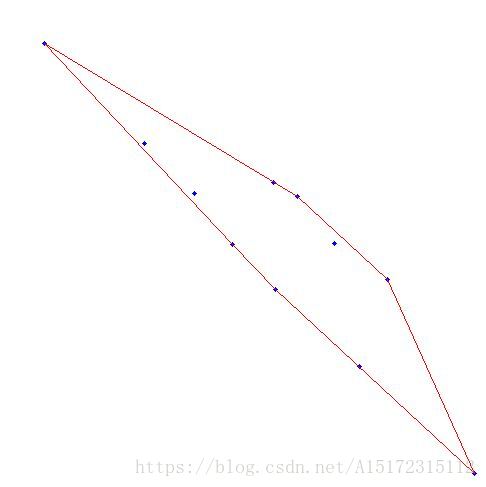
最小包圍凸包
阿新 • • 發佈:2019-01-27
最近看了最小凸包繪製,官方程式碼沒看,常見的有Graham's scan演算法
其實原理比較簡單,先將點集排序,之後根據左轉進行棧掃描。
1.點集排序:一般取x座標最小的,並且儘量y大的,靠左下角的點作為起始點。然後連線起始點P0與其他點,計算連線與豎直向下方向的夾角,按照大小順序排列。
2.然後根據排序之後的點,依次判定該點是否左轉,若是左轉,入棧,否則,取下一點。判斷左轉可以根據向量面積法:
S(P1,P2,P3)=|y1 y2 y3|= (x1-x3)*(y2-y3)-(y1-y3)*(x2-x3) 第一點為P1,向量方向為P1P2,判斷P3點,若S為正,P3在向量P1P2的左側。
1.點集排序:
void sort(vector<Point>& pss) { //pss是裝著原本的點 //bound是排好序的點 //首先排序 int count = pss.size(); int first_Point = 0; float* Aangle = new float[count]; //動態陣列存放角度 int Min_x = pss[0].x ; int Max_y = pss[0].y ; for(int i=0;i<pss.size();i++) //取橫座標最小的點 y最大 { if ( (pss[i].x < Min_x)||((pss[i].x == Min_x)&&(pss[i].y>Max_y))) { Min_x = pss[i].x; Max_y = pss[i].y; first_Point = i; } } Point temp = pss[0]; //將起始點放到首位置 pss[0] = pss[first_Point]; pss[first_Point]= temp; //計算連線與豎直方向夾角 for(int i=0;i<pss.size();i++) { float angle = -1.0* (float)(pss[i].y -pss[0].y )/(float)(pss[i].x -pss[0].x );//影象座標系有點區別 Aangle[i] = angle; } //根據夾角排序 for(int i = 1;i<count-1;i++) { for(int j = i+1;j<count;j++) { if(Aangle[j]<Aangle[i]) { float temp = Aangle[i]; Aangle[i] = Aangle[j]; Aangle[j] = temp; Point temp1 =pss[i]; pss[i] = pss[j]; pss[j] = temp1; } } } delete []Aangle; }
2.棧掃描
void scan(vector<Point>& pss,vector<Point>& bound) { int i = 1;//記錄拐點索引 int pop_count= 0;//記錄彈出次數 bound.push_back(pss[0]); bound.push_back(pss[1]); bound.push_back(pss[2]); //根據已排好序列的點連線線段 do { //計算夾角 float angle = ((bound[i].y - bound[i+1].y)*(bound[i-1].x - bound[i+1].x) - (bound[i-1].y - bound[i+1].y)*(bound[i].x - bound[i+1].x)); if(angle<=0.0)//左轉 { bound.push_back(pss[(i+2+pop_count)%pss.size()]);// 壓棧 i++;//索引加1 } else//右轉 { bound.erase(bound.end()-2);//彈出倒數第二個點 pop_count++;//彈出次數加1 i--;.//索引減1 } } while (pss[0] != *bound.rbegin() );//回到起始點 }
測試:
void test(vector<Point> point)
{
vector<Point> bound;
sort(point);
scan(point,bound);
for (int i =0;i<bound.size()-1;i++)
{
line(img,bound[i],bound[i+1],Scalar(0,0,255),2,8,0);
}
line(img,bound[0],bound[bound.size()-1],Scalar(0,0,255),2,8,0);
imshow("dst",img);
}結果: