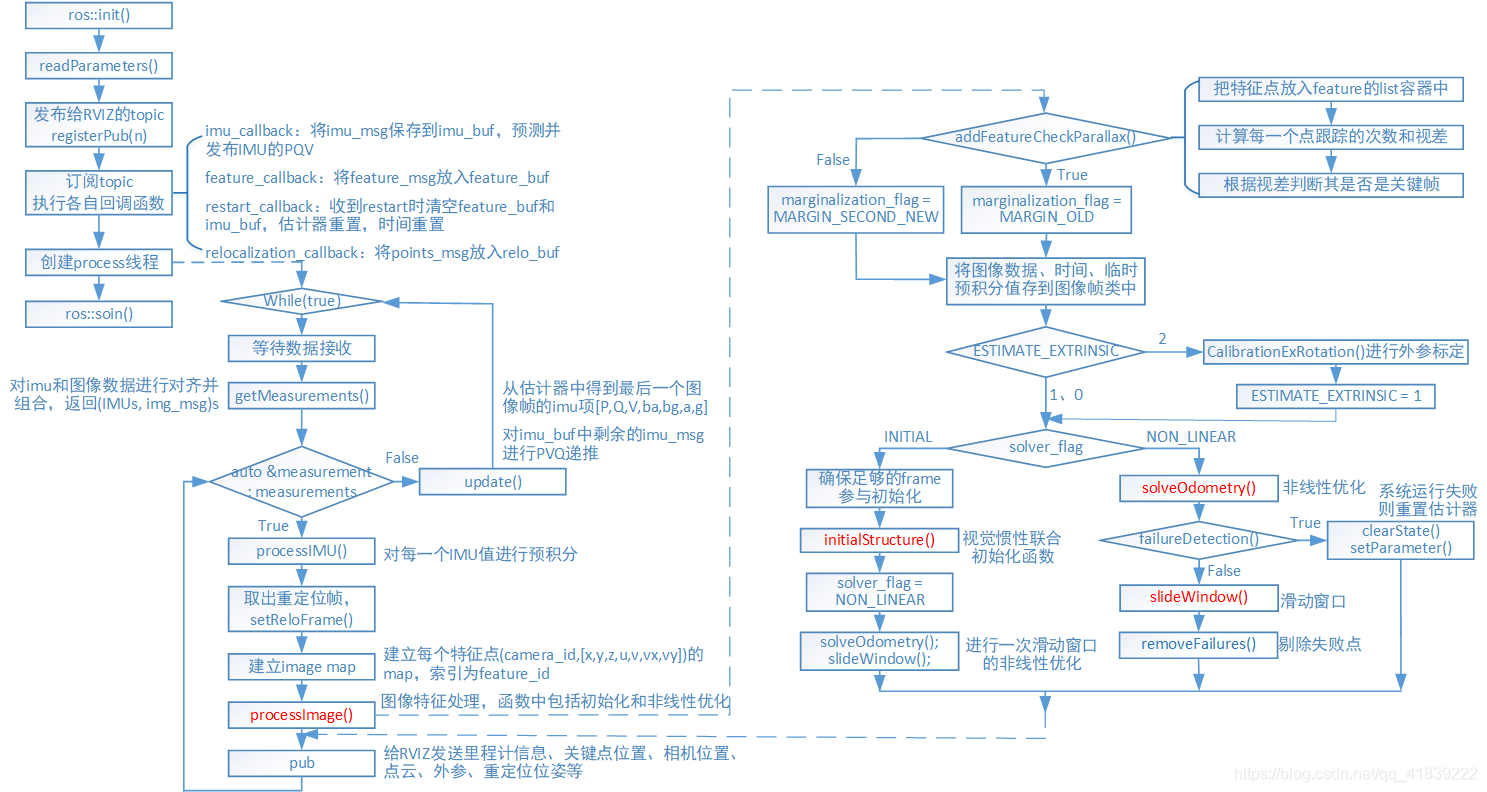
首先放上流程圖!
vins_estimator資料夾
- factor:
- imu_factor.h:IMU殘差、雅可比
- intergration_base.h:IMU預積分
- marginalization.cpp/.h:邊緣化
- pose_local_parameterization.cpp/.h:區域性引數化
- projection_factor.cpp/.h:視覺殘差
- initial:
- initial_alignment.cpp/.h:視覺和IMU校準(陀螺儀偏置、尺度、重力加速度和速度)
- initial_ex_rotation.cpp/.h:相機和IMU外參標定
- initial_sfm.cpp/.h:純視覺SFM
- solve_5pts.cpp/.h:5點法求基本矩陣
- utility:
- CameraPoseVisualization.cpp/.h:相機位姿視覺化
- tic_toc.h:記錄時間
- utility.cpp/.h:各種四元數、矩陣轉換
- visualization.cpp/.h:各種資料釋出
- estimator.cpp/.h:緊耦合的VIO狀態估計器實現
- estimator_node.cpp:ROS 節點函式,回撥函式
- feature_manager.cpp/.h:特徵點管理,三角化,關鍵幀等
- parameters.cpp/.h:讀取引數
程式碼實現
輸入輸出
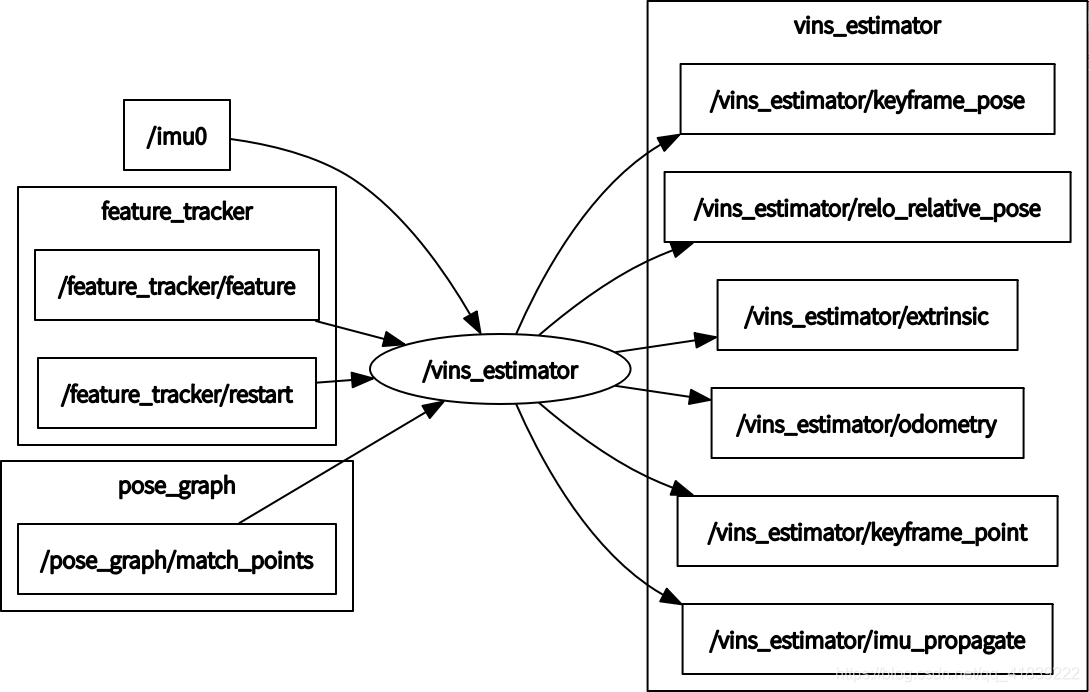
輸入:
1、IMU的角速度和線加速度,即訂閱了IMU釋出的topic:IMU_TOPIC="/imu0"
2、影象追蹤的特徵點,即訂閱了feature_trackers模組釋出的topic:“/feature_tracker/feature"
3、復位訊號,即訂閱了feature_trackers模組釋出的topic:“/feature_tracker/restart"
4、重定位的匹配點,即訂閱了pose_graph模組釋出的topic:“/pose_graph/match_points"
輸出:
1、線上程void process()中給RVIZ傳送里程計資訊、關鍵點位置、相機位置、點雲、外參、重定位位姿等
pubOdometry(estimator, header);//"odometry"
pubKeyPoses(estimator, header);//"key_poses"
pubCameraPose(estimator, header);//"camera_pose"
pubPointCloud(estimator, header);//"history_cloud"
pubTF(estimator, header);//"extrinsic"
pubKeyframe(estimator);//"keyframe_point"、"keyframe_pose"
if (relo_msg != NULL)
pubRelocalization(estimator);//"relo_relative_pose"
2、在回撥函式void imu_callback(const sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr &imu_msg)中將IMU的預測值作為最近一次里程計資訊PQV進行釋出
if (estimator.solver_flag == Estimator::SolverFlag::NON_LINEAR)
pubLatestOdometry(tmp_P, tmp_Q, tmp_V, header);//"imu_propagate"
estimator_node.cpp
| 函式 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| void predict | 從IMU測量值imu_msg和上一個PVQ遞推得到當前PVQ |
| void update() | 得到視窗最後一個影象幀的imu項[P,Q,V,ba,bg,a,g],對imu_buf中剩餘imu_msg進行PVQ遞推 |
| getMeasurements() | 對imu和影象資料進行對齊並組合 |
| void imu_callback | imu回撥函式,將imu_msg儲存到imu_buf,IMU預測值併發布[P,Q,V,header] |
| void feature_callback | feature回撥函式,將feature_msg放入feature_buf |
| void restart_callback | restart回撥函式,收到restart訊息時清空feature_buf和imu_buf,估計器重置,時間重置 |
| void relocalization_callback | relocalization回撥函式,將points_msg放入relo_buf |
| void process() | VIO的主執行緒 |
| int main() | 程式入口 |
程式入口 int main(int argc, char **argv)
1、ROS初始化、設定控制代碼
ros::init(argc, argv, "vins_estimator");
ros::NodeHandle n("~");
ros::console::set_logger_level(ROSCONSOLE_DEFAULT_NAME, ros::console::levels::Info);
2、讀取引數,設定狀態估計器引數
readParameters(n);
estimator.setParameter();
3、釋出用於RVIZ顯示的Topic,本模組具體釋出的內容詳見輸入輸出
registerPub(n);
4、訂閱IMU、feature、restart、match_points的topic,執行各自回撥函式
ros::Subscriber sub_imu = n.subscribe(IMU_TOPIC, 2000, imu_callback, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
ros::Subscriber sub_image = n.subscribe("/feature_tracker/feature", 2000, feature_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_restart = n.subscribe("/feature_tracker/restart", 2000, restart_callback);
ros::Subscriber sub_relo_points = n.subscribe("/pose_graph/match_points", 2000, relocalization_callback);
5、建立VIO主執行緒
std::thread measurement_process{process};
4個回撥函式
這裡需要注意的一點是:節點estimator,以及建立了一個process,必須考慮多執行緒安全問題:
1、佇列imu_buf、feature_buf、relo_buf是被多執行緒共享的,因而在回撥函式將相應的msg放入buf或進行pop時,需要設定互斥鎖m_buf,在操作前lock(),操作後unlock()。其他互斥鎖同理。
2、在feature_callback和imu_callback中還設定了條件鎖,在完成將msg放入buf的操作後喚醒作用於process執行緒中的獲取觀測值資料的函式。
std::condition_variable con;
con.notify_one();
3、在imu_callback中還通過lock_guard的方式構造互斥鎖m_state,它能在構造時加鎖,析構時解鎖。
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lg(m_state);
VIO主執行緒 void process()
通過while (true)不斷迴圈,主要功能包括等待並獲取measurements,計算dt,然後執行以下函式:
stimator.processIMU()進行IMU預積分
estimator.setReloFrame()設定重定位幀
estimator.processImage()處理影象幀:初始化,緊耦合的非線性優化
其中measurements的資料格式可以表示為:(IMUs, img_msg)s s表示容器(vector)
1、 等待上面兩個接收資料完成就會被喚醒,在執行getMeasurements()提取measurements時互斥鎖m_buf會鎖住,此時無法接收資料。
getMeasurements()的作用是對imu和影象資料進行對齊並組合,之後會具體分析
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(m_buf);
con.wait(lk, [&]
{
return (measurements = getMeasurements()).size() != 0;
});
lk.unlock();
2、對measurements中的每一個measurement (IMUs,IMG)組合進行操作
for (auto &measurement : measurements)
2.1、對於measurement中的每一個imu_msg,計算dt並執行processIMU()。
processIMU()實現了IMU的預積分,通過中值積分得到當前PQV作為優化初值
estimator.processIMU(dt, Vector3d(dx, dy, dz), Vector3d(rx, ry, rz));
2.2、在relo_buf中取出最後一個重定位幀,拿出其中的資訊並執行setReloFrame()
// set relocalization frame
sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr relo_msg = NULL;
while (!relo_buf.empty())
{
relo_msg = relo_buf.front();
relo_buf.pop();
}
if (relo_msg != NULL)
{
/*...*/
estimator.setReloFrame(frame_stamp, frame_index, match_points, relo_t, relo_r);
}
2.3、建立每個特徵點的(camera_id,[x,y,z,u,v,vx,vy])s的map,索引為feature_id
map<int, vector<pair<int, Eigen::Matrix<double, 7, 1>>>> image;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < img_msg->points.size(); i++)
{
int v = img_msg->channels[0].values[i] + 0.5;
int feature_id = v / NUM_OF_CAM;
int camera_id = v % NUM_OF_CAM;
/* double x,y,z,p_u,p_v,velocity_x,velocity_y */
ROS_ASSERT(z == 1);//判斷是否歸一化了 Eigen::Matrix<double, 7, 1> xyz_uv_velocity;
xyz_uv_velocity << x, y, z, p_u, p_v, velocity_x, velocity_y;
image[feature_id].emplace_back(camera_id, xyz_uv_velocity);
}
2.4、處理影象,這裡實現了視覺與IMU的初始化以及非線性優化的緊耦合
estimator.processImage(image, img_msg->header);
2.5、向RVIZ釋出里程計資訊、關鍵位姿、相機位姿、點雲和TF關係,這部分在之前輸入輸出已經介紹了
2.6、更新IMU引數[P,Q,V,ba,bg,a,g],注意執行緒安全
m_buf.lock();
m_state.lock();
if (estimator.solver_flag == Estimator::SolverFlag::NON_LINEAR)
update();//更新IMU引數[P,Q,V,ba,bg,a,g]
m_state.unlock();
m_buf.unlock();
std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>> getMeasurements()
該函式的主要功能是對imu和影象資料進行對齊並組合,返回的是(IMUs, img_msg)s,即影象幀所對應的所有IMU資料,並將其放入一個容器vector中。
IMU和影象幀的對應關係在新版的程式碼中有變化:對影象幀j,每次取完imu_buf中所有時間戳小於它的imu_msg,以及第一個時間戳大於影象幀時間戳的imu_msg (這裡還需要加上同步時間存在的延遲td)。
因此在新程式碼中,每個大於影象幀時間戳的第一個imu_msg是被兩個影象幀共用的,而產生的差別在processIMU()前進行了對應的處理。
(這一部分我不知道自己理解的對不對,若有錯誤請指出!)
img: i -------- j - -------- k
imu: - jjjjjjjj - j+k kkkkkkkk -
std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>>
getMeasurements()
{
std::vector<std::pair<std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr>, sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr>> measurements;
while (true)
{
//直到把快取中的影象特徵資料或者IMU資料取完,才能夠跳出此函式
if (imu_buf.empty() || feature_buf.empty())
return measurements;
//對齊標準:IMU最後一個數據的時間要大於第一個影象特徵資料的時間
if (!(imu_buf.back()->header.stamp.toSec() > feature_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() + estimator.td))
{
//ROS_WARN("wait for imu, only should happen at the beginning");
sum_of_wait++;
return measurements;
}
//對齊標準:IMU第一個資料的時間要小於第一個影象特徵資料的時間
if (!(imu_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() < feature_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() + estimator.td))
{
ROS_WARN("throw img, only should happen at the beginning");
feature_buf.pop();
continue;
}
sensor_msgs::PointCloudConstPtr img_msg = feature_buf.front();
feature_buf.pop();
std::vector<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr> IMUs;
//影象資料(img_msg),對應多組在時間戳內的imu資料,然後塞入measurements
while (imu_buf.front()->header.stamp.toSec() < img_msg->header.stamp.toSec() + estimator.td)
{
//emplace_back相比push_back能更好地避免記憶體的拷貝與移動
IMUs.emplace_back(imu_buf.front());
imu_buf.pop();
}
//這裡把下一個imu_msg也放進去了,但沒有pop
//因此當前影象幀和下一影象幀會共用這個imu_msg
IMUs.emplace_back(imu_buf.front());
if (IMUs.empty())
ROS_WARN("no imu between two image");
measurements.emplace_back(IMUs, img_msg);
}
return measurements;
}
estimator.cpp/.h
構建了一個estimator類,這次我們主要討論流程問題,因而暫時只分析一下processImage()
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| void Estimator::setParameter() | 設定部分引數 |
| void Estimator::clearState() | 清空或初始化滑動視窗中所有的狀態量 |
| void Estimator::processIMU() | 處理IMU資料,預積分 |
| void Estimator::processImage() | 處理影象特徵資料 |
| bool Estimator::initialStructure() | 視覺的結構初始化 |
| bool Estimator::visualInitialAlign() | 視覺慣性聯合初始化 |
| bool Estimator::relativePose() | 判斷兩幀有足夠視差30且內點數目大於12則可進行初始化,同時得到R和T |
| void Estimator::solveOdometry() | VIO非線性優化求解里程計 |
| void Estimator::vector2double() | vector轉換成double陣列,因為ceres使用數值陣列 |
| void Estimator::double2vector() | 資料轉換,vector2double的相反過程 |
| bool Estimator::failureDetection() | 檢測系統執行是否失敗 |
| void Estimator::optimization() | 基於滑動視窗的緊耦合的非線性優化,殘差項的構造和求解 |
| void Estimator::slideWindow() | 滑動視窗法 |
| void Estimator::setReloFrame() | 重定位操作 |
void Estimator::processImage()
1、addFeatureCheckParallax()新增之前檢測到的特徵點到feature容器list中,計算每一個點跟蹤的次數,以及它的視差並通過檢測兩幀之間的視差決定是否作為關鍵幀
param[in] frame_count 視窗內幀的個數
param[in] image 某幀所有特徵點的[camera_id,[x,y,z,u,v,vx,vy]]構成的map,索引為feature_id
param[in] td 相機和IMU同步校準得到的時間差
if (f_manager.addFeatureCheckParallax(frame_count, image, td))
marginalization_flag = MARGIN_OLD;//=0
else
marginalization_flag = MARGIN_SECOND_NEW;//=1
2、 將影象資料、時間、臨時預積分值存到影象幀類中
ImageFrame imageframe(image, header.stamp.toSec());
imageframe.pre_integration = tmp_pre_integration;
all_image_frame.insert(make_pair(header.stamp.toSec(), imageframe));
3、更新臨時預積分初始值
tmp_pre_integration = new IntegrationBase{acc_0, gyr_0, Bas[frame_count], Bgs[frame_count]};
4、判斷是否需要進行外參標定
if(ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC == 2)//如果沒有外參則進行標定
{
ROS_INFO("calibrating extrinsic param, rotation movement is needed");
if (frame_count != 0)
{
vector<pair<Vector3d, Vector3d>> corres = f_manager.getCorresponding(frame_count - 1, frame_count);
Matrix3d calib_ric;
if (initial_ex_rotation.CalibrationExRotation(corres, pre_integrations[frame_count]->delta_q, calib_ric))
{
ROS_WARN("initial extrinsic rotation calib success");
ROS_WARN_STREAM("initial extrinsic rotation: " << endl << calib_ric);
ric[0] = calib_ric;
RIC[0] = calib_ric;
ESTIMATE_EXTRINSIC = 1;
}
}
}
5、solver_flag==INITIAL 進行初始化
5.1、確保有足夠的frame參與初始化,有外參,且當前幀時間戳大於初始化時間戳+0.1秒
5.2、執行視覺慣性聯合初始化
result = initialStructure();
initial_timestamp = header.stamp.toSec();
5.3、初始化成功則進行一次非線性優化,不成功則進行滑窗操作
if(result)//初始化成功
{
solver_flag = NON_LINEAR;
solveOdometry();
slideWindow();
f_manager.removeFailures();
ROS_INFO("Initialization finish!");
last_R = Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_P = Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];
last_R0 = Rs[0];
last_P0 = Ps[0];
}
else
slideWindow();
6、solver_flag==NON_LINEAR進行非線性優化
6.1、執行非線性優化具體函式solveOdometry()
6.2、檢測系統執行是否失敗,若失敗則重置估計器
if (failureDetection())//失敗
{
ROS_WARN("failure detection!");
failure_occur = 1;
clearState();
setParameter();
ROS_WARN("system reboot!");
return;
}
6.3、執行視窗滑動函式slideWindow();
6.4、去除估計失敗的點併發布關鍵點位置
f_manager.removeFailures();
ROS_DEBUG("marginalization costs: %fms", t_margin.toc());
// prepare output of VINS
key_poses.clear();
for (int i = 0; i <= WINDOW_SIZE; i++)
key_poses.push_back(Ps[i]);
void update()
這個函式在非線性優化時才會在process()中被呼叫
1、從估計器中得到滑動視窗中最後一個影象幀的imu更新項[P,Q,V,ba,bg,a,g]
latest_time = current_time;
tmp_P = estimator.Ps[WINDOW_SIZE];
tmp_Q = estimator.Rs[WINDOW_SIZE];
tmp_V = estimator.Vs[WINDOW_SIZE];
tmp_Ba = estimator.Bas[WINDOW_SIZE];
tmp_Bg = estimator.Bgs[WINDOW_SIZE];
acc_0 = estimator.acc_0;
gyr_0 = estimator.gyr_0;
2、對imu_buf中剩餘的imu_msg進行PVQ遞推
(因為imu的頻率比影象頻率要高很多,在getMeasurements()將影象和imu時間對齊後,imu_buf中還會存在imu資料)
queue<sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr> tmp_imu_buf = imu_buf;
for (sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr tmp_imu_msg; !tmp_imu_buf.empty(); tmp_imu_buf.pop())
predict(tmp_imu_buf.front());
