二叉樹演算法整理
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-14
演算法1, 序列化二叉樹(二叉樹的先序遍歷)
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.index = 0
self.listS = []
def RecursionSe(self, root):
series = ''
if root == 測試:
root = TreeNode(11)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
series = Solution().Serialize(root)
輸出:
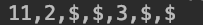
演算法2,反序列化二叉樹
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__( 測試:
root = Solution().Deserialize(series)
print(root.val)
print(root.left.val)
print(root.right.val)
print(root.right.right)
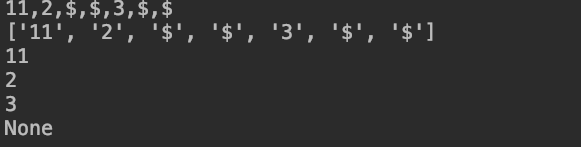
演算法3,層次化遍歷二叉樹
使用一個佇列層次遍歷
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回從上到下每個節點值列表,例:[1,2,3]
def PrintFromTopToBottom(self, root):
# write code here
list = []
result = [] #注意兩個列表如果相等賦值,那麼一下就會更新兩個
#### list = result = [] !!!!錯誤
if root == None:
return list
list.append(root)
while list != []:
treeNode = list.pop(0)
result.append(treeNode.val)
if treeNode.left:
list.append(treeNode.left)
if treeNode.right:
list.append(treeNode.right)
return result
演算法4,層次遍歷,每一層在一行輸出,“之”字型遍歷二叉樹
為了將每一層進行單獨輸出,需要統計這一行的個數toPrint,然後統計下一行的個數nextPrint
參考我之前的部落格:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_36372879/article/details/83994160
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回二維列表[[1,2],[4,5]]
def Print(self, pRoot):
# write code here
if pRoot == None:
return []
queue = []
toPrint = 1
queue.append(pRoot)
nextPrint = 0
results = []
result = []
while queue != []:
popNode = queue.pop(0)
result.append(popNode.val)
toPrint -= 1
if popNode.left:
queue.append(popNode.left)
nextPrint += 1
if popNode.right:
queue.append(popNode.right)
nextPrint += 1
if toPrint == 0:
results.append(result) #這層遍歷完畢,加入到結果中
toPrint = nextPrint #下層需要遍歷的資料
result = [] #這層遍歷完畢,清零
nextPrint = 0 #下下層清零
return results
“之字形列印二叉樹”:可以使用棧
演算法5,根據前序序列和中序序列重建二叉樹
演算法思想就是:先序遍歷的肯定是根節點,然後在中序遍歷序列中,找到這個節點,將樹的構造一分為二即可。
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回構造的TreeNode根節點
def construct(self, pre, tin, startPre, endPre, startTin, endTin):
if startPre <= endPre:
root = TreeNode(pre[startPre])
i = startTin
while tin[i] != pre[startPre]: #在中序遍歷中,找到根節點,然後一分為二
i += 1
leftLength = i - startTin #左子樹的長度
if leftLength:
root.left = self.construct(pre, tin, startPre + 1, startPre + leftLength, startTin, i - 1)
if endTin - i:
root.right = self.construct(pre, tin, startPre + leftLength + 1, endPre, i + 1, endTin)
return root
def reConstructBinaryTree(self, pre, tin):
# write code here
return self.construct(pre, tin, 0, len(pre) - 1, 0, len(tin) - 1)
演算法6,二叉樹和為某一值的路徑(回溯遍歷演算法)
題目描述
輸入一顆二叉樹的跟節點和一個整數,打印出二叉樹中結點值的和為輸入整數的所有路徑。路徑定義為從樹的根結點開始往下一直到葉結點所經過的結點形成一條路徑。(注意: 在返回值的list中,陣列長度大的陣列靠前)
演算法思想:為了記住中間的遍歷路徑,使用一個數組來記錄,最後判斷陣列的和,往左邊遍歷之後,需要回溯陣列,然後往右邊遍歷
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回二維列表,內部每個列表表示找到的路徑
def __init__(self):
self.results = []
def ListSum(self, l):
sum = 0
for i in l:
sum += i
return sum
def RecursionFindPath(self, root, expectNumber, result):
result.append(root.val)
temp = result[:] #儲存之前的結果
if root.left == None and root.right == None and self.ListSum(result) == expectNumber:
self.results.append(result)
if root.left:
self.RecursionFindPath(root.left, expectNumber, result)
result = temp[:] #回溯過程
if root.right:
self.RecursionFindPath(root.right, expectNumber, result)
def QuickSort(self, results, start, end): #對陣列進行快速排序
if start >= end:
return
low, high = start, end
pivot = results[start]
while low < high:
while low < high and len(results[high]) <= len(pivot):
high -= 1
if low < high:
results[low] = results[high]
while low < high and len(results[low]) >= len(pivot):
low += 1
if low < high:
results[high] = results[low]
results[low] = pivot
self.QuickSort(results, start, low - 1)
self.QuickSort(results, low + 1, end)
def FindPath(self, root, expectNumber):
# write code here
if root == None:
return []
self.RecursionFindPath(root, expectNumber, [])
if self.results == []:
return []
self.QuickSort(self.results, 0, len(self.results) - 1)
return self.results
測試:
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
root.right.right = TreeNode(2)
root.right.right.left = TreeNode(1)
root.right.right.right = TreeNode(5)
expectNum = 7
print(Solution().FindPath(root, expectNum))
輸出:
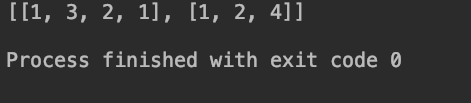
演算法7,遍歷樹的第k個節點
例如下面這個二叉搜尋樹,找出第k個節點

演算法思想就是設定一個全域性的k,然後使用中序遍歷
需要注意的是程式碼的寫法,不能根據k判斷,而是要根據結果判斷,因為需要先遍歷,再k–。
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.k = 0
def InOrder(self, Root):
ans = None
if Root:
if ans == None and Root.left:
ans = self.InOrder(Root.left) #往左遍歷
if ans == None and self.k == 1:
ans = Root #遍歷到目標節點
if ans == None and self.k != 1: #沒有遍歷到目標節點,k--
self.k -= 1
if ans == None and Root.right: #往右遍歷
ans = self.InOrder(Root.right)
return ans
def KthNode(self, Root, k):
if Root == None or k <= 0:
return None
self.k = k
return self.InOrder(Root)
演算法8,遍歷倒數第k個節點
遍歷倒數第k個節點,可以使用中序遍歷,只不過先遍歷右子樹,再遍歷左子樹
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回對應節點TreeNode
def __init__(self):
self.k = 0
def ReverseInOrder(self, pRoot):
ans = None
if pRoot:
if ans == None and pRoot.right:
ans = self.ReverseInOrder(pRoot.right)
if ans == None and self.k == 1:
ans = pRoot
if ans == None and self.k != 1:
self.k -= 1
if ans == None and pRoot.left:
ans = self.ReverseInOrder(pRoot.left)
return ans
def KthNode(self, pRoot, k):
# write code here
if pRoot == None and k < 1:
return None
self.k = k
return self.ReverseInOrder(pRoot)
演算法9,樹的子結構
部落格:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_36372879/article/details/83831191
輸入兩棵二叉樹A,B,判斷B是不是A的子結構。(ps:我們約定空樹不是任意一個樹的子結構)
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def Tree1HasTree2(self, pRoot1, pRoot2):
if pRoot2 == None:
return True
elif pRoot1 == None:
return False
if pRoot1.val == pRoot2.val:
return self.Tree1HasTree2(pRoot1.left, pRoot2.left) and self.Tree1HasTree2(pRoot1.right, pRoot2.right)
else:
return False
def HasSubtree(self, pRoot1, pRoot2):
# write code here
if pRoot1 == None or pRoot2 == None:
return False
ans = False
if pRoot1.val == pRoot2.val:
ans = self.Tree1HasTree2(pRoot1, pRoot2)
if ans == False:
ans = self.Tree1HasTree2(pRoot1.left, pRoot2)
if ans == False:
ans = self.Tree1HasTree2(pRoot1.right, pRoot2)
return ans
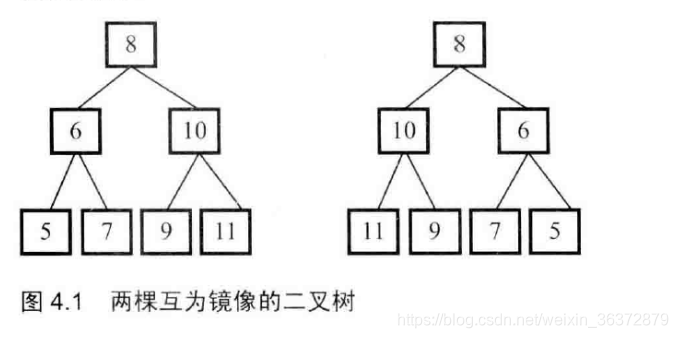
演算法10 二叉樹的映象(將二叉樹的左子樹和右子樹交換)
class Solution:
# 返回映象樹的根節點
def Mirror(self, root):
# write code here
if root == None:
return None
if root.left == None and root.right == None:
return root
root.left, root.right = self.Mirror(root.right), self.Mirror(root.left)
return root
演算法11 對稱二叉樹
判斷二叉樹是否對稱。
class Solution:
def RecursionSymmetry(self, root1, root2):
if root1 == None and root2 == None:
return True
elif root1 == None or root2 == None:
return False
if root1.val == root2.val:
return self.RecursionSymmetry(root1.left, root2.right)
else:
return False
def isSymmetrical(self, pRoot):
# write code here
return self.RecursionSymmetry(pRoot, pRoot)
