Python 使用requests時的編碼問題
官網說明:
Compliance
Requests is intended to be compliant with all relevant specifications and RFCs where that compliance will not cause difficulties for users. This attention to the specification can lead to some behaviour that may seem unusual to those not familiar with the relevant specification.
Encodings
When you receive a response, Requests makes a guess at the encoding to use for decoding the response when you access the Response.text attribute.
Requests will first check for an encoding in the HTTP header, and if none is present, will use chardet to
attempt to guess the encoding.
The only time Requests will not do this is if no explicit charset is present in the HTTP headersand
Content-Type header contains text.
In this situation, RFC
2616 specifies that the default charset must be ISO-8859-1. Requests follows the specification in this case. If you require a different encoding, you can manually set the Response.encoding property,
or use the rawResponse.content.
意思就是:
當你收到一個響應時,Requests會猜測響應的編碼方式,用於在你呼叫 Response.text 方法時 對響應進行解碼。Requests首先在HTTP頭部檢測是否存在指定的編碼方式,如果不存在,則會使用 charade 來嘗試猜測編碼方式。
只有當HTTP頭部不存在明確指定的字符集,並且 Content-Type 頭部欄位包含 text 值之時, Requests才不去猜測編碼方式。
在這種情況下, RFC
2616 指定預設字符集 必須是 ISO-8859-1 。Requests遵從這一規範。如果你需要一種不同的編碼方式,你可以手動設定 Response.encoding 屬性,或使用原始的 Response.content 。
測試
經過測試發現也有不準確的時候,下面看例子。
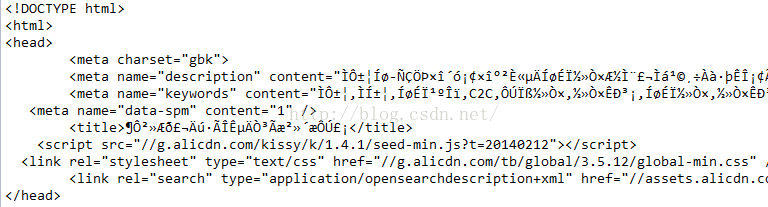
下面是獲得的response內容:
很明顯header部分有指定charset="gbk",按文件中的說明應該不會使用預設的編碼ISO-8859-1進行解碼,但結果卻不是這樣。
r = requests.get(url)
print r.encoding
#結果:ISO-8859-1r = requests.get(url)r.encoding='gbk'
print r.headers['content-type']
data = r.text
print data#列印結果無亂碼